Search
Search Results
-
Comparative examination of a mineral fertiliser and a bacterial fertilizer on humic sandy soil
111-116Views:239In our pot experiment, the impact of a bacterial fertilizer, Bactofil® A10 and a mineral fertilizer Ca(NO3)2 applied in different rates was studied on some soil chemical and microbiological characteristics of a humic sandy soil (Pallag). Perennial rye-grass (Lolium perenne L.) was used as a test-plant. Samples were collected four and eight weeks after sowing in each year. The experiment was set up in 2007-2009 in the greenhouse of
the UD CASE Department of Agrochemistry and Soil Science. The available (AL-extractable) nutrient contents of soil, among the microbial parameters the total number of bacteria, the number of microscopic fungi, cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria, the sacharase and urease enzyme activity, as well as the soil respiration rate were measured.
Statistical analyses were made by means of the measurements deviation, LSD values at the P=0.05 level and correlation coefficients were calculated. Results of our experiment were summarised as follows:
− The readily available nutrient content of humic sandy soil increased as affected by the treatments, in case of the available (AL-extractable) phosphorus and potassium content the higher value was measured in high-dosage artificial fertilizer treatment.
− The treatments had also positive effect on several soil microbial parameters studied. The higher-dosage mineral fertilizer treatments had a beneficial effect on the total number of bacteria, cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria. No significant differences were obtained between the effect of treatment in case of the total-number of bacteria, the number of microscopic fungi and nitrifying bacteria.
− On the sacharase enzyme activity the artificial fertiliser treatments proved to be unambiguously stimulating, the urease activity significantly increased on the effect of the lower-dosage Ca(NO3)2 artificial fertilizer treatment.
− The soil respiration increased in all treatments in related to the amounts applied, significantly increased in the highest rate of Ca(NO3)2 fertilizer addition.
− Some medium and tight positive correlations were observed between the soil chemical and microbiological parameters studied in case of both nutrient sources.
Summarizing our results, it was established that the organic and all the mineral fertilizer treatments had beneficial effects on the major soil characteristics from the aspect of nutrient supply. In majority of the examined soil parameters (AL-extractable phosphorus- and potassium, total number of bacteria, number of cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria, activity of sacharase enzyme) the high rate of Ca(NO3)2 mineral fertilizer treatment proved to be more stimulating, but at the same time the high rate bacterium fertilizer resulted in significant increases in
the nitrate-N content, the AL-potassium content of soil, the total number of bacteria, the number of cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria and the urease enyme activity.
Our examinations showed that the mineral fertilizer treatments proved to be more stimulating on most of the soil parameters studied but according to our results, it was established that Bactofil is efficiently applicable in the maintenance of soil fertility and the combined application of
mineral fertilizer and bacterium fertilizer may be a favourable opportunity – also in aspect of the environmental protection – in maintaining soil fertility. -
The effect of sulphur and nitrogen supply on the growth and nutrient content of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
65-70Views:384Sulphur is an essential element for plants. Decreasing sulphur deposition from the air, and the use of more concentrated phosphate fertilizers, which contain no sulphur, has led to reports of sulphur deficiencies for wheat. Sulphur deficiency significantly affects yield and also the quality of wheat. The pot experiment was set up on calcareous chernozem soil at Látókép, Hungary, test plant was spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Seven treatments were used where nitrogen and sulphur were supplied as soil fertilizers in increasing rates (NS1, NS2, NS3) and in foliar fertilizer as well (NS1+fol., NS2+fol., NS3+fol.). Plant aboveground biomass production was determined in samples taken in the stages of development BBCH 29-30, 51-59, 61-69, 89. The nitrogen and sulphur content of straw and grain were measured. N/S ratios of grain and straw were calculated. The weights of grain were ranging between 8.6–16.1 g/pot. NS2 and NS2+fol. treatments produced the highest values. Foliar fertilizer had no further effect on grain. Analysing the values of the straw, it was observed that tendencies were similar to values of grain. The NS2 treatment produced the highest weight of straw and the NS3 rate already decreased that amount. The obtained results show the unfavourable effect of excessively high rate applied in NS3 treatment. The supplementary foliar fertilizer had no significant influence on the weight of straw. Both N and S-uptake of plant was very intensive at the stem elongation stage, then the N and S-content of plant continuously decreased in time in all treatments. The N-content of grain ranged between 2.215–2.838%.The N-content of grain slightly increased with increasing of nitrogen doses. In the higher doses (NS2, NS3) foliar fertilization slightly increased the nitrogen content of grain, although this effect was not statistically proved. The N-content of straw varied from 0.361 to 0.605%. The growing dose of soil fertilizer also considerably increased the nitrogen content of straw. Foliar fertilization further increased the nitrogen content of straw. The S-content of grain ranged between 0.174–0.266%. The lowest fertilizer dose (NS1) significantly increased the sulphur content of grain. The further increasing fertilizer doses (NS2, NS3) did not cause additional enhance in sulphur content of grain.The foliar fertilizer also did not change the sulphur value of plant. The increasing amount of soil fertilizer and the supplementary foliar fertilizer had no effect on the sulphur content of straw. The treatments influenced the N/S ratios of grain and straw. On the basis of experimental results it can be concluded that the examined nitrogen and sulphur containing soil fertilizer had positive effect on the growth and yield of spring wheat grown on the calcareous chernozem soil. The soil fertilizer application enhanced the grain nitrogen and sulphur content. The highest rate of fertilizer (600 kg ha-1) proved to have decreasing effect on the yield. The sulphur and nitrogen containing foliar fertilizer did not have significant effect on the yield parameters but slightly increased the nitrogen content of plant. -
The impact of different fertilization methods on some microbiological soil characteristics
119-126Views:275In our experiment, we studied the impact of an organic fertilizer, Bactofil® A10 (half- and full dosage applied in field practice) and an artificial fertilizer of Ca(NO3)2 content in different dosages (20-40 mg kg-1) – in addition to control treatments – on two different soils (calcareous chernozem, humus sandy soil) in 2005-2006, the experiment was complemented with treatments applying 250% dosage (100 mg kg-1 N, Bactofil® A10 2.5 times the field dosage) and a compost from urban sewage (25 g kg-1 compost) was also tested on these two soil types. In the
experiment, several soil microbial parameters were studied. The experiment was set up at the Department of Agrochemistry and Soil Science using 1-kg pots.
Our laboratory experiments were performed at the soil microbiology laboratory of UD CAS Department of Agrochemistry and Soil Science, the total number of bacteria, microscopic fungi, nitrifying and aerob cellulose-decomposing bacteria were determined together with the CO2-production of soil, N content of the biomass and urease enzyme activity.
Statistical analysis of the data was done using the program SPSS 13.0, means of the measurements, deviation and significance values were calculated.
In 2005-2006, the effect of the different dosages of Bactofil® A10, and the Ca(NO3)2 fertilizer on the examined microbial parameters of calcareous chernozem and humus sandy soils can be summarized as follows:
• Concerning the total number of bacteria, both treatments were effective on calcareous chernozem soil, the higher (significant) increment in bacteria number was observed in the artificial fertilizer treatments, while in the humus sandy soil Bactofil treatments had a beneficial effect. The number of microscopic fungi also increased in both treatments, higher numbers were observed in the average of two years in the Bactofil treatments.
• The number of nitrifying bacteria was 2.5 times higher in both high-dosage treatments on calcareous chernozem soil, while on humus sandy soil a slight (not significant) increment was observed only int he high-dosage Bactofil treatment. The amount of aerob cellulose-decomposing bacteria significantly increased on calcareous chernozem soil in both the highdosage artificial fertilizer and the small-dosage Bactofil treatment, however, on humus sandy soil no significant increase was observed in either treatment.
• The CO2-production increased in both soil types, although it was not significant in either treatment. A higher (though not significant) soil respiration was observed in the Bactofil treatments in both soil types.
• The microbial biomass N values were significantly higher in the high-dosage Bactofil treatments, however, the high-dosage artificial fertilizer treatment also increased these values significantly on calcareous chernozem soil.
• On calcareous chernozem soil, urease activity was significantly increased and reduced by high-dosage artificial fertilizer treatments and Bactofil treatments, respectively. On humus sandy soil, urease activity was also reduced except for the high-dosage artificial fertilizer treatment. In 2007, the pot experiment with 250% dosages was complemented with the application of compost rich in organic matter, the results of these treatments are sumnmarized as follows:
• In the case of the total number of bacteria, all three treatments resulted in a significant increase on calcareous chernozem soil with the highest values in the Bactofil treatment. The Bactofil treatment was the most effective on the humus sandy soil, but the artificial fertilizer treatment also
resulted in a significant increment. In the case of the total number of fungi, Bactofil treatments resulted in the highest values on both soils, but the compost treatment also increased the number of fungi in calcareous chernozem significantly.
• The number of nitrifying bacteria was increased most (significantly) by the Bactofil and compost treatments on both soil types. The amount of cellulose-decomposing bacteria was significantly increased by he compost treatment on calcareous chernozem soil, while its effect was not significant on humus sandy soil. The number of these bacteria was increased significantly by the Bactofil treatment on humus sandy soil.
• On calcareous chernozem soil, all three treatments significantly increased CO2-production, while the compost treatments had the resulted in the largest increment in soil respiration on both soil types.
• The soil biomass N content was significantly increased in both soils by the compost treatment, while in the case of the humus sandy soil, the Bactofil treatment also resulted in a significant increment.
• Urease enzyme activity was significantly increased by the artificial fertilizer treatment on both soils. In calcareous chernozem soil, the Bactofil treatment resulted in a slight (not significant) reduction in enzyme activity. In humus sandy soil, the Bactoful treatment also resulted in a slight reduction, while the compost treatment increased (though not significantly) the urease activity.
Based on our results, it can be stated that all three treatments were effective with respect to the studied soil microbial parameters. For both the calcareous chernozem and the humus sandy soil, the organic fertilizer Bactofil and the compost with high organic matter content had a stronger effect on some soil microbial parameters than the artificial fertilizer. -
Studies of the influences of different N fertilizers and Microbion UNC bacterial fertilizer on the nutrient content of soil
134-140Views:223A field experiment was conducted to examine the effects of different nitrogen fertilizers in combination with bacterial fertilizer on
nutrient uptake of horseradish and plant available nutrients of the soil. Three different N fertilizers, ammonium-nitrate, urea and calciumnitrate
(116 kg ha-1 N) in combination with Microbion UNC bacterial fertilizer (2 kg ha-1) were applied as treatments in a randomized
complete block design in three replications. In this paper we presented the results of soil measurements. The soil of the experimental area
was chernozem with medium sufficiency level of N and P and poor level of K.
Our main results:
The amount of 0.01M CaCl2 soluble inorganic nitrogen fractions, NO3
--N and NH4
+-N and also the quantity of soluble organic-N were
almost the same in the soil. N fertilizers significantly increased all the soluble N fractions. The amount of NO3
--N increased to the greatest
extent and the increase of organic N was the slightest. We measured the largest CaCl2 soluble NO3
- -N and total-N contents in the plots
treated with ammonium-nitrate, the largest NH4
+-N in the plots treated with calcium-nitrate and the largest organic-N fraction in plots
treated with urea.
Bacterial inoculation also increased both soluble inorganic nitrogen forms and also total-N content of soil compared to the control. In
the case of combined (artificial and bacterial fertilizer) treatments we measured lower NO3
--N, organic-N and total-N compared to the
values of plots having only nitrogen fertilizer treatments. On the contrary in the plots with combined treatments the CaCl2 soluble NH4
+-N
content of soil in more cases were higher than that of values with artificial fertilizer treatment.
As a function of calcium-nitrate application increased AL-P2O5 and AL-K2O values were measured compared to control. Microbion
UNC supplement of calcium nitrate yielded also increase in AL-P2O5 and AL-K2O values, till then supplement of ammonium-nitrate fertilizer
yielded a decrease in these values compared to the control.
All nitrogen fertilizers resulted in a significant decrease in AL-Mg content of soil compared to the control. Nevertheless bacterial
fertilizer increased AL-Mg values in any cases. -
The effect of and interaction between the biological bases and the agrotechnical factors on maize yield
83-87Views:254The effect of and interaction between the biological bases and the agrotechnical factors on maize yield In our research, we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons.We analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with a control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In 2015, the highest yield was produced by hybrid P9241 with N80+PK and 70 thousand plants per hectare. With the N160+PK fertilizer dosage, the same hybrid responded the best, followed by hybrids P9486 and DKC4717. Using the same fertilizer treatment, the 80 thousand plants per hectare population density resulted in decrease in the yield with most of the examined hybrids. In 2016, with the increase in the number of plants per hectare, even with non-fertilised treatment (control treatment), the yield could be increased in the case of each hybrid.Averaged over the different hybrids and fertilizer treatments, applying 80 thousand plants ha-1 instead of 60 thousand resulted in 1.0 ha-1 yield increase. In 2017, the number of plants had a slighter effect. With N160+PK treatment, in most cases no significant difference can be observed. The value of LSD5%: plant number: 0.20 t ha-1, hybrid: 0.28 t ha-1, interaction: 0.48 t ha-1. With N160+PK treatment, the hybrids produced yields between 10.07 and 12.45 t ha-1. When examining the three years in the average of the number of plants, with treatment without fertilisation, the average yield of hybrids reached 7.53 t ha-1. With N80+PK treatment, this value was 9.71 t ha-1 and with doubling the fertilizer dosage, this value increased to 10.42 t ha-1. No economic profit was gained as a result of applying double dosage of fertilizer; therefore, the N80+PK dosage can be considered ideal. -
Environmental Consequences of Efficient Use of Nitrogen Fertilizers
41-46Views:184Nitrogen fertilizer represents major economic burden. For this reason, although the efficiency of nitrogen utilization varies highly, its actual use generally remains at low levels; these averaging between 25 and 50%. We set up an experiment at the Oradea Research Station, using 15N labeled fertilizers, in order to investigate the possibility of increasing N fertilizer efficiency in winter wheat under irrigation conditions.
Fertilizers labeled with 15N allows us to individually determine its effect on yield formation, as well as the use efficiency of N from fertilizer following application rate and time. The amount of N derived from fertilizer as determined in straw and grain yield is high. When the labeled fertilizer is applied at tillering time, the values of this indicator rise when higher N levels we applied.
In separate experiments, we investigated a series of aspects connected to chemical fertilizer regarding the determination of the type of fertilizer, optimum time and rates of application; all these as a function of the special pedoclimatic conditions.
The results obtained in the field show that the effectiveness of N utilization in wheat is most variable and generally low, often ranging between 25 and 33%, owing to N loss within the system through leaching and NH3 volatilization.
A readily achievable increase in efficiency of 5 percentage points would result in considerable savings, and can be brought about by reducing nitrogen losses. The added benefits to the environment in terms of reduced ground/water contamination and lowered nitrous oxide (N20) emissions would also be substantial.
The figures for N fertilizer use efficiency (% N range from 35.5 to 72.6, the highest value being recorded with an N application of 120 kg/ha at tillering, when the previous crop was sunflower).
INTRODUCTION -
Correlation between the weather in 2017 and the productivity of maize
89-93Views:356In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In Hajdúszoboszló in 2017, up to October, 445.8 mm of rain fell, which is in line with the average values of 30 years, and is only 45.7 mm less than those. In 2017, the effect of increasing the plant number was slighter. Averaged over the observed fertilizer treatments and hybrids, the yield was 9.10 t ha-1 with 60 thousand plants ha-1, 9.11 t ha-1 with 70 thousand plants ha-1 and 9.12 t ha-1 with 80 thousand plants ha-1. Without fertilization, in most cases, increasing the plant number from 60 thousand plants ha-1 to 70-80 thousand plants ha-1 does not increased the yield but decreased it. With N80+PK treatment the yield changed between 8.90 and 11.27 t ha-1. The effect of increasing the plant number was just slightly observable and did not show a clear tendency. The effect of changing the plant number, even with the highest dosage of fertilizers, could not be detected adequately. In contrast with the plant number, the effect of the different fertilizer treatments was expressly traceable. Compared to the control treatment (treatment without fertilization), with N80+PK fertilizer dosage with 60 thousand plants ha-1 the yield increased by 3.36–4.99 t ha-1. The smallest demonstrable proof, i.e. the LSD5% was 0.22 t ha-1, which means that fertilization, in each case, significantly increased the yield. When analysing the effect of fertilization in the average of the hybrids and the different plant numbers, a yield of 5.61 t ha-1 could be detected, which value was 10.12 t ha-1 with N80+PK treatment and 11.61 t ha-1 with N160+PK treatment. Thus, it can be calculated that compared to the treatment without fertilization, the N80+PK treatment increased the yield by 4.51 t ha-1, while compared to the N80+PK treatment, the N160+PK treatment increased the yield by 1.49 t ha-1. In addition to agrotechnical factors, in maize production, the impact of the crop year is specifically of high importance.The average yield of hybrids (in the average of the different fertilizer treatments) was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 and 9.11 t ha-1 in 2017. When comparing the yield results against the precipitation data, it is clearly visible that the amount of rain fell in the January– October period is directly proportional to the average yield of maize. The effect of the crop year can be defined in a 5.05 t ha-1 difference in the yield. -
Effect of Ferilizer on the Yield of Maize (Zea mays L.)
40-46Views:280The effect of fertilization on the yield of maize was examined on chernoem soil with lime deposits at the experimental station at Látókép of the Center for Agricultural Sciences, University of Debrecen. The yields of maize were evaluated using quadratic regression function, in three years – between 2000 and 2002 – in non-irrigated and irrigated treatments. After calculating the regression equations, by derivation of the functions, we have determined the amount of fertilizers needed for maximum yield.
In the non-irrigated treatments, maximum yield and the active substance amount of fertilizer was as it follows: in 2000, yield of 9,133 t/ha with the application of 384 kg/ha mixed active substance, while in 2002 a yield of 6,289 t/ha with the application 236 kg/ha NPK active substance was achieved. In 2001, due to the favourable precipitation, a yield of 9,864 t/ha was achieved with the application of 245 kg/ha fertilizer. In the case of maximum yield, compared to the unfertilized control, the yield increase was 2,5-5 t/ha. The average increase for 1 kg of NPK fertilizer was 13-19 kg.
We also determined the necessary fertilizer dosage for maximum yield in irrigated treatments. In 2000, 10,003 t/ha with a dosage of 423 kg/ha, in 2001, 11,542 t/ha with a dosage of 277 kg/ha and in 2002, 8,596 t/ha of maximum yield could be achieved with a fertilizer treatment of 277 kg/ha in the examined three years. The yield increase, in irrigated treatments, varied between 3,9-5,9 t/ha so it was greater than in the case of non-irrigated experimetal plots. The yield increase for 1 kg fertilizer varied between 12-21 kg. -
The effect of season and fertilizer on the LAI, the photosynthesis and the yield of the maize hybrids with different genetic characteristics
27-34Views:263The experiment was carried out in Debrecen, at the Experimental Station of the University of Debrecen Centre of Agricultural Sciences, Department of Crop Production and Applied Ecology. We tested 10 various hybrids with their own genetic characteristics for five different fertilizer doses, in addition to the parcels without fertilization. The three factors of production technology jointly determine the successfully of maize production, but in different measure. The yield and the stability of yield of maize can be increased with hybrid-specific technologies.
In 2004-2005 experiment years the favorable results reached were due to the rainy season. There were significant difference between the productivity of maize hybrids. The N 40, P2O5 25, K2O 30 kg/ha treatment caused the highest increase of yield (3-5 t/ha) compared to the control (parcels without fertilization). The reaction of hybrids to the further fertilizer doses was different. The agro-ecological optimum of NPK fertilization was N 120, P 75, K 90 kg of the most hybrids.
During the experiment, we tested the moisture loss of the five hybrids. The seed moisture content at harvest was higher than in previous years due to the rainy seasons. The seed moisture content of harvest of FAO 200-300 hybrids were about 20%. It changed between 21-24% in the case of hybrids with longer vegetation period (FAO 400), the seed moisture content of Mv Vilma (FAO 510) was 24.21-25.04% in the average of fertilizer treatments. There is an important difference between the moisture loss ability of hybrids which changed 0.2-0.6%/day. The moisture loss of hybrids changed depending on the fertilizer treatment; usually, it was more favorable in the optimal fertilizer dose (N120+PK).
In the case of tested hybrids, we measured the highest LAI and photosynthetic activity at the optimal treatment, N 120, P2O5 75, K2O 90 kg/ha in the respect of efficiency and environmental protection, and the yield was high also for this treatment. There are significant difference between the LAI, the photosynthetic activity and the yield of hybrids, and these values could change depending on the treatment of fertilization. -
Effect of tillage practices, fertilizer treatments and crop rotation on yield of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids
43-48Views:414This research was conducted at the University of Debrecen Látókép Research Station and is part of an ongoing long-term polyfactorial experiment. The impact of three tillage systems (Mouldboard plowing-MT, Strip tillage-ST, Ripper tillage-RT) and two levels of fertilizer treatments (N80 kg ha-1, N160 kg ha-1) along with a control (N0 kg ha-1) on the yield of maize hybrids (Armagnac- FAO 490 & Loupiac-FAO 380) cultivated in rotation with winter wheat was evaluated during a two-year period (2017–2018).
Amongst the three tillage treatments evaluated, ripper tillage (RT) had the highest average yield (10.14 t ha-1) followed by mouldboard tillage (MT) and strip tillage (ST) with 9.84 and 9.21 t ha-1 respectively. Yield difference between RT and MT was not significant (P>0.05), as compared to ST (P<0.05). Soil moisture content varied significantly with tillage practices and was highest in ST, followed by RT and MT (ST>RT>MT). Yield of RT was 7–9% higher than MT in monoculture plots, while MT reign superior in biculture plots (monoculture: RT>MT>ST; biculture: MT>RT>ST).
A positive interaction between tillage and fertilization was observed, with higher yield variation (CV=40.70) in the non-fertilized (N0) plots, compared to those which received the N80 (CV=19.50) and N160 kg ha-1 (CV=11.59) treatments.
Incremental yield gain from increase fertilizer dosages was significantly higher in monoculture, compared to biculture. There was no significant difference in yield between N160 and N80 in the biculture plots (12.29 vs 12.02 t ha-1). However, in monoculture plots, N160 yield was 23% higher than the N80 kg ha-1 (N160=11.74 vs N80=9.56 t ha-1).
Mean yield of maize in rotation with winter wheat was 28% (2.47 tons) higher than monoculture maize. The greatest benefit of crop rotation was observed in the control plots (N0) with an incremental yield gain of 4.39 tons ha-1 over monculture maize (9.92 vs 5.43 t ha-1).
Yield increased with higher fertilizer dosages in irrigated plots. Fertilizer application greatly increased the yield of maize and accounted for 48.9% of yield variances. The highest yield (11.92 t ha-1) was obtained with N160 kg ha-1 treatment, followed by N80 kg ha-1 (10.38 t ha-1) and N0 kg ha-1 (6.89 t ha-1) respectively.
Overall mean yield difference between the two hybrids was not statistically significant, however, yield of FAO 380 was 3.9% higher (9.06 vs. 8.72 t ha-1) than FAO 490 in monoculture plots, while in biculture plots, FAO 490 was 4.1% higher than FAO 380.
Average yield in 2018 was 13.6% (1.24 t ha-1) higher than 2017 for the same set of agrotechnical inputs, thus, highlighting the significant effect of cropyear.
Armagnac (FAO 490) cultivated in rotation with winter wheat, under ripper tillage and N80 kg ha-1 is the best combination of treatments for optimum yield.
-
Effect of divided nitrogen and sulfur fertilization on the quality of winter wheat
27-31Views:381The ecological characteristics and agro-ecological conditions in Hungary provide opportunities for quality wheat production. For the successful wheat production besides the favorable conditions; the proper use of expertise and appropriate cultivation techniques are not negligible. Successful cultivation affected by many factors. To some extent we can affect, influence and convert the abiotic factors.
Today, a particularly topical issue is the question of nutrition and that the species’ genetic code can be validated using the appropriate quantity and quality fertilizer. Beyond determining the fertilizer requirements of the winter wheat it is important to align the nutrient to the plant’s nutrient uptake dynamics and to ensure its shared dispensing. In any case, it is important to note the use of autumnal base-fertilizer as complex fertilizer. Hereafter sharing the fertilizer during the growing season with the recommended adequate nitrogen dose.The first top dressing of winter wheat in early spring (the time of tillering) can be made, the second top dressing at the time of stem elongation, and the third top dressing at the end of the blooming can be justified. Determining the rate of fertilizer application depends on the habitat conditions and the specific nutrient needs of plants. In autumn the 1/3 of the planned amount of basic fertilizer should be dispensed (in case of N). During setting our experiment we used 3 doses (0 kg ha-1 N-1 active ingredient; 90 kg ha-1 N-1 active ingredients and 150 kg ha-1 N-1 active ingredient). Application dates beyond the autumn basic fertilization are the following: in one pass in early spring, divided in early spring and the time of run up, early spring and late flowering. In addition to nitrogen the replacement of sulfur gets a prominent role as a result of decreased atmospheric inputs. The proper sulfur supply mainly affects the quality parameters. It influences positively the wheat flour’s measure of value characteristics (gluten properties, volume of bread, dough rheology.
In terms of nitrogen doses; the larger amounts (150 kg ha-1 N-1 drug), is the proposed distributed application, while in the case of lower nitrogen (90 kg ha-1 N-1 drug) in a single pass in the early spring can achieve better results. After using sulfur the quality values among the nutritional parameters that can be associated with gluten properties took up higher values than the samples not treated with sulfur.
-
The Development of a Plot Fertilizer and Distributor, Analyses of How it Works
35-38Views:174stribution of the different types of fertilizers is essential. In my study, I recommend a solution for the mechanization of fertilizer distribution on probe parcels. I have designed and constructed a new plot fertilizer distributor. This machine of moderate price can be controlled easily; it provides accurate distribution and versatility. In my paper I give an outline of its basic principles of operation.
The spreading pattern of the complete plot fertilizer distributor was investigated on the top of a test-desk. I constructed a test-desk, which has 16 collecting trays in transversal direction and 1o collecting trays in longitudinal direction. I developed a new method for data interpretation. A map of distribution was designed to process the data of the measured 16o trays. In the distributor, a map precisely traced the pattern of granule distribution and the amount of fertilizer as well. After this, I defined the transversal and longitudinal coefficient of variations for spreading. On the basis of my investigations I can conclude that the plot fertilizer distributor has excellent, even spreading (longitudinal and transversal) patterns. -
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:330During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: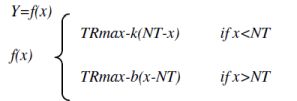
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Effect of different N doses on maize yield and quality
97-101Views:356The effect of N doses on the yield and nutritional values of the Sushi (FAO 340) maize hybrid were analysed in three years (2018, 2019, and 2020). The analyses were performed at the Látókép Experimental Station of the University of Debrecen on calcareous chernozem soil, in a striped, small-plot, non-irrigated long-term field experiment. In the experiment, in addition to the non-fertilized treatment (A0), the N-fertilizer doses were applied as basic fertilizer and top dressing. The 60 and 120 kg N ha-1 dose (A60, A120) applied as spring basic fertilizer were followed by two phases of top-dressing in V6 (V690, V6120) and V12 (V12150, V12180) phenophases; the amounts were +30 and +30 kg N ha-1.
Maize yields were affected to varying degrees by crop year. The highest yields in 2018 and 2020 were recorded in the same V6150 treatment, while in 2019 the highest yield was obtained in the A120 treatment.
Increasing the N doses resulted in an increase in the protein content of the maize kernel. Depending on the fertilizer treatments and the crop year effect, the protein content of maize kernels varied between 6.2–10.2 g x 100 g-1. In all three years, the protein content was the lowest in the control treatment (A0) and the highest in the V6150 treatment.
The starch content ranged from 70.7 to 77.9 g x 100 g-1 in the average of the three years. In 2020, it was significantly higher in all nutrient treatments than in the other examined two years. The highest starch content - except for 2020 (A120, 77.9 g x 100 g-1) - was recorded in the A0 treatment (74.2, 72.3 g x 100 g-1).
The oil content of maize kernels varied between the values of 3.8 and 5.2 g x 100 g-1 in the average of three years. In terms of oil content, the results for 2018 and 2019 can be considered the same, while in 2020 it was significantly lower. Fertilizer treatments did not significantly affect the oil content of maize in any of the years.
The fertilizer dose applied in the V12 phenological phase was not effective in terms of yield and nutritional content (protein, starch and oil content).
-
The effect of different microbial preparations on some soil characteristics
83-86Views:296In pot experiment the effect of different microbial inoculants and their combinations with NPK fertilizer and wheat straw on some soil properties (physical, chemical, and microbiological parameters) were studied. The experiment was set up in 2011 at the Institute of Agricultural Chemistry and Soil Science, in a three replications, in a random block design. The studied soil type was calcareous chernozem soil from Debrecen (Látókép) with ryegrass (Lolium perenne, L.) test plant.
At the end of the experiment in our laboratory the nitrate-nitrogen content of soil, the AL-soluble phosphorus and potassium content of soil, the urease enzyme activity of soil, the total number of bacteria and the number of microscopical fungi were determined.
The results of the study were the following:
– The straw treatment and the straw + biofertilizer combinations influenced positively the nitrate content of soil.
– The NPK fertilization and the straw+bacterial fertilizer combinations had significant positive effect on the AL-soluble phosphorus content of the soil.
– The biofertilization and the straw+biofertilizer combinations stimulated the AL-soluble potassium content of soil occasionally.
– The total number of bacteria was influenced by the NPK fertilization, the bacterial fertilization and the straw+bacterial fertilizer combinations significantly.
– In case of the number of microscopic fungi caused in some cases significant changes the NPK+bacterial fertilizer and straw+bacterial fertilizer combinations.
– The soil urease enzyme activity was increased in all cases strongly especially by the straw+bacterial preparation combinations. -
Efficiency of Fertilization in Sustainable Wheat Production
59-64Views:310In sustainable (wheat) production plant nutrition supply and fertilization play decisive roles among the agrotechnical elements, because of their direct and indirect effects on other agronomical factors.
In long-term experiments, we studied the roles of agroecological, genetic-biological and agrotechnical factors in the nutrient supply, fertilization and its efficiency in wheat production under continental climatic conditions (eastern part of Hungary, Trans-Tisza) on chernozem soil. Our results have proved that there are different (positive and negative) interactions among ecological, biological, and agrotechnical elements of wheat production. These interaction effects could modify the nutrient demand, fertilizer (mainly nitrogen) response of wheat varieties and efficiency of fertilization in wheat production.
The optimum N-doses (+PK) of wheat varieties varied from 60 kg ha-1 (+PK) to 120 kg ha-1 (+PK) depending on cropyears, agrotechnical elements and genotypes. The winter wheat varieties could be classified into 4 groups according to their fertilizer demand, natural and fertilizer utilization, fertilizer response and yield capacity.
Appropriate fertilization (mainly N) of wheat could affect both the quantity and quality of the yield. By using optimum N (+PK) fertilizer doses, we could manifest genetically- coded baking quality traits of winter wheat varieties and reduce quality fluctuation caused by ecological and other management factors. The efficiency of fertilization on different baking quality parameters (wet-gluten, valorigraph index etc) were variety specific (the changes depended on genotypes).
Our long-term experiments proved that appropriate fertilization provides optimum yield, good yield stability and excellent yield quality in sustainable wheat production. We could this get better agronomic and economic fertilization efficiency with less harmful environmental effects. -
Technological development of sustainable maize production
83-88Views:255In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize.
The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly eight ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2, this it was a half-industrial experiment. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. Yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare at a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants per ha.
In Hajdúszoboszló, in 2016 the amount of rainfall from January to October was 605 mm, which was more than the average of 30 years by 160 mm. The yield of hybrids without fertilization changed between 9.63–11.6 t ha-1 depending on the number of plants.
The six tested hybrids is 10.65 t ha-1 in the average of the stand density of 60, 70 and 80 thousand plants per hectare without fertilization, while it is 12.24 t ha-1 with N80+PK fertilizer treatment. That increase in the yield is 1.6 t ha-1, it is significant.
Da Sonka hybrid is sensitive to weather, it is able to produce 6 t ha-1 additional yield in case of favourable condition. However, it has a low stress tolerance. The most stable yields were observed at Kamaria and Pioneer hybrids. The effect of vintage is also an important factor on the yield. In average, the yield of maize was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, which was a drought year and 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 that was a favourable year. -
The Effect of Sowing Time and Nutrient Supply on the Yield Stability of Maize
75-80Views:316Sowing time, nutrient supply and plant number play crucial roles in the yield stability of maize. The productivity of various hybrids, each with its own genetic characteristics, was tested for three different sowing times and five different fertilizer doses. The highest yields were achieved at the third sowing time (17. V.), which is unusual, because the second half of the summer was rainy and was favourable for late sowing. The seed moisture content at harvest was higher than the optimal 14-15% at the third sowing time, the hybrids, which have intensive bleeding dynamics, couldn’t reach the lower seed moisture content at harvest of the early sowing. In that case we have to decision whether the plus yield of the third sowing time cover the drying costs.
Some hybrids produced the highest yields by N 120, P2O5 75, K2O 90 kg/ha active agent but the higher fertilizer doses depress the yield. The other part of the hybrids were able to produce high yield by bigger fertilizer doses. On the whole the agro-ecological optimum of the NPK fertilization was N 120-160, P 25-100, K 90-120 kg/ha active agent, but the N 80, P2O5 50, K2O 60 kg/ha fertilizer doses was the most effective. -
Examination of Hybrid-specific nutrient supply at corn on chernozem soli
91-95Views:421The effect of increasing fertilizer dosages on the yield of eight different maize hybrids (SY Ondina, NK Kansas, NK Lucius, NK Octet, NK Thermo, SY Flovita, SY Brillio, NX 47279) has been investigated in the crop-year of 2011. According to our results it can be stated that contrarily to the control treatment the application of different nutrient-levels has resulted a significant yield increment (2 000–5 800 kg ha-1).
Based upon the results of this experiment we have drawn the conclusion that the nutrient level of 120 kg N+PK was the optimal for the investigated hybrids. The highest yield (14 475 kg ha-1–15 963 kg ha-1) of the hybrids with different genotypes has been produced in case of this fertilizer treatment. With the comparison of the control and the optimum-fertilizer treatments the yield-increasing effect of mineral fertilization and the different reaction of hybrids towards increasing fertilizer dosages have been proven. In case of the control treatments the best-yielding hybrids were NK Thermo (11 917 kg ha-1) and NX 47279 (11 617 kg ha-1). Contrarily on the optimal nutrient supply level the hybrids SY Brillio (15 876 kg ha-1) and NX 47279 (15 963 kg ha-1) have produced the highest yields. Summarizing, we can state that the hybrid NX 47279 has resulted stable and high yields in the fertilized treatments. Analysing the yield-increasing effect of 1 kg fertilizer active substance it was proven, that the hybrids SY Flovita (45.43 kg ha-1), SY Brillio (44.47 kg ha-1) and NX 47279 (42.33 kg ha-1) had a good reaction towards even lower nutrient supply levels as well. In case of the control treatment the average water utilization coefficient of the hybrids was significantly lower (35.2 kg mm-1), than in case of the optimal nutrient supply level (N120+PK) treatments (48.9 kg mm-1).
Therefore the hybrid specific difference between the water utilization of genotypes could be revealed. -
Effect of cropping technologies on the yield of dry bean variety ’Diana’
37-41Views:230An experiment on three dry bean varieties (Start, Hópehely, Diana), using different sowing-times, fertilizers and plant densities was performed on sandy soil in the University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural Sciences, Research Institute of Nyíregyháza in 2015. The aim of the experiment was to study which treatment gives the highest yield, and whether the different treatments result in significant differences in the yields. In this paper the dry bean yield at ‘Diana’ variety is analyzed.
The treatments were done with three fertilizer doses and three plant densities at different sowing-times (April 24; May 8; May 18). As a result of the high temperature and the drought during the growth season, the yields we harvested were in low, which shows the ecological sensitivity of the plant we examined.
We concluded that the poorest yield was harvested at the third sowing-time. There was no significant difference in the yields at the first and second sowing- time. Examining all the three fertilizer treatments we applied at the experiment, we achieved the highest yields in the control plots. It might be due to the weak efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer under the extremely dry conditions. The highest yield was harvested at the control treatments during the second sowing-time. Regarding the effect of the plant densities, the highest crop yield was achieved at the treatment using 400 000 germs ha-1, followed by 300 000 germs ha-1 and 200 000 germs ha-1.
-
Evaluate the nutritional reaction at winter wheat after different forecrops
77-80Views:214Our field researches took place on the Látókép test farm of Agricultural Science Centre of University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences, in long-term experiment, on calcareous chernozem soil, in growing season of 2014/2015. In our experiment we examined the fertilizer reaction and the yield of different winter wheat genotypes (GK Öthalom, GK Csillag, Mv Csárdás, Mv Toldi) with grain maize and sweetcorn forecrops. According to our results, the sweetcorn forecrop strongly affected the yield. In the average of the fertilizer treatments and the varieties, after sweetcorn forecrop 6.9 t ha-1, after grain maize forecrop 5.4 t ha-1 average yield was gained. According to our data, the fertilizer reactions of the varieties were significantly different.
-
Comparative examination of a bacterium preparation (BACTOFIL® A10) and an artificial fertilizer [CA(NO3)2] on calcareous chernozem soil
75-80Views:274In a small-pot experiment a bacterium preparation, Bactofil® A10 and an artificial fertilizer containing Ca(NO3)2 in different dosages were studied on calcareous chernozem soil, concerning the readily available nutrient content of soil (nitrate-nitrogen, AL-phosphorus, ALpotassium content of soil, some soil microbial characteristics (total number of bacteria and fungi, cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria, CO2-production of soil), and the amount of the plant biomass.
The readily available nutrient content of the calcareous chernozem soil increased due to the treatments, except for the change in the soil nitrate-nitrogen content, which did not measure up to the control due to the effect of high-dosage Bactofil.
The treatments also influenced the examined microbial characteristics of the soil positively. The artificial treatments significantly increased the total number of bacteria and the number of cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria. The low-dosage Bactofil significantly increased the number of cellulose-decomposing bacteria and both Bactofil dosage significantly increased the number of nitrifying bacteria. The measure of the soil respiration grew in all treatments, but significantly only in Ca(NO3)2 fertiliser treatments.
The quantity of the plant biomass was grew in a low-dosage Bactofil and significantly in the artificial fertiliser treatments. The highest plant biomass quantity was measured in the high-dosage artificial fertiliser treatment.
In the correlation analyses we found some medium positive correlation between the soil chemical, microbiological parameters examined, and the plant biomass in the case of both treatment-forms.
Based on our results Ca(NO3)2 artificial fertiliser treatments on calcareous chernozem soil proved to be more stimulating regarding the
examined soil characteristics and the amount of the plant biomass, but the low-dosage Bactofil also positively influenced the majority of the
soil characteristics examined in terms of nutrient supply. -
The effect of NPK fertilization and the number of plants on the yield of maize hybrids with different genetic base in half-industrial experiment
103-108Views:377In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize.
The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2, this it was a halfindustrial experiment. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. Yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare at a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants/ha.
In Hajdúszoboszló, in 2015 the amount of rainfall from January to October was 340.3 mm, which was less than the average of 30 years by 105.5 mm. This year was not only draughty but it was also extremely hot, as the average temperature was higher by 1.7 °C than the average of 30 years. In the critical months of the growing season the distribution of precipitation was unfavourable for maize: in June the amount of rainfall was less by 31mm and in July by 42 mm than the average of many years.
Unfavourable effects of the weather of year 2015 were reflected also by our experimental data. The yield of hybrids without fertilization changed between 5.28–7.13 t ha-1 depending on the number of plants.
It can be associated also with the unfavourable crop year that the yield of the six tested hybrids is 6.33 t ha-1 in the average of the stand density of 60, 70 and 80 thousand plants per hectare without fertilization, while it is 7.14 t ha-1 with N80+PK fertilizer treatment. That increase in the yield is only 0.81 t ha-1, but it is significant. Due to the especially draughty weather the yield increasing effect of fertilizers was moderate. In the average of the hybrids and the number of plants, increasing the N80+PK treatment to N160+PK, the yield did not increase but decreased, which is explicable by the water scarcity in the period of flowering, fertilization and grain filling.
The agroecological optimum of fertilization was N 80, P2O5 60 and K2O 70 kg ha-1. Due to the intense water scarcity, increased fertilization caused decrease in the yield. As for the number of plants, 70 000 plants ha-1 proved to be the optimum, and the further increase of the number of plants caused decrease in the yield.
-
Comparative study of a winter wheat variety and hybrid sown after different pre-crops on chernozem soil
63-69Views:428Wheat production is a determining branch within Hungarian crop production (produced on nearly one million hectares). Weather anomalies caused by climatic change confirmed the importance of the biological background (variety, hybrid) in wheat production. The adapting ability and reaction of different wheat genotypes towards nutrient supply were studied in a long-term field experiment on chernozem soil type in the case of different pre-crops (sunflower and maize). According to the experimental results of the vegetation of 2017/2018, the yield of the variety Ingenio sown after the sunflower as previous crop ranged between 4168 and 8734 kg ha-1, while in the case of maize as previous crop, this value ranged between 2084 and 7782kg ha-1, depending on the applied nutrient supply level. The studied genotypes produced rather significant yield surplus as a response to the application of mineral fertilization (4.6–5.1 t ha-1 after sunflower and 5.7–6.3 t ha-1 after maize). Optimal mineral fertilizer dosage was determined by both the genotype and the pre-crop. N-optimum values of wheat genotypes was determined using regression analysis. In the case of the variety Ingenio sown after sunflower, the optimum range was N144-150+PK, while after maize, it was
N123-150+PK, respectively. For the hybrid Hyland, these optimum ranges were N114-120+PK, just as N150-153+PK, resp. The application of optimal mineral fertilizer dosages improved water utilization of the studied wheat genotypes to a significant extent. WUE values of the control, unfertilized treatments ranged between 4.1–8.3 kg mm-1, while in optimal fertilizer treatment, it ranged between 15.5 and 17.4 kg mm-1. -
Effect and interaction of crop management factors and crop year on the yield of maize (Zea mays L.)
31-41Views:422The aim of this study was to determine the combination of treatment levels of crop management factors which can optimize and sustain maize yield under varying climatic conditions. The effect of winter wheat forecrop, three tillage systems (Mouldboard-MT, Strip-ST, Ripper-RT), two planting densities (60,000 & 80,000 plants ha-1), three fertilizer levels (N0-control, N80, N160 kg ha-1) with four replications in irrigated and non-irrigated treatments were evaluated over a five year period, 2015–2019. The obtained results revealed that growing season rainfall positively correlated with yield, whereas, temperature negatively correlated with yield. Impact of adverse weather on yield was less severe in biculture, irrigated plots, at lower planting density (60,000), lower fertilizer rate (N80) and in RT and ST, compared to MT. In years with favorable rainfall, yields of MT and RT were significantly (P<0.05) higher than ST. However, in a less favorable year, such as 2015, with 299 mm growing season rainfall and the lowest July rainfall (59% below mean) there was no significant difference (P>0.05) in yield among the three tillage treatments. Higher planting density (80,000), and fertilization rate (N160) in tandem with MT are treatments combination conducive for high yield under favorable climatic conditions, whereas, in years with low rainfall and high temperatures, RT and ST offer alternative to MT for optimum yield with 60,000 plants ha-1 and N80 treatment level. Crop year effect accounted for 20.7% of yield variance, fertilization 35.8%, forecrop 12.8%, plant density 3.4%, tillage 1.2% and irrigation <1%. It is conclusive that with proper selection of the appropriate levels of agrotechnological inputs the adverse effect of weather on yield can be mitigated.