Search
Search Results
-
On the connection between spatial development and sustainable landscape in the Northern Great Plain region
145-148Views:145This paper tries to find connection between sustainable landscape and spatial development policy of the Northern Great Plain region on the basis of specific examples explained in scientific literature. Searching for the common roots of spatial development and sustainability the paper explains two interpretations of sustainability from the view point of landscape, than the most significant element of current landscape change – the polarization of landscapes – will be introduced. This trend in landscape change basically determines the direction of spatial development. This paper analyses the Northern Great Plain region from two different approaches. In the first grouping the region is exposed from the view point of spatial development. In the second partitioning the area is divided into subject matters based on the principles of sustainability and polarization of landscape. This research – analyzing development plans and strategies – considers the current situation within the subject matters.
-
The management and economical aspects of GPS based machine-control and tractor-implement sincronisation
161-167Views:282Precision farming has an array of technological equipment, elements and complete systems which are in themselves suitable to create conditions for efficient farming, to reduce environmental load and to provide farmers with optimal return on their investment.
On the leading edge of my research is to introduce the economic benefits of precision logistic optimization with satellite navigation in wheat and maize harvesting. My hypothesis, claiming that a well-organized system can increase the number of working days by 4 days per harvesting season in maize, and 2 days in wheat crop. If the farmer makes contract works for harvesting it means for him 2 or 4 days extra work by using the precision farming technologies with satellite communication system. Overall, as pertains to wheat and maize harvest seasons, yearly revenues can be increased by 7 760 000 HUF. I would like to introduce that the precision technologies increase combine costs by merely 5.4% which can be return in the first year of using.
-
The potential of biological control on invasive weed species
73-75Views:249Sorghum halepense is one of the invasive species in Europe. This study was made to identify the morphology of fungi on invasive weed species samples on the roots of Sorghum halepense. The samples were collected in the region of Debrecen. The experiment was conducted under laboratory conditions to determine the microscopic form of fungi. The samples were put on PDA and for identification of fungi is based on the morphological characteristics of the features and colonies of conidia that were developed in Petri dishes.
The examination of the culture revealed that the fungus from the root of Sorghum halepense was Aspergillus niger. Pathogenicity and the relationship between the fungus and Sorghum halepense are still uncertain so in the future pathogenicity tests and re-isolations from plants are very important steps.
-
Some Practical and Biotechnological Methods for Improving Reproduction Traits in Sheep
15-20Views:240However, reproduction in sheep is seasonal, many breeds of sheep are able to mate not only in autumn, but out-of-season as well. The main factor determining seasonality is the photoperiod, but other factors can influence reproductive pattern, such as genetics, management practices and social cues. The fertility of spring and early summer breeding is usually lower; this imposes the need for alternative methods (e.g. hormonal treatments, biotechnological practice), to increase the conception rate.
The author summarize the main practical techniques and biotechnological methods for controlling reproduction completed with some own experimental results in connection with different topics. -
Economics of site specific crop density in precision sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) production
91-96Views:374In this research, the crop density of sunflower was examined, which, thanks to the tools available for precision crop production and knowledge of the market environment of sunflower production, best fits the heterogeneous areas of the given production zones and meets the economic requirements. These components together directly influence the effectiveness of sunflower production. In the year of 2021 and 2022, we carried out a site-specific crop density sunflower experiment in two fields with the same soil type, by sowing significantly different amounts of seeds within the given zones. We have established that the sunflower, although a plant with excellent adaptability, reacts sensitively to the place of production and the effect of the year, in zones with heterogeneous productivity, and shows a reaction to sowing with a variable number of seeds per zone, even when examined based on economic aspects.
-
Establishing regional cultivating districts on the basis of the Kreybig practical soil mapping system
20-25Views:375With the help of this report evaluating the current situation of the region, characteristics of the development in agricultural production and regional differences can be clarified. By mapping out the regional soil, land use and climatic conditions and organizing these into a geographical information system, one can easily determine which plants are the most ideal to cultivate in that particular region. Moreover, it is a useful tool that enables us to
establish the most favorable land use structure suited to ecological demands and also helps to determine the methods of soil protection.
During our work, we chose administrative units in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County, based on the latest aspects of regional cultivation.
Our pilot areas are: the small regions of Nyíregyháza, Nyírbátor, Nagykálló, Mátészalka and Csenger.
Using the database, we separated and uncovered the soil conditions of the pilot areas: the chemical and physical properties of the soil layer which is exploited by the roots of the plants, the humus content, the nutrient supply, the thickness of the cultivated layer and the water management conditions.
We separated the districts of regional cultivation, where the basic elements of the traditional Kreybig color systems were applied (light yellow, dark yellow, light brown, dark green, blue, pink, red, gray, greenish brown, reddish purple, light purple, dark purple, light green).
By using the data collected from the pilot areas, we compiled a map database, which is suitable to illustrate the plant cultivating characteristics of the region. We made recommendations to determine the most favorable plants to cultivate in the specific region with the given meteorological and soil conditions, as well as for the shifting of crops.
Our recommendations were also illustrated in a map with a resolution of 1:25000. -
Viability and Economies of Scale in EU Farms
332-338Views:121With this study, the author intends to draw up the main characteristics of the institutional background of the Farm Accountancy Data Network, operated by the European Union. Among the factors that contribute to the formation of the institutional background of the FADN database, special emphasis is laid on the Commission and member state level legal framework, in order to provide potential Hungarian users of the database with authentic and substantial information. Also, much attention is paid to definitional misunderstandings which cause, or might cause the farm business management type utilization of the database to be imperfect. As for this goal, some of the elements of the FADN information structure are investigated in a conventional Hungarian cost structure. In order to facilitate an easier understanding of the database, the different relations of economic size classes are also reviewed in this study. The author of this study is – in the first place – trying to analyze the meaning of Standard Gross Margin, the index used in the FADN structure to categorize farms, by localizing the position of the different cost constituents of SGM in a conventional Hungarian cost matrix. Last, but not least, the author is trying to draw all researcher’s attention on the possibilities, hidden in the FADN database by introducing some analyses from his own field of interest based on FADN information.
-
The occurrence and phenology of moth pests in different granary of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County
70-75Views:187The aims of my studies were the followings: primarily to find correlation between the conditions of granary and the occurrence of moth pests. Secondly I studied the effect of disinfection on individual numbers in the population of moths. My studies were started in May 2009 in six different places of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County. Indianmeal moth (Plodia interpunctella) and Mediterranean Flour Moth (Ephestia kuehniella) traps with pheromone were installed in four repetitions as well as Angoumois Grain Moth (Sitotroga cerealella) traps in also four repetitions. Control traps without attractant were also placed at every place.
From my researches, it became clear that the disinfection alone is not enough to protect cereals from moths. As in the case of crop protection, we need to apply integrated pest management.
We have to make differences between preventive protections from moth pests and the elimination of them by chemicals.
Up to my opinion, the regular checking and cleaning of the granary are important as well as the prognosis of the possible occurrence of moths. The prognosis is considered important because the studied moths do not feed at the adult stage or only at a low level. However, the caterpillars coming from the eggs placed by females can cause a significant damage in the stored cereals.
The studied sex pheromone traps are proved to be useful for the reduction of number of moths since the traps caught lots of them. These traps are relatively cheap because only the temporarily changes of pheromones increase the cost. -
The R&D and innovation activity of agribusiness enterprises in Hajdú-Bihar County
67-71Views:201Economic changes have significantly accelarated in the 21th century. In this turbulent market environment enterprises are forced to adapt continously as they must be flexible in order to meet changing market needs. To achieve flexibility companies require innovation. The economic relevance of innovations is significant in every market sector and agriculture is no exception. Re-dynamizing agricultural innovations is a possibility for the outburst of the Hungarian agriculture. Agricultural enterprises have to face competitors as well and they should give priority to efficiency, sustainability and competitiveness in order to preserve their position in BOTH global and domestic markets. This study examines the innovation potential of the agricultural enterprises in the North Great Plain region based on own databases and case studies.
-
Comparison of Reproductive Performance of the Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus, L.) Among Different Regions
41-46Views:188The potential and actual number of offspring of roe deer and the difference between these figures (prenatal and postnatal loss) significantly vary in each population yearly. The objective of this study is to examine the potential and actual number of offspring, the number of losses, and to find a link between the most important biological characteristics of does (body weight – BW, condition – KFI) and the number of raised offspring on four territories on the Great Hungarian Plain.
Where the number of corpora lutea (CL) is the highest, there the losses are the highest as well, and the number of raised offspring is the lowest (region I.). Here, the rearing loss is double that of the weakest territory (region IV.). Rearing losses can be associated with the fenotype of does (BW, KFI) but environmental factors also have determinative importance. Where the number of twin-calving does was the highest, I found four times more does without a fawn than where the number of twin-calving does was the lowest. The nursing success was the best (the losses were lowest) in the region where the potential offspring (number of CL) was also the lowest, but the coverage of the habitat and the proportion of forests were largest. The food supply for the animals in autumn and winter are not enough, the structure of the habitat has to be improved as well, so that it might become adequate for game protection in extreme weather conditions.
The results have to be considered as preliminary ones. It is essential to continue and extend the research to increase the reliability of the results. -
Research of the interrelations between actors and strategic goals in decision making
71-75Views:130management, although there are many chiseled methodologies plenty of professional literature.
The problem is more complex in strategic planning of regional communities – societies – of different range. These societies are very diverse, and accordingly the strategic goal setting can, and has to be very different than the strategic goal setting of enterprises.
The group of methods for morphologic and structural analysis and the computer based MACTOR program could be used.
The output data are presented in a large number of matrixes, vectors, graphs and histogram’s, which describe very fair the possible scenarios for preparation and decision making about
strategic plans. -
Seasonal changes of photosynthetical parameters as a results of forest gap model
133-136Views:323Photosynthetic parameters of English oak (Quercus robur L.) as a member of Querco robori-Carpinetum were investigated in two different habitat in terms of gap forest management: in the gap and in the host forest. The artifical opening process of the forest resulted in more light for growing saplings and need for acclimatization. Photosynthesis is one of the most important way for plant life and plant production. In the centre of photosynthetic efficiency the quality and quantity traits of photosynthetic pigments are standing. During our work some photosynthetic parameters of plants (in the gap and in the forest as well) were measured: relative chlorophyll content as SPAD index, chlorophyll a and b content, total chlorophyll content and ratio of chlorophyll a and b. Based on our results no significant differences among our data in early spring. Although, during the summer significant differences occurred between the measured values in the gap and in the forest area. Lower total chlorophyll content was experienced in the gap, than in the forest area due to the lower chlorophyll-b content. Because of the high light intensity higher chla/chlb ratio was measured in the gap. The lower chlorophyll contents of gap habitat may have a part of the acclimatization process of photosynthetic apparatus against high light stress, which can determinate the survival chance of individual.
-
The importance of millet production in regional production, with special emphasis on climate change
141-146Views:359Regional production is a traditional production structure developed adjusting to the geographical, climatic, biological and soil conditions in given production regions, a certain territorial specification of agricultural production, and a type of farming that best fits the natural conditions and takes the biological needs of plant and animal species into account as fully as possible. The most probable element of risk in plant production is the changeable, extreme weather. That is the reason why the specific characteristics of the place of production and the characteristics of regional production should be considered to a greater extent. The establishment of the range of varieties appropriate for the place of production is the key issue in regional production. One of our historically grown cereal plants that perfectly fits regional production is millet. Due to its short growing season, favourable reproduction ratio and the fact that it is relatively undemanding, it used to be grown in larger quantities in the middle ages. Its good nutritional values made it an important food item, but over time, as a result of industrialisation and technological progress; it has been eclipsed by other cereal crops. In our country it is mainly used to cook porridge, but it is also used in the form of flour and as a base material in the spirit drinks sector. In the recent decades, millet has been applied only in a small area, mostly as a secondary crop in areas that dried out from drainage water in late spring, or as a replacement of extinct sowings due to its late sowing time. Water will be the most significant factor for the future of agriculture, especially considering climate change.My examinations took place in the area of the Institutes for Agricultural Research and Educational Farm of University of Debrecen, in the Research Institute of Nyíregyháza, in a small-plot experiment with four replications in 2016. -
The effect of grazing of various cattle breeds on botanical composition of low-lying pasture in Hortobágy
57-63Views:596Coenological surveys were conducted in the Hortobágy National Park (Pap-ere and Zám-puszta) in May 2015 and 2016. During the tests,a total of 40 permanent plots were analyzed on grasslands grazed by extensive cattle (Hungarian Grey) and mixed genotype intensive cattle. The presence of plant species, percentages of total coverage of species and vegetation cover were recorded. Two habitat types were chosen according to their moisture content: wet salt marsh meadow (Bolboschoenetum maritimi) and drier salt meadows (Beckmannion eruciformis).
We compared the impact of increased number of animals (2016 years) and the low number of animals (2015 years, initial state) and the grazing exclusion on vegetations.
We tested: (i) what is the impact of grazing on the vegetation, (ii) how do species composition and vegetation charachteristics differ in the two habitat types (iii) and is there a difference in the impact of different cattle breeds (Hungarian gray, intensive beef cattle) grazing on the grasslands species composition? During the investigation we found, (i) that the greatest number of species was recorded in 2015, on the area that received moderate to intensive grazing (14.3 species per m2). Somewhat the number of species was reduced in 2016 due to more intensive grazing. The control group had the lowest number of species (11.7 species per m2). The undergrass and legumes cover significantly increased on intensive grazed lands. (ii) Our results indicate that the effects of different grazing differ in the two studied habitat types. On the drier grasslands greater number of species were found (16.2 species per m2), oppositely to the wet grassland (11.2 species per m2). The cover of the undergrasses was higher in the drier habitat than in the wet. (iii) The extensive beef cattle left a bigger number of species (16 species per m2) than the intensive beef cattle (11.4 species per m2). The grass cover was more intense on areas grazed by intensive cattle. The absolute and potential weeds cover showed a higher value on areas grazed by Hungarian Grey. Our two-year results suggest that grazing by both extensive and intensive cattle breeds can be a proper tool for the conservation management of alkali grasslands. -
Estimating the amount and heating value of wood waste burned in households based on FICM HWP model output data
79-84Views:376A 2009 study published by the Regional Centre for Energy Policy Research (RCEPR) sparked significant debate within the Hungarian forestry and wood industry sectors. The study suggested a substantial shortfall in the balance of solid bioenergy biomass usage and sources, which it attributed to large-scale illegal logging. The Bio Screen CCE Project updated this analysis and quantified a 37.2 PJ (43%) deficit in the solid bioenergy biomass balance for 2019. This study investigates the extent to which household wood waste burning could account for this shortfall. Using the Forest Industry Carbon Model (FICM) HWP submodel, the authors estimate that over 1.2 million m³ of wood waste may be burned annually in households. The heating value of this burned wood waste for 2019 is estimated at 14 PJ, explaining 39% of the shortfall identified in the Bio Screen CCE Project’s 2021 report.
-
Examination of different fungicides against Macrophomina phaseolina in laboratory conditions
65-69Views:327In Hungary, sunflower is the third most important arable crop, which has a lot of pathogenic fungi. One of these fungi is the Macrophomina phaseolina, which is a well-known fungus in all over the world, since this pathogen has more than 700 host plants. In Hungary, several host plants can be found as well. The M. phaseolina produces microsclerotia, which can survive in the soil and residues for almost 10 years. For now, there is no efficient treatment against this pathogen because of this fungus, since it is extremely resistant and cannot be destroyed easily. The only effective treatment against the fungus is genetic defence. In this study, three different fungicides were tested in vitro against the fungus. The Mirage (prochloraz) seemed to be the most effective fungicide as it completely arrested the hyphal growth. In contrast, the Amistar Xtra (azoxystrobin and ciprochonazol) has only a minor effect on the growth of M. phaseolina. Thirdly, the Retengo (pyrachlostrobin) arrested the hyhpal growth of the fungus with 71% at 100 ppm, in other words, the use of this fungicide seems promising.
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:328During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: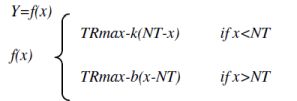
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Procurement as enterprise function at vegetable and fruit processing companies
228-235Views:130The first main element of the supply chain is procurement; which has a great influence on the quality of products and services. The most important role of the procurement is the purchase of inputs which are necessary for the operation of companies. This includes procurement planning and the development of procurement strategy, so procurement is a process that is even more than simply buying raw materials. The functions of procurement are the selection of suitable suppliers, contracting, controlling and improvement of suppliers, and coordination of activities with other parts of the company.
Planning of procurement, strategy formulation, supplier selection and evaluation, monitoring of the procurement process, and modification of original plan are important tasks of entrepreneurial procurement. The importance of procurement in a business organization is reflected by its position in the hierarchy of the firm. There are subjective and objective methods to select suppliers accomplishing their tasks on time and with good quality. Efficient purchasing management activity contributes to an increased competitiveness of the enterprise. The aim of this publication is to describe the procurement activities, to examine supplier selection and evaluation methods, to determine the position of procurement in the organization, and to prove the strategic importance of procurement. -
Comparative examination of a bacterium preparation (BACTOFIL® A10) and an artificial fertilizer [CA(NO3)2] on calcareous chernozem soil
75-80Views:267In a small-pot experiment a bacterium preparation, Bactofil® A10 and an artificial fertilizer containing Ca(NO3)2 in different dosages were studied on calcareous chernozem soil, concerning the readily available nutrient content of soil (nitrate-nitrogen, AL-phosphorus, ALpotassium content of soil, some soil microbial characteristics (total number of bacteria and fungi, cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria, CO2-production of soil), and the amount of the plant biomass.
The readily available nutrient content of the calcareous chernozem soil increased due to the treatments, except for the change in the soil nitrate-nitrogen content, which did not measure up to the control due to the effect of high-dosage Bactofil.
The treatments also influenced the examined microbial characteristics of the soil positively. The artificial treatments significantly increased the total number of bacteria and the number of cellulose-decomposing and nitrifying bacteria. The low-dosage Bactofil significantly increased the number of cellulose-decomposing bacteria and both Bactofil dosage significantly increased the number of nitrifying bacteria. The measure of the soil respiration grew in all treatments, but significantly only in Ca(NO3)2 fertiliser treatments.
The quantity of the plant biomass was grew in a low-dosage Bactofil and significantly in the artificial fertiliser treatments. The highest plant biomass quantity was measured in the high-dosage artificial fertiliser treatment.
In the correlation analyses we found some medium positive correlation between the soil chemical, microbiological parameters examined, and the plant biomass in the case of both treatment-forms.
Based on our results Ca(NO3)2 artificial fertiliser treatments on calcareous chernozem soil proved to be more stimulating regarding the
examined soil characteristics and the amount of the plant biomass, but the low-dosage Bactofil also positively influenced the majority of the
soil characteristics examined in terms of nutrient supply. -
Different soil fertility conditions depending on different land use methods
169-172Views:182In precision nutrient management the most important aspect is adaptation but we should consider the possibility of the long-term improvement of soil fertility within the less fertile landscape zones. This possibility can be evaluated principally by long-term field experiments, which are running on similar soil types. The results of these field experiments can indicate that which soil fertility status should be attained. Some more important soil fertility data, (such as pH, P-, K- and soil organic matter (SOM) content) of a long-term field experiment with increasing farmyard manure(FYM) doses or equivalent NPK fertilizers, set up on an Eutric cambisol, are presented. The yieldincreasing capacity of FYM doses was only 82%, as compared to the equivalent amount of mineral NPK, but long-term FYM treatments resulted in 10% higher SOM content than that of equivalent NPK
fertilizer doses. The studies indicate that SOM content is a function of local climate and clay content of the soil, and neither long-term high FYM doses can increase SOM content steadily above a supposed steady-state value. However we have to make efforts to keep the optimum level. The lowest soil reactions developed both with the highest NPK doses and without any fertilization. AL-P2O5 content of soil was increased more by mineral fertilization than by FYM treatments, but in case of AL-K2O content there was no difference between the fertilization variants. However the highest doses of both fertilization variants increased soil nutrient content to an excessive degree. Wecould get very valuable data from the unfertilized control plots as well, where long-term yield data suppose 48 kg ha-1 year-1 air-borne N-input. -
The Role of transformal leadership in local governments’ efficiency
33-41Views:210Local governments had to respond to the challenges of the dynamically changing environment. A key element of the rapid adaptation lies in the right leadership. The local governments also recognized that the traditional management principles are found not to be effective in today's economic, political and social challenges.
The employees of the organizations are successful in the attainment of leadership, which are planning the next year, performance-based, as well as the leading is diplomatic, charismatic-development, group integrators. The investigated local governments’ middle level leaders believe that in the current economic and political situation only those organizations able to keep up, which emphasize the trans-formal leadership.
-
Spent mushroom compost (SMC) – retrieved added value product closing loop in agricultural production
185-202Views:1384Worldwide edible mushroom production on agro-industrial residues comprises of more than 11 million tons of fresh mushrooms per year. For 1 kg of mushrooms there is 5 kg of spent mushroom compost (SMC). This enormous amount of waste results in disposal problems. However, SMC is a waste product of the mushroom industry, which contains mycelium and high levels of remnant nutrients such as organic substances (N, P, K). The spent mushroom compost is usually intended for utilization, but there are increasing numbers of experiments focusing on its reuse in agricultural and horticultural production. Recently, the increase of the global environmental consciousness and stringent legislation have focused research towards the application of sustainable and circular processes. Innovative and environmentally friendly systems of utilisation of waste streams have increased interest of the scientific community. Circular economy implies that agricultural waste will be the source for retrieving high value-added compounds. The goal of the present work was to carry out a bibliographic review of the different scenarios, regarding the exploitation of this low cost feedstock with huge potential for valorisation.
-
Inhibition of the spread of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in aquaponics
5-8Views:570Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, which causes white mold, is a widespread pathogen. In 2020, a new host plant of this fungus, the watercress (Nasturtium officinale) was identified in Hungary in an aquaponic system. During the cultivation of watercress S. sclerotiorum was detected on the plant, the fungus caused a 30% yield loss. Fungicides should not be used against fungi in aquaponic systems. Non-chemical methods of integrated pest management should be used. These include biological control (resistant species, predators, pathogens, antagonist microorganisms), manipulation of physical barriers, traps, and the physical environment. In the aquaponic system, the removal of the growing medium (expanded clay aggregate pellets) solved the damage of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum 100%. By removing the expanded clay aggregate pellets, the environmental conditions became unfavorable for the development and further spread of the S. sclerotium fungus.
-
Efficiency of Fertilization in Sustainable Wheat Production
59-64Views:305In sustainable (wheat) production plant nutrition supply and fertilization play decisive roles among the agrotechnical elements, because of their direct and indirect effects on other agronomical factors.
In long-term experiments, we studied the roles of agroecological, genetic-biological and agrotechnical factors in the nutrient supply, fertilization and its efficiency in wheat production under continental climatic conditions (eastern part of Hungary, Trans-Tisza) on chernozem soil. Our results have proved that there are different (positive and negative) interactions among ecological, biological, and agrotechnical elements of wheat production. These interaction effects could modify the nutrient demand, fertilizer (mainly nitrogen) response of wheat varieties and efficiency of fertilization in wheat production.
The optimum N-doses (+PK) of wheat varieties varied from 60 kg ha-1 (+PK) to 120 kg ha-1 (+PK) depending on cropyears, agrotechnical elements and genotypes. The winter wheat varieties could be classified into 4 groups according to their fertilizer demand, natural and fertilizer utilization, fertilizer response and yield capacity.
Appropriate fertilization (mainly N) of wheat could affect both the quantity and quality of the yield. By using optimum N (+PK) fertilizer doses, we could manifest genetically- coded baking quality traits of winter wheat varieties and reduce quality fluctuation caused by ecological and other management factors. The efficiency of fertilization on different baking quality parameters (wet-gluten, valorigraph index etc) were variety specific (the changes depended on genotypes).
Our long-term experiments proved that appropriate fertilization provides optimum yield, good yield stability and excellent yield quality in sustainable wheat production. We could this get better agronomic and economic fertilization efficiency with less harmful environmental effects. -
Relationships of Fruit Production and Regional Development in the Northern Great Plain Region
181-187Views:202The role of retaining population in agriculture is stronger and more significant in the long run in the North Great Plain Region compared to other regions. The region has a significant processing industry along with a good basis for producing raw materials, developed food processing capicity and high quality agricultural products typical of the region. The GDP in agriculture, forestry and game management is somewhat higher than the national average.
Variety is of cardinal importance when establishing the quality of horticultural products and determining the product value. The Hungarian breeding results of apple, quince, apricot, cherry, raspberry, red and black currant are promising.
The regulation system of EU the vegetable and fruit market is based on Retail Cooperatives Producers. With the establishment of national vegetable- and fruit production and retail organizations, the market regulation, production and quality development issues of the sector can be handled and solved. Reaching EU standards in fruit production can only be achieved with up-to-date plantation systems and breed selection. A key issue in development is establishing the required financial resources for investments and updating production. In order to reach these standards, significant state subsidies and good credit conditions are needed. By solving these tasks, the sector is expected to become self-financed without government help.
The pursuit of safer production, improving quality and increasing yields require the establishment of up-to-date irrigation systems. The improvement of family farms, motivating land concentration is necessary for increasing average size of plants. Establishing the above mentioned conditions is important since the vegetable-fruit sector is of great significance in the employment of rurally based population, improving their living conditions and executing rural development programs.