Search
Search Results
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:112During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: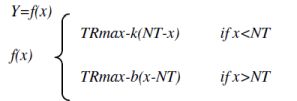
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Analysis of maize and sunflower plants treated by molybdenum in rhizobox experiment
11-14Views:183In this study, maize (Zea mays L. cv. Norma SC) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus L. cv Arena PR) seedlings treated by molybdenum (Mo) that were cultivated in special plant growth boxes, known as rhizoboxes. During our research we tried to examine whether increasing molybdenum (Mo) concentration effects on the dry mass and absorption of some elements (molybdenum, iron, sulphur) of shoots and roots of experimental plants.
In this experiment calcareous chernozem soil was used and Mo was supplemented into the soil as ammonium molybdate [(NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O] in four different concentrations as follow: 0 (control), 30, 90 and 270 mg kg-1.
In this study we found that molybdenum in small amount (30 mg kg-1) affected positively on growth of maize and sunflower seedlings, however, further increase of Mo content reduced the dry weights of shoots and roots. In case of maize the highest Mo treatment (270 mg kg-1) and in case of sunflower 90 mg kg-1 treatment caused a significant reduction in plant growth.
In addition, we observed that molybdenum levels in seedling were significantly elevated with increasing the concentration of molybdenum treatment in comparison with control but the applied molybdenum treatments did not affect iron and sulphur concentration in all cases significantly.
-
Studies of the effects of N fertilizers and Microbion UNC biofertilizer on microelement content of horseradish (Armoracia macrocarpa)
41-45Views:115A field experiment on calcareous chernozem soil was performed to study the effects of different N and bacterial fertilizers on the nutrient content of horseradish (Armoracia macrocarpa). In the experiment the trials were arranged in a randomized block design with three replications, applying three levels of NH4NO3 and different N fertilizers, namely ammonium-nitrate, urea and calcium-nitrate, with or without application of Microbion UNC biofertilizer.
In the present paper the changes and distribution of manganese, zinc and copper contents of the horseradish plant are summarized by the
effect of different treatments.
The Mn content of leaves were higher in all cases than those of roots, but Zn mainly accumulated in the roots. The distribution of copper within the horseradish plant was more equalized than that of Zn and Mn. Different N fertilizers and increasing doses of ammonium-nitrate had effects mainly on the microelement contents of leaves. The highest Mn contents of plant were measured in treatments of Ca(NO3)2 and Ca(NO3)2+Microbion. The lowest ammonium nitrate dose (N1) decreased the Mn content of leaves compared to control, but further doses
(N2, N3) did not alter these values any longer. Microbion UNC biofertilizer did not have any effect on the Mn content of roots, but we measured higher Mn in leaves in some combined treatments. Ca(NO3)2 increased the zinc content in leaves and roots in a noticable manner. With the increasing of NH4NO3 doses, the Zn content of leaves and roots augmented significantly. Neither N fertilizers (or the increasing doses of NH4NO3) nor the biofertilizer application influenced the Cu content of horseradish plant.
N fertilizers had higher effects on the microelement content of horseradish, the biofertilizer’s effect was smaller and was not the same in every treatment. -
Complex evaluation of agrotechnical factors in rape seed
59-63Views:95A polifactorial field trial with rape was carried out in the crop-years of 2007/2008 and 2008/2009 at the Látókép Research Centre of University of Debrecen, 15 km away from Debrecen. The soil type of the research area was a calcaric chernozem, with a levelled and homogeneous surface. Our investigations on the dynamics of lodging proved that rape can easily be lodged under unfavourable weather conditions, which results in a significant crop failure: In crop-year 2009 yields were 1.0-1.5 t ha-1 higher than in 2008, when the weather conditions were more unfavourable. In both crop-years the influence of sowing time on the crop yield of rape was examined in three soil cultivation systems, with ploughing, loosening or disking. Different sowing time influenced the yield of rape in both crop-years significantly. In the crop-year of 2007/2008 – due to mild winter – we got the highest yield in the first sowing time (at the end of August) with loosening (3930 kg ha-1) and disking (3727 kg ha-1), while in case of ploughing we experienced the highest yield (3770 kg ha-1) in the second sowing time. There were no significant differences between the first and second sowing time (the end of August and the beginning of September), and in the third sowing time (end of September) also a moderate crop failure (-6.7%) cold be obtained, due to the favourable weather in winter and the water supply of the crop-year 2007/2008. In 2008/2009 all the three cultivation systems showed the best yield-results in the second sowing time (ploughing: 4886 kg ha-1, loosening: 5186 kg ha-1, disking: 5090 kg ha-1), and the first sowing time hardly differed from this (-4.1%), while the late September sowing time resulted in a significant crop failure of -11.1%.
-
Changes in the Macro-, Mezo-, and Microelement Contents of Maize Hybrids in Relation to the Level of Nutrient Supply
126-130Views:64n my research, I measured the effect of NPK fertilisation on the macro- meso- and microelements content of maize hybrids in 2001. The experiment was set in the demonstration garden of the Department of Crop Production and Applied Ecology in the Agricultural Centre, at the University in Debrecen. The soil of the experiment is calcerous chernozem soil. Five fertilisation steps were applied. Besides the control the smallest rate was 40 kg N; 25 kg P2O5; 30 kg K2O of active ingredients. The largest rate was five times more than the smallest one: 200 kg N; 125 kg P2O5; 150 kg K2O, which is equal to 475 kg mixed active ingredients. The NPK treatment significantly influenced the macrolement content in several cases. The N content was the lowest in the control treatment. Compared to this the fertiliser treatments significantly increased the N content of hybrids. However the highest amounts of potassium and phosphorus could be measured in the control and the lowest amounts could be measured at the N 200+PK kg/ha treatment.
The Ca content of hybrids was the highest in the N 120+PK kg/ha treatment, while their Mg and Zn content was the highest in the control treatment. The lowest amounts were weighed in the N 200+PK kg/ha treatments, that in several cases resulted in statistically proved decreasement compared to the control or the lower fertilizer doses. Considering the two mesoelements and Zn the most favourable results were obtained in the case of the Norma SC and DK 366 SC hybrids.
Summing up what has been said moderate amounts of fertiliser doses (N 40-120+PK kg/ha) had a favourable influence on the micro- and macroelement content of hybrids. -
The effect of water supply and crop year on the yield potential of sweet maize (Zea mays L. convar. saccharata Koern.) hybrids with different genotypes
203-210Views:156The successfulness of crop production is significantly affected by not only the the average yields that provide cost effectiveness, but also the success of striving for yield safety, therefore, varieties and hybrids tolerant to environmental stress factors are worth being included into the sowing structure. Our aim was to further the decision making of producers in prepaering the right sowing structure by the evaluation of sweet maize hybrids’ tolerance to excess rainfall.
We performed our examinations in an extremely wet year (2010) on chernozem soil on three sweet maize hybrids (GSS 8529, GSS 1477, Overland) in 12 replications. Comparing the yields of 2010 with those that can be expected under optimal rainfall conditions, we showed that the examined hybrids react to the amount of rainfall higher than their needs with yield depression. The excess rainfall tolerance of the examined hybrids is different in the case of each hybrid. -
Site and hybrid-specific agrotechnical models in sweet corn production
105-108Views:92The effect of three agrotechnical factors (sowing time, fertilization, plant density) and two genotypes on the crop yield of sweet corn was examined on chernozem soil in the Hajdúság region in two different crop years. Compared to the 30-year average, the climate was dry and warm in 2009 and humid in 2010. The experiments were conducted at the Látókép Research Site of the University of Debrecen. In the experiments we applied two sowing times (end of April, end of May), six fertilization levels (control, N30+PK, N60+PK, N90+PK, N120+PK, N150+PK) and two crop density levels (45 thousand ha-1, 65 thousand ha-1). The hybrids we used were Jumbo and Enterprise. As regards the requirements of sweet corn production, the crop year of 2009 was dry and warm. The effect of moisture deficiency was more adverse on the crop yields with the second sowing time. On the contrary, the other examined year (2010) was significantly humid; the precipitation was 184 mm above the 30-year average and the temperature was average.
In the dry and hot crop year, the best yields were obtained with the hybrid Jumbo (25677 kg-1) at 65 thousand ha-1 plant density level on the average of the fertilization levels. The crop yields of Enterprise were also the highest at high plant density level (24444 kg ha-1). With the second sowing time the highest yields were obtained at the higher plant density level (65 thousand ha-1) with both hybrids (Jumbo 18978 kg ha-1, Enterprise 18991 kg ha-1), which confirmed the good adaptation capability of these hybrids at high plant density level. In humid crop year with early sowing time the highest yielding hybrid was Enterprise (at 45 thousand ha-1 crop density level 20757 kg-1), at the same time, Jumbo was best yielding at the higher plant density level (18781 kg-1). With the second sowing time the highest crop yield was obtained with Enterprise again (20628 kg ha-1 at 65 thousand ha-1 plant density level). With this sowing time the average yields of Jumbo, was 18914 kg ha-1 respectively. We found that dry crop year and early sowing time provided the best conditions for sweet corn production; the highest yields were obtained under these circumstances, which might be the results of the outstanding water management of chernozem soils. -
Effect of NPK fertilization on the yield and yield stability of different maize genotypes
101-104Views:118The yielding capacity and quality parameters of 11 maize hybrids were studied in 2011 on calcareous chernozem soil in a 25-year long-term fertilization experiment in the control (without fertilization), in the base treatment of N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 and in five treatments which were the multiplied doses of the base treatment. The N fertilizer was applied in the autumn and in the spring, while P and K fertilizers were applied in the autumn.The sowing time was 17–18 April, the time of harvest was 8 October. The 30-year average of precipitation (April–Sept) was 345.1 mm, the amount of precipitation did not differ greatly from that, however, its distribution was very unfavourable.
It was found that the largest yield increment (as compared to the control) was in the treatment N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 in the long-term experiment. The largest yields were obtained for the hybrids P9494, PR37N01 and PR35F38 (13.64–13.71 t ha-1). Due to the dry period at the end of the summer – beginning of autumn, the grain moisture content at harvest was favourably low, 12–18% depending on the treatment and the growing season.The N fertilization significantly increased the protein content of the kernel, but the starch content of the kernel decreased (significantly in several cases) with increasing fertilizer doses and yields as compared with the control.
The highest protein content was measured in hybrids GK Boglár and Szegedi 386. The oil content was above 4% for GK Boglár, but the two hybrids were not among the best yielding hybrids in spite of their good inner content. The starch content was around 75 % without fertilization, it decreased with fertilization.
For the tested hybrids, the fertilizer dose N 120 kg ha-1, P2O5 75 kg ha-1, K2O 90 kg ha-1 can be recommended with respect to efficacy and environmental considerations. -
Evaluate the nutritional reaction at winter wheat after different forecrops
77-80Views:126Our field researches took place on the Látókép test farm of Agricultural Science Centre of University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences, in long-term experiment, on calcareous chernozem soil, in growing season of 2014/2015. In our experiment we examined the fertilizer reaction and the yield of different winter wheat genotypes (GK Öthalom, GK Csillag, Mv Csárdás, Mv Toldi) with grain maize and sweetcorn forecrops. According to our results, the sweetcorn forecrop strongly affected the yield. In the average of the fertilizer treatments and the varieties, after sweetcorn forecrop 6.9 t ha-1, after grain maize forecrop 5.4 t ha-1 average yield was gained. According to our data, the fertilizer reactions of the varieties were significantly different.
-
The Effect of Year and Irrigation on the Yield Quantity and Quality of the Potato
12-16Views:90In Hungary, the growing area of potato area reduced dramatically in the last few decades, additionally we are lagging behind the Western European countries as regards yields and the competitiveness of production is further decreased by the great alternation in yields from year to year, the unpredictable market conditions, bad consumption habits and many times unfortunately the lack of quality products.
The ecological and climatic conditions of Hungary are not everywhere suitable for potato, in the area of Debrecen the amount of rainfall was lower, and the monthly average temperature was higher than the requirement of potato in its growing season in 2002 and 2003.
The experiment was carried out at the experimental site of the University of Debrecen, Farm and Regional Research Institute, at Látókép. In our experiment we examined the yield and some quality parameters of 8 and 9 medium-early varieties in large parcels in 2002 and 2003 respectively. Out of the examined varieties 3 are of Dutch, and 6 are of Hungarian breeding.
The experiment was set up on 49.5 m2 parcels on calcareous chernozem soil after winter wheat as a forecrop in both years. The 9 varieties were examined in 4 repetitions in randomized blocks, out of which two repetitions were irrigated, and two were non-irrigated.
We examined the yields of the varieties, the distribution of tubers according to size and their percentages, and the changes in specific parameters of quality and inner content due to irrigation. We studied the dry matter content, the starch content, the under-water mass, the amount of reducing sugars, the colour index of frying and the element contents of tubers.
Summing up, it can be stated that among the agrotechnical year effect, variety and irrigation factors have considerable impact on potato yield quality and quantity. On the basis of our results, it can be stated that in potato production variety should be chosen in accordance with the aim of production and technology should be adapted to that specific variety. -
The significance of biological bases in maize production
61-65Views:159The comparative trial has been set up in the Demonstration Garden of the Institute of Crop Sciences of the University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Studies, Faculty of Agricultural and Food Sciences and Environmental Management in 2012, with 24 hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing periods. The soil of the trial is lime-coated chernozem, with a humus layer of 50–70 cm.
The weather of the trial year was quite droughty; the monthly average temperature was 3–4 oC higher than the average of 30 years. High temperature, together with lack of precipitation occurred during the most sensitive phenophases of maize (flowering; fecundation, grain saturation).
The following characteristics have been observed: starting vigour, date of male and female flowering, plant and cob height, dry-down dynamics during maturation and the change of yield composing elements has also been quantified. The yield was recalculated to 14% moisture content grain yield after harvesting.
The beginning of the growing period was advantageous, therefore the analysed hybrids could grow a high (above 300 cm) and strong stem. The yield of the hybrids changed between 10.33 and 11.87 t ha-1, but as a result of the unfavourable climatic extremes, their genetic yield potential prevailed only at a rate of 30–40%. However, moisture content by the time of harvesting was good despite its early date (12th September); it remained under below 14% in most cases. Dry-down was measured on a weekly basis between 14th August and 5th September.
The analysis of the qualitative parameters of the maize hybrids (protein %, oil % and starch %) resulted in significant differences. The most significant difference has been observed in the case of protein content (LSD5%=2.01). Oil content was the most advantageous in the case of hybrids belonging to the mid-late growing group (FAO 400). The X9N655 and 36V74 hybrids had the highest oil content (around 4%), while hybrids P9915 and 37F73 had significantly lower oil content. Starch content was above 70% in the case of every hybrid.
Hybrid selection is highly important in terms of yield and yield security of maize, as well as the application of modern biological fundamentals and hybrid specific technology for the improvement of the level of cultivation technology.
-
Examining reaction of sunflower genotypes on planting time on chernozem soil
93-99Views:104We studied the effect of planting time on plant pathological factors, leaf area index and yield production by applying various fungicid treatments on two different sunflower genotypes in 2013.
By delaying planting time, both the extent of Diaporthe, Alternaria and Phoma infections decreased. The differences between the volume of infections were significant in the case of the early and late sowing time results. The application of fungicide treatments induced a notable decrease in the extent of infections for all three pathogens examined. The LAI-values varied between 0.3 and 5.6 m2/m2 in 2013 depending on the hybrid, sowing time and treatment. Stocks planted at distinct times reached maximum leaf coverage at different times. The planting time and the fungicide treatment had a significant effect on the formation of the leaf area. In the case of average and late planting times, fungicide treatments elongated the preservation of the green leaf area.
With respect to the yield amount, average planting time (27 April, 2013) turned out to be optimal in 2013 (control – NK Ferti: 4.621 kg ha-1, PR64H42: 4.196 kg ha-1; double-treated: NK Ferti: 5.282 kg ha-1, PR64H42: 5.090 kg ha-1). Fungicide treatments resulted in significant yield growth in all cases during our research.
We applied Person correlation analysis to evaluate the hybrids’ sensibility to infections and our results varied in the case of Diaporthe and Phoma (r=-0.343*, -0.379**). Infections of the three pathogens were significantly reduced by delaying the planting time and applying fungicides. Late sown stocks preserved the green leaf area for a longer period. Besides, the application of the fungicide treatment and the hybrid itself also led to the preservation of the green leaf area. However, pathogens examined notably decreased the leaf area by the end of the growing year. The fungicide treatment had a remarkable effect on yield growth (r=0.603**). Furthermore, the presence of higher LAI-values in the period prior to August also induced higher yields.
-
Correlation between the weather in 2017 and the productivity of maize
89-93Views:152In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In Hajdúszoboszló in 2017, up to October, 445.8 mm of rain fell, which is in line with the average values of 30 years, and is only 45.7 mm less than those. In 2017, the effect of increasing the plant number was slighter. Averaged over the observed fertilizer treatments and hybrids, the yield was 9.10 t ha-1 with 60 thousand plants ha-1, 9.11 t ha-1 with 70 thousand plants ha-1 and 9.12 t ha-1 with 80 thousand plants ha-1. Without fertilization, in most cases, increasing the plant number from 60 thousand plants ha-1 to 70-80 thousand plants ha-1 does not increased the yield but decreased it. With N80+PK treatment the yield changed between 8.90 and 11.27 t ha-1. The effect of increasing the plant number was just slightly observable and did not show a clear tendency. The effect of changing the plant number, even with the highest dosage of fertilizers, could not be detected adequately. In contrast with the plant number, the effect of the different fertilizer treatments was expressly traceable. Compared to the control treatment (treatment without fertilization), with N80+PK fertilizer dosage with 60 thousand plants ha-1 the yield increased by 3.36–4.99 t ha-1. The smallest demonstrable proof, i.e. the LSD5% was 0.22 t ha-1, which means that fertilization, in each case, significantly increased the yield. When analysing the effect of fertilization in the average of the hybrids and the different plant numbers, a yield of 5.61 t ha-1 could be detected, which value was 10.12 t ha-1 with N80+PK treatment and 11.61 t ha-1 with N160+PK treatment. Thus, it can be calculated that compared to the treatment without fertilization, the N80+PK treatment increased the yield by 4.51 t ha-1, while compared to the N80+PK treatment, the N160+PK treatment increased the yield by 1.49 t ha-1. In addition to agrotechnical factors, in maize production, the impact of the crop year is specifically of high importance.The average yield of hybrids (in the average of the different fertilizer treatments) was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 and 9.11 t ha-1 in 2017. When comparing the yield results against the precipitation data, it is clearly visible that the amount of rain fell in the January– October period is directly proportional to the average yield of maize. The effect of the crop year can be defined in a 5.05 t ha-1 difference in the yield. -
Effects of the cropyear and the agronomical factors on agronomical elements of different sweet corn (Zea Mays L. convar. saccharata Koern.) genotypes in long-term experiment
105-110Views:97In the crop season of 2010 (rainy year), we studied the effect of three agrotechnical factors (sowing time, fertilization, plant density) and four different genotypes on the agronomical characteristics of sweet corn on chernozem soil in the Hajdúság. The experiments were carried out at the Látókép Experimental Farm of the University of Debrecen. In the experiment, two sowing dates (27 April, 26 May), six fertilization levels (control, N30+PK, N60+PK, N90+PK, N120+PK, N150+PK) and four genotypes (Jumbo, Enterprise, Prelude, Box-R) were used at two plant densities (45 thousand plants ha-1, 65 thousand plants ha-1). The amount of precipitation in the season of 2010 was 184 mm higher, while the average temperature was 0.8 oC higher in the studied months than the average of 30 years. Weather was more favourable for sweet maize at the first sowing date, if we consider the yields, however, if we evaluate the agronomical data and yield elements (number of cobs, cob length and diameter, the number of kernel rows, the number of kernels per row) it can be stated that the size of the fertile cobs was greater at the second sowing date due to the lower number of cobs. The largest number of fertile cobs was harvested in the case of the hybrid Enterprise (72367.9 ha-1) in the higher plant density treatment (65 thousand ha-1) at the fertilization level of N120+PK when the first sowing date was applied. The largest cobs were harvested from the hybrid Box-R (cob weight with husks: 516.7 g, number of kernels in one row: 45.7) at the lower plant density (45 thousand plants ha-1) in the second sowing date treatment. Cob diameter and the number of kernel rows were the highest for the hybrid Prelude.
-
Efficiency of Fertilization in Sustainable Wheat Production
59-64Views:94In sustainable (wheat) production plant nutrition supply and fertilization play decisive roles among the agrotechnical elements, because of their direct and indirect effects on other agronomical factors.
In long-term experiments, we studied the roles of agroecological, genetic-biological and agrotechnical factors in the nutrient supply, fertilization and its efficiency in wheat production under continental climatic conditions (eastern part of Hungary, Trans-Tisza) on chernozem soil. Our results have proved that there are different (positive and negative) interactions among ecological, biological, and agrotechnical elements of wheat production. These interaction effects could modify the nutrient demand, fertilizer (mainly nitrogen) response of wheat varieties and efficiency of fertilization in wheat production.
The optimum N-doses (+PK) of wheat varieties varied from 60 kg ha-1 (+PK) to 120 kg ha-1 (+PK) depending on cropyears, agrotechnical elements and genotypes. The winter wheat varieties could be classified into 4 groups according to their fertilizer demand, natural and fertilizer utilization, fertilizer response and yield capacity.
Appropriate fertilization (mainly N) of wheat could affect both the quantity and quality of the yield. By using optimum N (+PK) fertilizer doses, we could manifest genetically- coded baking quality traits of winter wheat varieties and reduce quality fluctuation caused by ecological and other management factors. The efficiency of fertilization on different baking quality parameters (wet-gluten, valorigraph index etc) were variety specific (the changes depended on genotypes).
Our long-term experiments proved that appropriate fertilization provides optimum yield, good yield stability and excellent yield quality in sustainable wheat production. We could this get better agronomic and economic fertilization efficiency with less harmful environmental effects. -
Examination of nutrient reaction of winter wheat after sunflower forecrop
9-13Views:141We tested the fertilizer reaction of four different winter wheat varieties in three different crop years, on chernozem soil, in long-term experiment. We examined the optimum fertilizer requirements and the maximum yield of the varieties. According to our results there were significant differences among the years: the yield of the winter wheat varieties changed between 1.4–6.1 t ha-1 in 2013, 3.8–8.6 t ha-1 in 2014 and 3.2–8.6 t ha-1 in 2015. The yield increasing effect of fertilization was significantly different in the tested years. The optimum level of fertilization was determined by, besides the genetic differences among the varieties, the crop year and the extent of fertilization. In milder winter months, due to the higher average temperatures, yields of winter wheat increased compared to an average crop year.
-
Correlation analysis of relative chlorophyll content and yield of maize hybrids of different genotypes
211-214Views:103In 2021, correlation between relative chlorophyll content and yield in three maize hybrids of different genotypes was examined. The data were collected at the Látókép Experimental Station of the University of Debrecen located on the Hajdúság loess ridge in Hungary. The soil of the small plot field strip plot trial, which was set up in 2011, was calcareous chernozem. Apart from the control treatment (without fertilisation), N fertiliser is applied in the form of base and top dressing. The base fertiliser containing 60 and 120 kg ha-1 N of nutrient applied in spring was followed by top dressing containing +30–30 kg ha-1 N in V6 and V12 phenophases. SPAD values measured at different phenological stages of the growing season increased by an average of about 28% up to 10 leaf stage for all three hybrids. In the pre-silking period (Vn), the relative chlorophyll content decreased by 8% on average. After an average increase of 14% in the tasselling and silking period, SPAD decreased by an average of about 29% at full maturity (R6).
For the different fertiliser treatments, higher N doses resulted in higher yields. In the basal fertiliser treatment, the A 60 N dose resulted in an average 34% increase in yield, and the A 120 N dose resulted in an average 94% increase in yield compared to the control. The 60 kg ha-1 N basal fertiliser (A60) increased in the V6 phenophase with an additional 30 kg ha-1 N resulted in an average yield increase of 26%. When 120 kg ha-1 N of basal fertiliser (A120) was increased by an additional 30 kg ha-1 N in the V6 phenophase, only the Merida hybrid showed a significant yield increase (7%). No further yield increase was observed when V690 and V6150 treatments were increased by an additional 30 kg ha-1 N in the V12 phenophase. The yield of the Armagnac hybrid decreased by almost 20%, the yield of Fornad by 3% and the yield of Merida by 1%.
-
Effect of weather conditions on the protein content and baking value of winter wheat flour
83-94Views:110We searched for connections between weather conditions (with its sub-parameters as precipitation and average temperature) and the yearly formation of two quality parameters (protein content and baking value) on three levels of mineral fertilization, based on the results of a variety comparison experiment on chernozem soil, to select those weather parameters and critical periods which have significant effects on the quality of winter wheat flour.
We established that the protein content of winter wheat flour can be increased with increasing levels of mineral fertilizers. Protein content is lower and has higher deviation during non-fertilized conditions in different cropping years than on higher fertilization levels. Thus, it seems proved again that quality (as protein content) is mainly formed by the crop year, but can be improved with adequate agricultural engineering (with mineral fertilization in the present case). The higher sum of precipitation in May, and the lower average temperature after flowering, have the highest increasing effect on the protein content of flour of the examined parameters. Based on the results of the examined period, the rainier and warmer term than average before flowering and lower – average amount of precipitation and colder circumstances are favourable for higher baking values. The analysis with data of decades, proves the importance of the first half of May and the middle of June as especially important periods for quality formation. An increasing nutrient supply has different effects on the varieties; mineral fertilization increased the baking value of GK Öthalom winter wheat variety in almost every case, but the second level of fertilization decreased it in half of the examined years. Additionally, mineral fertilization played a role in the stabilization of the quality of highlighted varieties. -
The effect of NPK fertilization and the plant density on maize yield and bioethanol production
13-18Views:88For industrial (bioethanol) production of maize, a new production technology is needed. I tested and selected hybrids appropriate for this purpose and set up fertilization and plant density experiments. The experiment were set up on chernozem soil in 2008.
In bioethanol production, the selection of a high-yielding hybrid with high starch content, a slight reduction of N, increase of potassium, the application of the highest plant densities of the optimum interval, harvest at full maturity (when starch content is the highest compared to protein content) are of great importance. -
Folic acid content of beetroot leaf and root by different growing stages and genotypes
115-119Views:219An increasing interest has been observed of beetroot leaf as a salad component due to recent studies focusing on their nutritional value. The randomized field experiment was carried out on lowland chernozem soil with 6 varieties, 3 replications and 2 sowing dates. Sampling was performed on 23 of August 2018 at the stage of 30 and 50 days of vegetation, where leaf (30 and 50 days) and root (50 days) were collected. Total dry matter, folic acid and nitrate content were evaluated.
The results of this investigation show that higher total dry matter content was measured in the root (8.47–10.30%) compared to the leaf in both developmental stages (6.47–9.20%). Nevertheless, higher folic acid content was found in the young leaves of 30 and 50 days of development (58.77–113.86 µg 100g-1). Among the examined varieties, Bonel has presented great amount of folic acid not only in the leaves (99.35–113.61 µg 100g-1), but also in the root (89.99 µg 100g-1). Finally, lower nitrate content was found in Libero (316.16 mg kg-1) at 30 days and in Akela (340.41 mg kg-1) at 50 days of development. Thereby, fresh consumption of beetroot leaves are highly recommended.
-
Agronomic research in Martonvásár, aimed at promoting the efficiency of field crop production
89-93Views:115The effect of crop production factors on the grain yield was analysed on the basis of three-factorial experiments laid out in a split-split-plot design. In the case of maize the studies were made as part of a long-term experiment set up in 1980 on chernozem soil with forest residues, well supplied with N and very well with PK. The effects of five N levels in the main plots and four sowing dates in the subplots were compared in terms of the performance of four medium early hybrids (FAO 200). In the technological adaptation experiments carried out with durum wheat, the N supplies were moderate (2010) or good (2011), while the P and K supplies were good or very good in both years. Six N top-dressing treatments were applied in the main plots and five plant protection treatments in the subplots to test the responses of three varieties.
The results were evaluated using analysis of variance, while correlations between the variables were detected using regression analysis.
The effect of the tested factors on the grain yield was significant in the three-factorial maize experiment despite the annual fluctuations, reflected in extremely variable environmental means. During the given period the effect of N fertilisation surpassed that of the sowing date and the genotype. Regression analysis on the N responses for various sowing dates showed that maize sown in the middle 10 days of April gave the highest yield, but the N rates required to achieve maximum values declined as sowing was delayed.
In the very wet year, the yield of durum wheat was influenced to the greatest extent by the plant protection treatments, while N supplies and the choice of variety were of approximately the same importance. In the favourable year the yielding ability was determined by topdressing and the importance of plant protection dropped to half, while no significant difference could be detected between the tested varieties. According to the results of regression analysis, the positive effect of plant protection could not be substituted by an increase in the N rate in either year. The achievement of higher yields was only possible by a joint intensification of plant protection and N fertilisation. Nevertheless, the use of more efficient chemicals led to a slightly, though not significantly, higher yield, with a lower N requirement. -
The effect of NPK fertilization and the number of plants on the yield of maize hybrids with different genetic base in half-industrial experiment
103-108Views:178In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize.
The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2, this it was a halfindustrial experiment. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. Yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare at a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants/ha.
In Hajdúszoboszló, in 2015 the amount of rainfall from January to October was 340.3 mm, which was less than the average of 30 years by 105.5 mm. This year was not only draughty but it was also extremely hot, as the average temperature was higher by 1.7 °C than the average of 30 years. In the critical months of the growing season the distribution of precipitation was unfavourable for maize: in June the amount of rainfall was less by 31mm and in July by 42 mm than the average of many years.
Unfavourable effects of the weather of year 2015 were reflected also by our experimental data. The yield of hybrids without fertilization changed between 5.28–7.13 t ha-1 depending on the number of plants.
It can be associated also with the unfavourable crop year that the yield of the six tested hybrids is 6.33 t ha-1 in the average of the stand density of 60, 70 and 80 thousand plants per hectare without fertilization, while it is 7.14 t ha-1 with N80+PK fertilizer treatment. That increase in the yield is only 0.81 t ha-1, but it is significant. Due to the especially draughty weather the yield increasing effect of fertilizers was moderate. In the average of the hybrids and the number of plants, increasing the N80+PK treatment to N160+PK, the yield did not increase but decreased, which is explicable by the water scarcity in the period of flowering, fertilization and grain filling.
The agroecological optimum of fertilization was N 80, P2O5 60 and K2O 70 kg ha-1. Due to the intense water scarcity, increased fertilization caused decrease in the yield. As for the number of plants, 70 000 plants ha-1 proved to be the optimum, and the further increase of the number of plants caused decrease in the yield.
-
Influence of Foliar Treatments on the Sugar Yield Changes of Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris L.)
108-111Views:69In our small block experiment in randomised blocks, we examined the effect of 6 foliar treatments at 3 different nutrition levels in 2002 on meadow chernozem soil.
The experiment consisted of 3 blocks, which corresponded to 3 different nutrition levels. The first block was the control, the fertilization rate of the second block was 20 kg ha-1 N, 40 kg ha-1 P2O5, 120 kg ha-1 K2O, on the third block 40 kg ha-1 N, 80 kg ha-1 P2O5, 240 kg ha-1 K2O were applied. We applied magnesium and strobilurin active ingredient (Juwel, BAS 51200), in different combination and with different application dates.
We found that the foliar treatments with bioactive fungicides significantly influenced the yield and some quality parameters in this field experiment. -
Results of the sensory analysis of precision maize production
59-62Views:175This research was carried out in 2018, at the Látókép Experimental Station of the University of Debrecen in a moderately warm and dry production area, on deep humus layered medium-hard calcareous chernozem soil. In the scope of the research, the chlorophyll content of maize (Zea mays L.) was examined under field circumstances by means of local sensory measurements and we were looking for correlation between the obtained values and the amount of yield. Our measurements were carried out with Minolta SPAD-502 and GreenSeeker devices at 3 measurement times (4 leaf stage, 10 leaf stage and silking). It was found that phenological phases had an effect on the obtained SPAD and NDVI values and were in a slightly significant correlation with the yield. The most significant correlation was found between the results obtained during silking and the amount of yield. This may be because the least time has passed between the measurement time and harvest. Results obtained during the 10-leaf stage show excessive values in each case, which can be due to a measurement error. It was found that the phenological phase had an effect on the correlation of SPAD and NDVI values and the amount of yield. As the phenological phase progressed, the correlation between the measured results and yield has increased.
-
The effect of and interaction between the biological bases and the agrotechnical factors on maize yield
83-87Views:144The effect of and interaction between the biological bases and the agrotechnical factors on maize yield In our research, we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons.We analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with a control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In 2015, the highest yield was produced by hybrid P9241 with N80+PK and 70 thousand plants per hectare. With the N160+PK fertilizer dosage, the same hybrid responded the best, followed by hybrids P9486 and DKC4717. Using the same fertilizer treatment, the 80 thousand plants per hectare population density resulted in decrease in the yield with most of the examined hybrids. In 2016, with the increase in the number of plants per hectare, even with non-fertilised treatment (control treatment), the yield could be increased in the case of each hybrid.Averaged over the different hybrids and fertilizer treatments, applying 80 thousand plants ha-1 instead of 60 thousand resulted in 1.0 ha-1 yield increase. In 2017, the number of plants had a slighter effect. With N160+PK treatment, in most cases no significant difference can be observed. The value of LSD5%: plant number: 0.20 t ha-1, hybrid: 0.28 t ha-1, interaction: 0.48 t ha-1. With N160+PK treatment, the hybrids produced yields between 10.07 and 12.45 t ha-1. When examining the three years in the average of the number of plants, with treatment without fertilisation, the average yield of hybrids reached 7.53 t ha-1. With N80+PK treatment, this value was 9.71 t ha-1 and with doubling the fertilizer dosage, this value increased to 10.42 t ha-1. No economic profit was gained as a result of applying double dosage of fertilizer; therefore, the N80+PK dosage can be considered ideal.