Search
Search Results
-
Studying the effects of traits in the genotype of three maize hybrids in Hungary
97-101Views:311In this study, we selected three hybrids (Armagnac, Loupiac, and Sushi) for evaluation of the effect of traits in genotype in Debrecen. In 2017, the total rainfall from May to October was 314 mm in Debrecen, which was 236 mm in the winter period before sowing. The obtained results showed that there was a positive correlation between the weight of the cob maize and the rate of seed/cob, number of rows with number of seeds in column and outer diameter ear with weight of cob and number of rows in grain per ear and the rate of seed / cob; Also, there was a negative correlation between grain weight in ear with seed/cob rate, outer diameter ear and the rate of seed/cob and outer diameter ear with the number of leaves. There was a positive correlation between stem diameter, Seed/cob rate and the number of nodes by GGE biplot. In addition, there are traits of weight of all seeds and outer ear diameter that had the highest effect on average yield. Moreover, the number of seeds per row showed the least effect on the average yield of hybrids.
-
Relation of availability and barley uptake of some potentially toxic elements
7-10Views:70A small-plot microelement load field trial was set up on brown forest clay soil with eight elements (Al, As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn), on 3 levels each (0/30, 90, 270 kg element ha-1). The soil was treated with soluble salts of elements once at initiation (1994). In the seventh year of the experiment (2001) winter barley was the test plant. The total element content was determined in plant samples (shoot, straw, grain) after microwave digestion using cc.HNO3+cc.H2O2. The element composition of the prepared samples was determined using ICP-MS technique. In the experiment toxic effects of treatments and yield loss could not be observed. Zn and As contents in barely shoots were only moderately increased by increasing microelement loads. Effects of Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb and Al treatments could not be observed. On the other hand, Cd accumulation was significant in the shoot. Cd content was also increased both in straw and grain. Results of this experiment prove that Cd remains mobile in the soil-plant system for a long time. Its accumulation can be observed both in vegetative and reproductive parts of plants without toxic symptoms and yield loss.
-
Agronomic research in Martonvásár, aimed at promoting the efficiency of field crop production
89-93Views:115The effect of crop production factors on the grain yield was analysed on the basis of three-factorial experiments laid out in a split-split-plot design. In the case of maize the studies were made as part of a long-term experiment set up in 1980 on chernozem soil with forest residues, well supplied with N and very well with PK. The effects of five N levels in the main plots and four sowing dates in the subplots were compared in terms of the performance of four medium early hybrids (FAO 200). In the technological adaptation experiments carried out with durum wheat, the N supplies were moderate (2010) or good (2011), while the P and K supplies were good or very good in both years. Six N top-dressing treatments were applied in the main plots and five plant protection treatments in the subplots to test the responses of three varieties.
The results were evaluated using analysis of variance, while correlations between the variables were detected using regression analysis.
The effect of the tested factors on the grain yield was significant in the three-factorial maize experiment despite the annual fluctuations, reflected in extremely variable environmental means. During the given period the effect of N fertilisation surpassed that of the sowing date and the genotype. Regression analysis on the N responses for various sowing dates showed that maize sown in the middle 10 days of April gave the highest yield, but the N rates required to achieve maximum values declined as sowing was delayed.
In the very wet year, the yield of durum wheat was influenced to the greatest extent by the plant protection treatments, while N supplies and the choice of variety were of approximately the same importance. In the favourable year the yielding ability was determined by topdressing and the importance of plant protection dropped to half, while no significant difference could be detected between the tested varieties. According to the results of regression analysis, the positive effect of plant protection could not be substituted by an increase in the N rate in either year. The achievement of higher yields was only possible by a joint intensification of plant protection and N fertilisation. Nevertheless, the use of more efficient chemicals led to a slightly, though not significantly, higher yield, with a lower N requirement. -
Examination of the angle position on the cone dispenser
204-207Views:76The most important distributing construction of small plot seed-drills and fertiliser dispensers is the cone dispenser. The cone dispenser can operate based on simple gravity or with an Oyjord-type cone-cell or Hege-type cone-belt structure. The unevenness of spreading of each type is significantly influenced by the aberration of the vertical angle position of the cone dispenser. An approximate method was improved modelling of the fault of the cone dispenser. In my article, I will provide information about the essence of the model and its derivations.
On the model, I cover the cone piston with a theoretical net and at random scale between each scale interval I count the forces acting on the grain and the movement of the grain. If I set the scale of the net close enough, with good proximity, I get the whole orbit. The unevenness of dispensing can be calculated from the position of the grains getting to the bottom of the cone in case of different geometric data. My measurements imply that an approximate method is able to model both the tendency and the value of the deviation caused by the fault of the angle position. Both the theoretical model and the measurement prove that 2-3° deviation results in significant change in the unevenness of dispensing. -
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:112During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: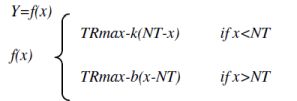
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Evaluation of decreasing moisture content of different maize genotypes
147-151Views:225An experiment was conducted to evaluate the decrease in grain moisture content in three maize hybrids in Debrecen in 2017. Armagnac, Sushi and Loupiac were the examined hybrids in this study. The culture medium and temperature conditions were applied uniformly for all three hybrids. According to the results obtained from the ratio of moisture content of seeds per day, the Armagnac variety in the intensive drying down phase loses more time and moisture content, so it can be concluded that the produced dry matter is more than in the case of other varieties. Armagnac requires more time to achieve yield, while the Sushi and Loupiac hybrids produce less harvest. Regarding the slope of the regression line, the rate of loss of moisture in the grain has been negatively correlated with the amount of “b” in the three examined hybrids. In regression analysis, the coefficient of explanation showed that the effect of day in the Armagnac was 97% in the Loupiac, 95% and in the Sushi 90% of the total dynamic value of moisture motion.
-
Describing Fusarium diseases on maize in 2013 using data from several production sites
60-64Views:137As in other parts of the world, the frequency of weather extremes has increased greatly in Hungary in recent years. This means that maize production is faced with greater risks from all aspects: nutrient replacement, irrigation, plant protection. This is especially true of fusarium diseases. In a continental climate, the pathogens causing the most serious problems are species belonging to the Fusarium genus. They infect the ears, which – besides reducing the yield – poses considerable risk to both human and animal health due to the mycotoxins produced by them. Depending on which Fusarium species are dominant at a given location, changes can be expected in the level of infection and in the quality deterioration caused by the mycotoxins they produce. Fusarium spp. not only damages the maize ears but when pathogen attacks the stalk, the plant dies earlier, reducing grain filling and resulting in small, light ears. In addition, the stalks break or lodge, resulting in further yield losses from ears that cannot be harvested. The degree of infection is fundamentally determined by the resistance traits of the maize hybrids, but also a great role in that region Fusarium species composition as well.
-
Búzalisztek minőségének becslése tészta nyújtás-szakítás alapján állományvizsgáló műszerrel
38-44Views:75Literature experience was utilised to develop a method for the extensograph analog testing of paste with a QTS25 Texture Analyser. 54 wheat flour samples from the same variety from variety-preservation experiments at the Szeged were tested with this method. A study was made to establish whether the method is suitable for the estimation of results derived by traditional classification (trial baking, farinograph and gluten tests).
A close and significant correlation was found between the hardness and area data measured with a QTS25 micro-extensograph, the farinograph values and the gluten spreading data, and also between the stretching index (BC/AC) and the water uptake capacity. These correlations correspond well with the findings from a previous experimental series on industrial flour samples. A close and significant correlation was likewise observed between the grain hardness established by the MININFRA method and all the QTS25 micro-extensograph data. In contrast with earlier QTS25 data, however a close correlation was not found between the QTS25 data and the loaf characteristics.
With the use of micro-extensograph data, the estimation of the baking industry value has been improved through stepwise variable selection, with the inclusion of several variables. The estimation of loaf volume could also be solved by means of stepwise variable selection with the inclusion of QTS25 and MININFRA data. -
Correlations of the growth indexes and yield of winter wheat in a long-term experiment
139-144Views:135The experiments were carried out at the Látókép experimental station of the Centre for Agricultural Sciences of University of Debrecen on chernozem soil in a long term winter wheat experiment. As forecrop rotation, we set up two models: a biculture (wheat and corn) and a triculture (pea, wheat and corn). We applied three levels of nutrients during the fertilization process (control, N50P35K40 and N150P105K120). The third variable studied was irrigation in case of which we tested non-irrigated variables (Ö1) and irrigation variables complemented up to the optimum (Ö3).
The effect of pre-crops, irrigation and nutrient-supply levels on some growth-parameters (LAI, LAD), weight of dry matter, just as SPADvalues and yield amounts of winter wheat has been investigated in this experiment. We tried to find out the extent of relationship between the different parameters, and we used the correlation analysis. The correlation analyses have confirmed that all of the investigated parameters had almost in all cases close positive correlation to the yield amount. These results have confirmed that the leaf area, the leaf duration, the SPADvalues, the fertilization and the forecrop have altogether resulted in the production of maximum grain yields.
-
The role and impact of N-Lock (N-stabilizer) to the utilization of N in the main arable crops
51-55Views:214The nitrogen stabilizer called N-Lock can be used primarily with solid and liquid urea, UAN and other liquid nitrogen, slurry and manure. In corn it can be applied incorporated before sowing or with row-cultivator or applied with postemergent timing in tank-mix. In postemergent timing need precipitation for long effect. In oil seed rape and autumn cereals the N-Lock should be applied with liquid nitrogen in tank mix late winter or early spring (February-March). The dose rate is 2.5 l/ha. N-Lock increases the yield of maize, winter oil seed rape, winter wheat and winter barley 5-20 %. The yield increasing can be given the thousand grain weight. In case of high doses of nitrogen it can be observed higher yield. The quality parameter also improved, especially the oil content of winter oil seed rape and protein and gluten contents of winter wheat. The use of N-Lock increases the nitrogen retention of soil and reduces nitrate leaching towards the groundwater and the greenhouse effect gas emissions into the atmosphere. The degradation of the applied nitrogen is slowing down and the plant can uptake more nitrogen in long period. The effect of N-Lock the nitrogen is located in the upper soil layer of 0-30 cm and increasing the ammonium nitrogen form. The product can be mixed with herbicide products in main arable crops.
-
Effect of molybdenum treatment on uptake of plant and soil molybdenum content in a field experiment
117-122Views:113Molybdenum is not a well-known microelement, but being a constituent of several important cellular enzymes it is an essential microelement. Molybdenum occurs in all foods, but at very low levels. There does not appear to be any particular foods or types of foods, which in the absence of extrinsic factors, naturally have high levels of molybdenum. However, environmental pollution, from natural or anthropogenic sources, can lead to high level of the metal in plants.
Our study is based on the long-term field experiments of Nagyhörcsök, where different levels of soil contamination conditions are simulated. Soil and plant samples were collected from the experiment station to study the behaviour of molybdenum: total concentration, available concentration, leaching, transformation, uptake by and transport within the plants, accumulation in different organs, phytotoxicity and effects on the quantity and quality of the crop. In this work we present the results of maize and peas and the soil samples related to them.
According to our data molybdenum is leaching from the topsoil at a medium rate and it appears in the deeper layers. In the case of plant samples we found that molybdenum level in the straw is many times higher than that is in the grain, so molybdenum accumulates in the vegetative organs of the plant. The data also show differences in the molybdenum-uptake of cereals and Fabaceae (or Leguminosae). -
Changes in the Quality of Winter Wheat Varieties in a Comparative Experiment
179-183Views:64The hungarian seed grain supply offers more and more varieties from the field crops for public cultivation in every year. The number of the admitted varieties by state doubled from 1996 to 2001. The question is what changes can the varieties newly inproved show in the quality parameters.
32 varieties admitted in different years was examined on quality parameters as wet gluten content, valorigraphic value and falling number from period 1996-2001. We established that the newer varieties surpassed the traditional varieties of the variety-comparativing experiment in accordion to they wet gluten content. In connection with formation of valorigraphical value we saw that the new varieties got place in the varieties admitted for public cultivation in quality based examining. The varieties showed different reaction of fertilizer on the formation of these two parameters. In connection with the formation of the value of falling number the examined varieties suited for the requirements of quality crop production in the experimental years excepted some of them. -
Examination of the impact of ecological and agrotechnical factors in a maize fertilisation experiment
13-17Views:106The year 2013 was rather extreme breeding year because of the uneven distribution of precipitaion and the summer heat. The experiment was set on with eight different genetic characteristics maize hybrids in 2013. In our study were included different kind of breeding season hybrids. We studied the effect of NKP fertilization and row spacing on the yield. The fertilizer doses are based on 25-year long-term experiment. Compared to control, the N40+PK treatment has also achieved a significant yield increase, although some hybrid of increasing fertilizer doses yield response to loss. The majority of hybrids reached higher yields using the 50 cm row spacing. The water release of hybrids was measured between 21th August and 17th September weekly, at the same time points. The rainy September slowed ripening hybrids and water release, so the grain wet content at harvest showed higher values.
-
Testing disease resistance in autumn wheat genotypes by means of field experiments
30-40Views:80According to our scientific results we can state that we have to use integrated pesticides management in crop protection against the diseases of winter wheat. One of the most important elements of IPM is to select a genotype characterised by good resistance to diseases (and by high yield ability and excellent baking quality). It is especially important that the wheat variety have tolerance against not only to one or two leaf and spike (grain) diseases, but „complex” tolerance. It is not necessary to give up the growing of a variety which has susceptibility to different diseases because we can protect it using appropriate chemical management. In the intensive growing stage of wheat (BBCH 32-37) we can use a noncompulsary fungicide-treatment (depending on e. g. the infection, ecological conditions) and, at the beginning of the flowering stage
(BBCH 59-65), we have to use a compulsary fungicide-treatment (in spite of e. g. special weather conditions, resistance genotype)to ensure high yield and good quality. -
Molybdenum - accumulation dynamics of cereals on calcareous chernozem soil
81-85Views:97This work is about the molybdenum-accumulation of cereals analyzing soil and plant samples from a field experiment set in
Nagyhörcsök by Kádár et al. in 1991.
In this long-term field experiment different levels of soil contamination conditions are simulated. Soil and plant samples were collected
from the experiment station to study the behaviour of molybdenum.
In this report results of maize, winter wheat, winter barley and soil analysis are presented. The conclusions are as follows:
– Analysing soil samples from 1991 we have found that roughly half of the molybdenum dose applied is in the form of NH4-acetate+EDTA soluble
– Comparing element content of grain and leaf samples we have experienced that molybdenum accumulation is more considerable in the vegetative plant parts
– Winter wheat accumulated less molybdenum then maize in its vegetative parts. Comparing molybdenum content of winter wheat to winter barley we found that the concentration of the element in wheat was lower by half than in the winter barley. It seemed that molybdenum accumulated to the least degree in winter wheat. -
Growth and clorophyll content dynamics of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in different cropyear
101-105Views:107The experiments were carried out at the Látókép experimental station of the University of Debrecen on chernozem soil in a long term winter wheat experiment in the season of 2011 and 2012 in triculture (pea-wheat-maize) and biculture (wheat-maize) at three fertilisation levels (control, N50+P35K40, N150+P105K120). Two different cropyears were compared (2011 and 2012).
The research focused on the effects of forecrop and fertilisation on the Leaf Area Index, SPAD values and the amount of yield in two different cropyears. We wanted to find out how the examined parameters were affected by the cropyear and what the relationship was between these two parameters and the changes of the amount of yield.
Examining the effects of growing doses of fertilizers applied, results showed that yields increased significantly in both rotations until the N150+PK level in 2011 and 2012. By comparing the two years, results show that in 2011 there was a greater difference in yields between the rotations (7742 kg ha-1 at N150+PK in the biculture and 9830 kg ha-1 at N150+PK in the triculture). Though wheat yields following peas were greater in 2012, results equalized later on at N150+PK levels (8109–8203 kg ha-1).
Due to the favorable agrotechnical factors, the leaf and the effects of the treatments grown to a great extent in 2011, while in 2012 the differences between treatments were moderate. Until the N150+PK level, nitrogen fertilisation had a notable effect on the maximum amount of SPAD values (59.1 in the case of the biculture and 54.0 in the triculture). The highest SPAD values were measured at the end of May (during the time of flowering and grain filling) in the biculture. In the triculture, showed high SPAD values from the beginning. The same tendency could be observed in the 2012 cropyear, although increasing doses of fertilizers resulted in higher SPAD values until N150+PK level only from the second measurement. Maximum SPAD values were reached at the end of May in both crop rotation system
-
Sorghum and millet as alternative grains in nutrition
91-95Views:231Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) and millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) are the fifth and sixth most important cereal crops in the world. Gluten-free grains, therefore persons with coeliac disease could consume them also. In addition, they have a lot of positive effects due to their phenolic compounds (phenol acid, flavonoid, tannin). The total phenol content of sorghum is high, but Panicum miliaceum and Eleusine coracana have higher antioxidant activity. Fiber and mineral contents are also high, the protein contents are also higher than in standard cereals. Sorghum use is similar to corn: starch, glucose, syrup, and oil can be produced. Moreover, it can be used in preparing whole grain products, bread, pancake, dumpling, mush, cake, pasta and beer from sorghum. Broom and forage are also can be prepeared from them. Millet used such as mush, steamed food, cake, bread, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages.
-
Investigation of the Quality of Winter Wheat in a Sulphur Fertilisation Experiment, 2001/2002
153-156Views:103We have started a small parcell and a factorial S fertilization experiment with winter wheat in the 2001/2002 cropping year to examine its effect on yield and quality. The scene of experiment was the Latokep Experimental Station of the DE ATC (calcareous chernozeem) in case of small parcell examination and the Agricultural Company of Felsőzsolca (brown forest soil) in case od factorial examination.
The protein and gluten content of the grain was investigated with PerCon Inframatic 9001 NIR Analyser, then we have measured these parameters with PerCon 8620 infra appliance. After the milling we measured the following parameters: glutenindex, farinographic parameters (farinographic index, water absorption capacity, dough development time, stability, softening, extension) and valorigraphic index.
Based on the results there’s no justified relation between the fertilization and the protein and gluten content. The valorigraphic index of the samples taken from Felsőzsolca factory characteristically increased as a result of the S-fertilization. In the small-parcell experiment the values of the water absorption capacity, the dough development time and the softening parameters from the valorigrphic parameters depended significantly from the mineral treatments. Signifikant quality improvement wasn’t experieced.
There was sampling in all of critical phenophase (…). The green plant samples were examined on element content with ICP-OES. These measurements are currently in progress. -
Effect of NPK fertilization on the yield and yield stability of different maize genotypes
101-104Views:118The yielding capacity and quality parameters of 11 maize hybrids were studied in 2011 on calcareous chernozem soil in a 25-year long-term fertilization experiment in the control (without fertilization), in the base treatment of N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 and in five treatments which were the multiplied doses of the base treatment. The N fertilizer was applied in the autumn and in the spring, while P and K fertilizers were applied in the autumn.The sowing time was 17–18 April, the time of harvest was 8 October. The 30-year average of precipitation (April–Sept) was 345.1 mm, the amount of precipitation did not differ greatly from that, however, its distribution was very unfavourable.
It was found that the largest yield increment (as compared to the control) was in the treatment N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 in the long-term experiment. The largest yields were obtained for the hybrids P9494, PR37N01 and PR35F38 (13.64–13.71 t ha-1). Due to the dry period at the end of the summer – beginning of autumn, the grain moisture content at harvest was favourably low, 12–18% depending on the treatment and the growing season.The N fertilization significantly increased the protein content of the kernel, but the starch content of the kernel decreased (significantly in several cases) with increasing fertilizer doses and yields as compared with the control.
The highest protein content was measured in hybrids GK Boglár and Szegedi 386. The oil content was above 4% for GK Boglár, but the two hybrids were not among the best yielding hybrids in spite of their good inner content. The starch content was around 75 % without fertilization, it decreased with fertilization.
For the tested hybrids, the fertilizer dose N 120 kg ha-1, P2O5 75 kg ha-1, K2O 90 kg ha-1 can be recommended with respect to efficacy and environmental considerations. -
Determining elements of variety-specific maize production technology
157-161Views:62Our aim was to work out such new maize fertilizer methods and models which can reduce the harmful effects of fertilization, can
maintain the soil fertility and can moderate the yield fluctuation (nowadays 50-60 %).
The soil of our experimental projects was meadow soil. The soil could be characterized by high clay content and pour phosphorus and
medium potassium contents. In the last decade, out of ten years six years were dry and hot in our region. So the importance of crop-rotation
is increasing and we have to strive for using the appropriate crop rotation.
The yields of maize in monoculture crop rotation decreased by 1-3 t ha-1 in each dry year during the experiment (1983, 1990, 1992,
1993, 1994, 1995, 1998, 2000, 2003, and 2007). The most favourable forecrop of maize was wheat, medium was the biculture crop rotation
and the worst crop rotation was the monoculture.
There is a strong correlation between the sowing time and the yield of maize hybrids, but this interactive effect can be modified by the
amount and distribution of precipitation in the vegetation period. At the early sowing time, the grain moistures were 5-12 % lower compared
to the late sowing time and 4-5 % lower compared to the optimum sowing treatment.
There are great differences among the plant density of different maize hybrids. There are hybrids sensitive to higher plant density and
there are hybrids with wide and narrow optimum plant densities.
The agro-ecological optimum fertilizer dosage of hybrids with a longer season (FAO 400-500) was N 30-40 kg ha-1 higher in favourable
years as compared to early hybrids.
We can summarize our results by saying that we have to use hybrid-specific technologies in maize production. In the future, we have to
increase the level of inputs and have to apply the best appropriate hybrids and with respect to the agroecologial conditions, we can better
utilize the genetic yield potential. -
Comparative analysis on the fertiliser responses of Martonvásár maize hybrids in long-term experiments
111-117Views:68The results of experiments carried out in the Agricultural Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences clearly show that in the case of hybrids grown in a monoculture greater fertiliser responses can be achieved with increasing rates of N fertiliser than in crop rotations. In the monoculture experiment the parameters investigated reached their maximum values at a rate of 240 kg/ha N fertiliser, with the exception of 1000-kernel mass and starch content. In both cases the starch content was highest in the untreated control, gradually declining as the N rates increased. Among the parameters recorded in the crop rotation, the values of the dry grain yield, the 1000-kernel mass, the protein yield and the starch yield were greatest at the 160 kg/ha N fertiliser rate, exhibiting a decrease at 240 kg/ha. Maximum values for the protein content and SPAD index were recorded at the highest N rate. It is important to note, however, that although the N treatments caused significant differences compared to the untreated control, the differences between the N treatments were not significant.
In the given experimental year the values achieved for the untreated control in the crop rotation could only be achieved in the monoculture experiment at a fertiliser rate of 160 kg/ha N, indicating that N fertiliser rates could be reduced using a satisfactory crop sequence, which could be beneficial from the point of view of environmental pollution, crop protection and cost reduction.
The weather in 2006 was favourable for maize production, allowing comparative analysis to be made of the genetically determined traits of the hybrids. Among the three hybrids grown in the monoculture experiment, Maraton produced the best yield, giving maximum values of the parameters tested at a fertiliser rate of 240 kg/ha N. The poorest results were recorded for Mv 277, which could be attributed to the fact that the hybrid belongs to the FAO 200 maturity group, while the other hybrids had higher FAO numbers. Maraton also gave the highest yields in the crop rotation experiment at the 160 kg/ha N level. All three hybrids were found to make excellent use of the natural nutrient content of the soil.
It was proved that the protein content of maize hybrids can only be slightly improved by N fertilisation, as this trait is genetically coded, while the starch content depends to the greatest extent on the ecological factors experienced during the growing season. -
The effect of drought and cropping system on the yield and yield components of maize (Zea mays L.)
51-53Views:122Different Cropping Systems have many advantages and ensure better crop growth and yielding. Its combination with other agronomic measures can ensure optimal crop density for maximum crop growth and photosynthesis efficiency. The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of different cropping systems on monoculture and biculture rotations [maize- wheat]. The study found that crop rotation does not have a significant effect on the grain nutrition quality, Leaf Area Index (LAI) and Normalized Difference Vegetative Index (NDVI) but has a significant effect on the Soil-Plant Analysis Development (SPAD). Yield and yield components were significantly influenced by crop rotation in this study as yield, plant height, cob weight and number of grains per row all recorded lower mean at 5% probability levels.
-
Technological development of sustainable maize production
83-88Views:144In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize.
The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly eight ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2, this it was a half-industrial experiment. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. Yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare at a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants per ha.
In Hajdúszoboszló, in 2016 the amount of rainfall from January to October was 605 mm, which was more than the average of 30 years by 160 mm. The yield of hybrids without fertilization changed between 9.63–11.6 t ha-1 depending on the number of plants.
The six tested hybrids is 10.65 t ha-1 in the average of the stand density of 60, 70 and 80 thousand plants per hectare without fertilization, while it is 12.24 t ha-1 with N80+PK fertilizer treatment. That increase in the yield is 1.6 t ha-1, it is significant.
Da Sonka hybrid is sensitive to weather, it is able to produce 6 t ha-1 additional yield in case of favourable condition. However, it has a low stress tolerance. The most stable yields were observed at Kamaria and Pioneer hybrids. The effect of vintage is also an important factor on the yield. In average, the yield of maize was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, which was a drought year and 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 that was a favourable year. -
Investigation of genetic diversity in irradiated maize lines and its relation to hybrid performance
20-26Views:152Knowledge of genetic diversity among available parental lines is fundamental for successful hybrid maize breeding. The aims of this study were to estimate (1) genetic similarity (GS) and genetic distance (GD) (based on Jaccard index) in four maize inbreed lines; (2) to classify the lines according to their GD and GS; (3) to determine hybrid performance based on GD and heterosis for yield ability in 4x4 full diallel system. We used morphological description and AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphisms) for estimation genetic polymorphism in four maize inbred lines. We estimated the applicability of genetic similarity in SC and reciproc hybrids for prediction of their performance.
Three primer combinations were used to obtain AFLP markers, producing 207 bands, 70 of whit were polimorphic. The dendogram based on genetic similarities (GS) and genetic distance (GD) and morphological description separated four inbred lines into well-defined groups. Morphological description just with AFLP analysis showed reliable results. In view of genetic distance, the UDL 1 line and their linear and reciprocal crosses showed significant heterosis effect, which was confirmed by heterosis calculation based on grain yield. -
The effect of NPK treatments on the Cu and Fe content of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
31-34Views:175In this study the effect of N, P and K nutrients on the Cu and Fe content of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains was investigated in a long-term fertilization experiment set up in Nagyhörcsök. Samples were also harvested from four experimental stations of the Hungarian national long-term fertilization trials. These are the following: Bicsérd, Iregszemcse, Karcag, and Putnok. Plant samples were collected in 2005 which was very wet. Our results from Nagyhörcsök were compared with the Cu and Fe content of samples which were harvested from control plots of other experimental stations. The Cu and Fe content of grain samples were measured using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) followed by digestion with HNO3-H2O2 solution. All data were subjected to ANOVA, and when significant differences (P<0.05) were detected, Duncan’s test was performed to allow separation of means.
The main conclusions are as follows: Cu and Fe content of wheat grains was higher and higher in every NPK treatments. Samples were harvested from the control plots of Iregszemcse and Bicsérd have higher Cu content than the treated samples from Nagyhörcsök.