Search
Search Results
-
Evaluation of egg quality parameters of two Hungarian ostrich populations
51-57Views:234The aim of our study was to evaluate the quality parameters, porosity and weight loss of eggs deriving from the two most significant ostrich farms in Hungary. Quality parameters included weight, length, width, shape index, egg volume, surface area, circumference and shell volume. The effect of storage conditions in both farms and the incubation technology on egg weight loss in farm “A” were also examined. The research objective was to impart a comprehensive knowledge on egg quality parameters of the main ostrich populations in Hungary and to compare the trios and the farms with each other and the international literature. We could reveal significant differences between trios in all egg quality traits. In conclusion, the shorter and the narrower the eggs were, the more spherical shape they had. Narrower eggs showed smaller surface area, volume, circumference and shell volume and vice versa. Eggs from farm “B” indicated significantly greater width, shape index, surface area, circumference and shell volume than farm “A”. A significant difference was observed in weight loss during storage between the farms. Weight loss in farm “A” was a multiple of farm “B”. In farm “B” there was a weak, positive correlation between storage period and weight loss (r=0.22, P≤0.05), in farm “A” it was not significant (P=0.52). There was no relationship between the initial egg weight and weight loss either in farm “A” or farm “B” (P=0,21, P=0,69). A slight positive correlation could be noted between egg porosity and weight loss (r=0.24, P≤0.05). Pores count presented here was less than the international results. Poultry eggs contain the most pores at the blunt end, less via the equator and the least at the pointed end. In ostrich egg we found more pores via the equator against the blunt end. To draw more precise conclusions, further investigation should be carried out on porosity. Considering the fact that the length of storage period and the weight loss during incubation are in strict correlation with hatchability, we intend to extend our research aims to these traits.
-
Growth and yield patterns of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) sample trees affected by site conditions: case studies
125-128Views:78The trees removed from the long-term experiment plots are available for the measurements as lying trees. Through the determination of the volume in sections along the stem, the stem form, the stem volume and other factors can be specified. The comparison of the stems of individual trees of first and third yield classes of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) stands shows that site conditions have a main effect on the yield (mean tree volume). The difference can be as high as 53% at the age of 30 depending on the sites. To determine the growth patterns based on tree volume is rather a new approach in the light of the relevant literature. The obtained results also highlight the importance of choosing the appropriate tree species for a given site.
-
Angle-count sampling method for estimating forest stand volume – a practical approach
99-102Views:197Point sampling, which is also known as angle-count sampling (ACS), can be considered an efficient way of estimating the basal area and volume of forest stands. It is possible to use it in forest management: providing more accurate estimates (precision <10%) of site and stand characteristics needed for management planning. 20 black locust (Robinina pseudoacacia L.) stands were selected at final cutting age to determine the regeneration criteria based on their total volume. It was verified that at P=5% there was no difference between the main volume values of stands indicated in the relevant forest plans as well as calculated by the ACS method.
-
Yield and crown structure characteristics in a red oak (Quercus rubra L.) stand: Case study
49-53Views:138The paper provides the results of a detailed analysis of timber volume and several important crown variables of red oak (Quercus rubra L.) based on an experimental plot in eastern Hungary. At the age 32 years the crop trees belonged to different height classes. If the volume of the mean tree from height class I was considered as 100%, the volume of the mean tree of class II was 59%, and the mean tree of class III was only 36%. It appeared that there was a significant correlation between crown indices and yield. For this reason, diameter at breast height showed a positive linear correlation with crown diameter (R2= 0.6211). Additionally, there was also positive linear relationship between crown diameter and volume (R2= 0.6908). The variation of crown indices is height even within the same stand and indicates the importance of following a selective thinning operation method.
-
Simplified volume equations for grey poplar (Populus × canescens Smith.) standing trees
27-31Views:72Grey poplar (Populus× canescens Smith.) is a natural hybrid of white poplar (Populus alba L.) and Eurasian aspen (Populus tremula L.). It can be found throughout Europe, where both parents are present. The above mentioned species of poplars (under the term of ‘domestic poplars’) cover approximately 5% of the forests of Hungary. Of these species, grey poplar holds significance in forestry, and its role in afforestation shows a growing tendency. For this reason, improving the growing technology of grey poplar is a timely topic. In this paper we introduce algorithms which help estimate grey poplar tree volumes without having to use volume tables. Based on the performed evaluations, both equations can be used for single tree volume estimation with an error of less than 5%.
-
Volume of Paulownia Shan Tong (Paulownia fortunei × Paulownia tomentosa) plantation in Eastern Hungary: a case study
43-46Views:199Volume tables for tree plantations are not unknown in international practice. In many places, this is due to the uniqueness of the species or variety composition of the plantations and the cultivation technology used. In most cases, this is also justified by specific soil (ecological) conditions. In Hungary, publications on Paulownia have not yet included a volume table. This is the first one we are publishing, thus it can be considered as a gap-filler. The research was conducted in Monostorpályi, a 1.8 hectare, 8-year-old municipal plantation. 8 trees were selected randomly and their parameters were studied.
-
Vegetative shoot growing and yield productivity of different plum cultivar and rootstocks combination
25-29Views:137We planted containers plum rootstocks and cultivar combinations for irrigation and rootstocks experiment. We planted Cacanska lepo tica, Katinka, Jojo, Topfive, Toptaste, Topper plum cultivar on Mirobalan, St Julien A, St Julien GF 655/2, Wavit, Wangenheim, and Fereley rootstocks. Before budding we measured the trunk diameter on trees, than I count the trunk cross area, we measured the high of trees, the high of crown, and the wide of crown, and counted the volume of crown from these data. We conclude the vigorous from the trunk cross area and the volume of crown. In the started growing less vigorous combinations look like Topfive/Wavit, Jojo/Mirobalan and Katinka/Mirobalan grafted on the basis trunk cross area and the volume of crown. In the vegetative period we measured the shoot growing on model branch every started of months. So we could determine the growing tendency. The smallest growing was Cacanska lepotika/Mirobalan.
In the flowering the grafted flowered in rich, excepted the Topfive cultivar on St Julien A, St Julien GF 655/2, and Fereley rootstocks, these didn’t flowered. The Topfive/Wavit combinations there were a richest flower.
In the harvest term we could pick up plum fruits from Topfive/Wavit combinations, and Cacanska lepotica, Jojo, Toptaste cultivar. And in addition the Topper cultivar was the highest yield on their all of rootstocks. -
Development of the reproductive tract of immature gilts
165-166Views:72Mechanisms of regulation of litter size in pigs are complex and depend on many factors, including genetic regulation and also physiological and anatomical development of the reproductive tract in gilts. Improvement of growth rate in present breed pigs raises the question as to whether, with the development of the reproductive tract, sexual maturity would also be attained.
The aim of the study was to assess the morphometric traits of reproductive tracts taken from gilts slaughtered at 100 kg body weight, i. e., just when they may become actively sexual mature.
This study was concluded on 80 prepubertal gilts of the Polish Landrace (PL) breed tested at the Pig Program Testing Station. The animals were kept in individual pens with control feeding and standard management. They were slaughtered after attaining 100 kg body weight. Immediately after slaughter, the reproductive tract was removed and carefully assessed. The morphometric estimation of the reproductive tract involved the
measurement of uterus weight with ligament, vagina-cervix length, uterine horns and oviducts length, ovaries weight, height and width. Uterus volume capacity was also determined, based on volumetric method of Kwaśnicki’s (1951) with own modification.
All pigs were divided into three groups in respect to age at slaughter: A – below 160 days (n=38), B – from 160 to 180 days (n=28) and C – above 180 days of age (n=14). The results were elaborated statistically computing the arithmetic means (x) for every traits and standard deviations (s). One-way analysis of variance ANOVA was performed. The significance of differences between age groups was estimated using Duncan’s test.
Calculations were performed with STATISTICA 8PL Software.
Obtained results are presented in the tables below. The most pronounced differences in the development of the reproductive tract are dependent on the age of gilts concerning only the uterus weight (P≤0.01) and uterus vagina-cervix length (P≤0.05). Gilts at age 160-180 days attained the full stage of reproductive tract development. Differences between the compared age groups of gilts dealing with the other morphometric traits
and ovary characteristics were statistically not significant. -
Seasonal variations in somereproductive parameters of Dorper Rams in Hungary
17-20Views:307The purpose of the present study was to test the hypothesis that season has an affect on semen quality and scrotal circumference of Dorper rams. The experiment was carried out with six Dorper rams aged between 15 and 18 month. Semen samples were collected with artificial vagina and volume, concentration (x 109/ml), total sperm number/ejaculate (x 109), mass motility (0–5), progressive motility (%), scrotal circumference (cm) was observed. Significant differences (P<0.05) were observed in concentration, total sperm number/ejaculate, scrotal circumference in different seasons. Volume was the highest in autumn (1.4±0.5 ml) and the lowest in the spring (1.3±0.4 ml). Concentration of semen was lower in spring (2.6±1.5 x 109) and summer (3.3±1.5 x 109) as compared to fall (4.1±1.1 x 109) (P<0.05). Regarding total sperm number/ejaculate (x 109), scrotal circumference (cm) all the seasons differed significantly (P<0.05), although the season had no effect on mass motility and progressive individual motility (P<0.05). In conclusion the present study showed that semen quality parameters and scrotal circumference of Dorper rams were better in autumn than in the other sea- sons.
-
Microbiological and Chemical Characterization of Different Composts
106-111Views:80Composting of agricultural waste is considered particularly important from the point-of-view of environmental protection. Degradation of organic substance results in a significant reduction of waste volume.
The end product of the composting process, mature compost, can be used as soil coverage against excess loss of wastes, for mulching, for organic manure etc. The problem of composting has come into limelight in environmental studies and in agriculture.
The quality of the mature compost is determined by physical, chemical and biological parameters of the composting process which, in turn, depend on initial composition of the raw materials, the technology, e.g. regular mixing and moistening and on environmental factors. Quality is the key question in compost use.
We studied the composting process in compost windrows of different raw material composition. We measured temperature, humidity content, pH, organic substance content, nitrogen and carbon content.
We counted the number of bacteria, microscopic fungy, ammonifying and cellulose decomposing microorganisms. We directed the composting process with turning weekly (to provide oxygen) and watering (to provide humidity content 40-60%).
We set up windrows of 1 m3 volume from dry plant substances (cornstalk, pea straw, tomato stalk and crop, weeds) and cow manure not older than 1 week. The cow manure was used at ratios of 0%, 35%, 50%, 65% and 100%, respectively.
We measured changes in compost temperature relationship with outside temperature until they were almoust the same. Humidity was 40-60% in most cases.
At the beginning of the process, pH was slightly acidic-neutral; it later becomes neutral-slightly alkaline (pH: 6.93-8.02) as ammonia is liberated from proteins.
At the end of the process, pH decreased again, due to humification.
Organic substance content decreased as microorganisms mineralized them. Organic carbon content decreased gradually due to microorganisms used it as an energy.
Total nitrogen content increased until middle of july and decreased gradually until than.
The carbon/nitrogen rate were higher in the beginning, it decreased until july-august and increased by smaller degree until end of the process.
The number of bacteria was higher in the first three weeks and between june-september. The number of cellulose degrading bacteria was the highest in the first three month, the number of ammonifying bacteria was the highest from the end of may until sepember.
The number of microscopic fungy was significant in the second part of process, after july. -
Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth kinetics study dairy byproduct
169-172Views:243By guess, annual volume of milk whey is 185–190 million tons and this volume probably will increase next years. Whey has significant biochemical oxygen demand due to its high organic matter content so whey as sewage is one of the most pollutant by-products in the food industry. Apart from environmental pollution, benefit of several whey constituents for human health is another reason to utilize whey. Corn and potato, as well as the processing of milk in the food industry in large quantities of by-products generated by low cost, substantial quantities of starch and lactic acid, which are due to high biological oxygen demand are considered as hazardous waste. Some of them are destroyed sewage storage tanks, and those products are excellent substrates for the growth of microorganisms could be. The traditional nutrient solution optimization methods are solution and time-consuming and are not able to determine the real optimum because of the interaction of factors involved.
-
Yield table for selected black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) cultivars
193-198Views:227In Hungary, the black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) can be considered as the most important fast-growing, stand-forming introduced tree species. Due to its positive growing technological characteristics as well as wood utilization possibilities, at the present, black locust is the most widely planted tree species in Hungary, covering 25% of the country’s total forest area. One of the important tasks ahead of Hungarian black locust growers is to improve the quality of black locust stands with introducing selected cultivars. For the estimation of the growth rate and yield a numerical yield table has been constructed on the basis of surveys of the experimental plots established in pure,managed ’Nyirségi’ ,’Üllői’ and ’Jászkiséri’ black locust cultivars’ plantations which can be suitable for sawlogs production. In the course of 56 stand surveys the key stand characteristics were measured, and then, were reconsidered the average height, diameter (DBH), volume, basal area and stem number given separately for the main (remaining), secondary (removal) and total stands per hectare. The programmable editing procedure allows to extention and formal change of information content of the yield table according to different demands.
-
Application of AquaCrop in processing tomato growing and calculation of irrigation water
183-187Views:342The area and volume of processing tomato production is increasing in Hungary. Irrigation is crucial for processing tomato growing. To save water and energy, it is important to know exactly how much water is needed to reach the desirable quality and quantity. AquaCrop is a complex software, developed by FAO, which is able to calculate irrigation water needs, several stress factors and to predict yields. A field experiment was conducted in Szarvas in processing tomato stands, under different irrigation treatments. These were the following: fully irrigated plot with 100% of evapotranspiration (ET) (calculated by AquaCrop), deficit irrigated plot with 50% of ET (D) and control (K) plot with basic water supply was also examined. Dry yield, crop water stress index and soil moisture were compared to modelled data. The yields in the plots with different access to water were not outstanding in the experiment. The model overestimated the yields in every case, but the actual and modelled yields showed good correlation. AquaCrop detected stomatal closure percentages only in the unirrigated plot. These values were compared to CWSI – computed from leaf surface temperature data, collected by a thermal cam in July – and showed moderately strong correlation. This result suggests that Aquacrop simulates water stress not precisely and it is only applicable in the case of water scarcity. Soil moisture data of the three plots were only compared by means. The measured and modeled data did not differ in the case of K and ET plots, but difference appeared in the D plot. The obtained results suggest that the use of AquaCrop for monitoring soil moisture and water stress has its limits when we apply the examined variables. In the case of dry yield prediction overestimation needs to be considered.
-
The effect of the plant density for the yield of the maize hybrids
50-61Views:111In order to enchance the yield stability of maize, the effect of plant density on yields was studied on a typical meadow soil in Hajdúböszörmény between 2002-2004. In the plant density experiment, we used the method of Béla Győrffy. The plant densities applied therefore 20 to 100 thousand plants/ha by ten thousand scale. The application of fertilizer rates for the maize hibrids in every year were N: 110 P: 90 K: 120 kg/ha. We used a manual soiling-gun in the experiment. In every year we used plant protection techniques against monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous weeds. The harvest was done by hand. The facts were read by variancie analysis and linear regression analysis. The moisture and the temperatures were extreme in 2002, 2003, 2004. We have to mention defficiery of moisture in 2003 which is shown that the hot days number increased. After evaluating our findings we can conclude that most hybrids showed a significant correlation between increased plant density and the volume of yields. On the basis of the experiments we divided the hybrids into four groups: the first group included the hybrids suitable for increased plant density with a wide range of optimal density values; the second group included hybrids, which did not require high plant density, were capable of good individual performance and tended to grow several ears; the third group included flexible corn types, which grew longer ears in favourable years, thus yielded more; and the fourth group included the hybrids, which were sensitive to increased plant density and which showed a narrow range of optimal density values. Finally, plant density determines the yield; we have to consider optimal plant density intervals as well as optimal plant density, and we also have to place a high emphasis on the use of hybrid-specific technologies.
-
A practical means of setting the scene for evaluating aggregated absorption risk in EU co-funded programmes related to project failure
63-66Views:119The main purpose of the mid-term evaluation of grant programmes is to assess relevance, progress, effectiveness and efficiency. There are several methodologies, tools and techniques applied in various evaluations to assess these programme aspects. An important area of the evaluation of both the financial progress and the effectiveness of the programme is to evaluate the risk of absorption which is indicated by various factors, inter alia risk of supported project failure. If a project fails in any EU co-funded programme in the stage of preparation or implementation, then the fund already committed to that particular project (assumed to have already been absorbed or “spent”) is to be reused again or is to face decommitment (funds have to be paid back to the EU). There are strict EU regulations governing the time scale of this re-use (n+2, n+3 rules), therefore it is of major importance to assess the risk severity (measured as the resultant of the volume of grant at risk and the chance of project failure) and build up an early warning mechanism which indicates if the risk reaches a critical level that requires immediate intervention.
-
Dimensionality Expressed by Caseendings and Spatial Prepositions
7-15Views:92The purpose of this essay is to investigate some of the uses of English prepositions and Hungarian case endings employed to express spatial relations. The observation of invariant mistakes Hungarian native speakers learning English make initiated the investigation. The questions raised are: (a) where do the two systems match and where do mismatches lie, (b) how do language users perceive the world, and (c) do speakers observe spatial relations as two-dimensional or three-dimensional cognitive models? Do different languages see the same thing as either three-dimensional, or two-dimensional?
Abondolo (1988) gives an adequate morphological analysis of ten Hungarian case-endings (inessive, illative, elative, superessive, delative, sublative adessive, ablative, allative and terminative) used in spatial reference, which give a closed set in references made to factors, such as (1) location which can be broken down as interior vs. exterior location with the latter being further analysable as superficial and proximal, and (2) orientation which can be analysed as zero orientation (position), source and goal. In addition to those in this list, two other case endings (genetive/dative and locative) are also used for expressing spatial relations but the last is only a variant of the inessive and superessive case-endings and is only used with place-names. The set is closed in the sense that the same item is meant to refer to the same sort of spatial relation in every case. Language textbooks, c.f. Benkő (1972) seem to suggest a neat match between the above Hungarian case endings and their English prepositional counterparts, e.g. London-ban (inessive) = in London.
The picture, however, is far from being so clear-cut. The data, which were taken from various dictionaries and textbooks, show that the choices of both the prepositions and the case endings listed above depend on how the speaker considers factors (1) and (2) and that proximity is very important. Instead of a one-to-one match between the prepositions and the case endings, we rather find that the above case endings will match a dual, and in some cases a tripartite system of prepositions with the correspondences found in the two languages, which yield the following chart: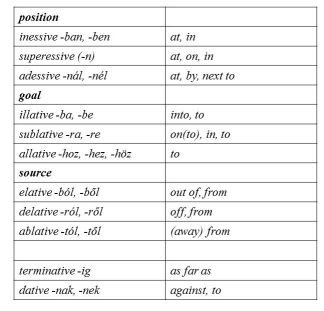
We suggest that languages may view or map the same physical entities in different ways, for example along surface vs. volume or goal vs. passage, etc.
Furthermore, we also find it possible that it is the language specific, inherent coding of the nominal phrase that decides – in many cases – upon the choice of prepositions and case endings. -
The effect of increasing compost rates on the yield and nutrient content of ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)
127-134Views:158Satisfaction of the increasing needs of humanity causes large environmental load. To provide a livable environment for future generations we have to satisfy our needs with the use of sustainable management. This is one of the biggest challenges of nowadays.
The amount of wastes emitted in increasing volume can be decreased by the recycling of them. The disposal of waste materials formed in the public spaces of cities and during the processing of agricultural row materials and by-products in landfills is inconceivable, so they must be recycled.
These materials mostly with organic compounds could be the primary substrates of composts. Completed with suitable additives, and applied appropriate treating technology, composts are capable to supply horticultural plants with nutrients. Composting wastes and byproducts not just decreases the amounts of deposited waste materials, but increases the nutrient (macro- and micronutrients) content of soils, so this is an environmentally friendly and alternative way of nutrient management of plants. -
The applicability of 10 ml cryotubes for sperm cryopreservation in a Hungarian carp landrace (Cyprinus carpio carpio morpha accuminatus)
93-97Views:245In our study, the comparison of 5 ml straw and 10 ml cryotube during sperm cryopreservation in a Hungarian carp landrace (Cyprinus carpio carpio morpha accuminatus) was carried out. Three different dilution ratios (1:1, 1:4 and 1:9) were also tested using the cryotube. A significantly higher pMOT was recorded using the cryotube in comparison with the straw. VCL and STR were similar in both groups. Cryopreservation had a negative effect on pMOT and VCl using the cryotube and also the straw where, STR was not reduced significantly. An increasing tendency was observed using higher dilution of sperm during cryopreservation; however, significant difference was not recorded between the three groups. VCL and STR were similar in all groups. Cryotube was applicable for the sperm cryopreservation of the Hungarian carp landrace. However, the standardization for the freezing method specified for this volume is recommended. The different dilution ratios needed be tested also during fertilization.
-
The effect Benefit PZ biostimulant on the fruit size and yield production of apricot varieties (Prunus Armeniaca)
16-18Views:141Fruit size is determined by the genetic makings of varieties the pomology and enviromental factors. The climate and the previous year’s harvested yield have a great effect on yield volume. It is not easy to harmonize the qualitative and quantitave parameters of the fruit. High yield usually causes smaller fruits.
The aim of our trials was to evalaute the effect of Benefit PZ biostimulant on fruit size. We examined two apricot varieties (Bergeron, Magyarkajszi C235) for the efficacy of the product. The three applications were made with 400 l/ha water with 2500 ppm. The optimal interval of application with Benefit PZ is during in the early phases of development. The size of the final fruits depends on the number of cells making up the fruits. The later application could not increase fruit size growth, there are no significant differences between the Benefit PZ sprayed and the control plots. The totally harvested fruit weight was 13.5% more on the trees of cv. Bergeron, it was caused by the higher fruit set. On the sprayed trees were 12.2% more fruit. Therefore were no differences between the average fruit weight. Fruit weights of the treated trees were 44.37 g on cv. Bergeron, 44.15 g on cv. Magyarkajszi C235 and on the no treated trees were 43.83 g as well as 45.33 g. -
Practical experiences of a designing and operating a pilot aquaponic system
27-32Views:335Aquaponics is the combination of fish farming (aquaculture) and the soilless cultivation of plants (hydroponics). The aquaponics system is an artificial, recirculating ecosystem, in which bacterial processes convert the waste materials in the water used for fish rearing into plant nutrients, and therefore with the generated heat it is suitable for culturing economically valuable plants, and thus it mitigates the nutrient laden and quantity of the intensive fish producing systems’ effluent water.
The primary goal of our 12 separate unit’s aquaponics system was to gain experience. We would like to find the right plant species, which are fit for that medium, and their crop can be sold. Besides the plants, our attention focused on the fish. Two fish species were included in the experiments, the common carp and barramundi. It was difficult to create them a perfect living space, besides a constantly changing conditions temperature. Apart the above mentioned we had a problem with the number of individuals per tank, the deformity of the fish body and the too high volume of pH (we registered continuous values above 8.4). We get by carps 4.7 grams of weight gain during 15 weeks, because of the bad conditions.
The main problems at the plants are caused by aphesis and protection against sunburn. Even so we have got the multiples of field yields for each plant species. At salad has grown twice of field yields, tomatoes one and half, kohlrabi than 3.5 times more. The causes of multiple yields are the continuous balanced water and the nutrient uptake of plants. Each plant species fit for cultivating in aquaponics and their crops are delicious, chemical -free, safe and marketable. The plants should be more concentrated. After the experiment, it has been determinated that the carp is suitable for aquaponics, but greater weight gain could be achieved with optimal selection of size of rearing units.
-
Önitatók konstrukciós és hidromechanikai vizsgálata
52-57Views:112Our research aimed to examine Hungarian automatic drinking system constructions and hydromechanics under laboratory conditions and in operation with special emphasison the small volume, valve types.
Considering that no Hungarian standard of automatic drinking system examination and qualification exists, on the basis of technical literature, the new examination method of automatic drinking systems has been elaborated.
For laboratory measurements, a universal measuring bench was assembled which is applicable to the hydromechanic testing of all automatic drinking systems (cattle, sheep, pig).
Summary of the laboratory measurements:
Upon comparison of the flow capacity of the valves, in the case of same opening values (h/dn), the rubber spring valve of SZI type automatic fountain has the highest flow capacity, although in the case of 100 kPa pressure even this type has only 15-16 l/min value which hardly surpasses the lower limit of the desired 15-25 l/min range.
The loss coefficients of the valves, on investigating in the range 100-200 kPa, showed the lowest value (2,2-5,8) with the steel spring self drinking device.
Summary of the operational investigations:
In the long term operational investigations, the rubber stripped valve and the rubber spring automatic fountains had the most favourable operational reliability values: K4=0,98 and K4=0,94, respectively.
From the aspect of animal operation of the valves, all the Hungarian types are frontal operated, thus such system automatic valve drinking devices can be used only in long and moderately long stands, directed toward the animal.
On the basis of hydromechanical and construction examinations of the Hungarian tied cattle production technology the construction modification of the rubber spring valve of SZI type automatic drinking fountain, which is the most frequantly used in this country, was carried out. Due to design modifications the valve parameters improved significantly.
The goals of the accomplished valve modification were
ζ'sz – loss coefficient to be reduced
q – flow capacity to be increased -
Evolution of some components of agroecosystems productivity from Vinga Plain in water stress situations
174-179Views:76The researches are inscribed on line of substantiation of durable agricultural system, having main objective the prominence of
quantitative and qualitative modifications made on agro-system level under the effect of no-tillage system for wheat, maize and soybeans.
The experimental field is placed on a cambium chernozem, with a medium content of clay, dominant in the Prodagro West Arad agrocentre
and representative for a large surface in the Banat-Crisana Plain.
The passing to no-till system change the structure of technological elements, through less soil works, so the impact on agro-system is
different comparing with conventional tillage, first less the intervention pressure on agro-system ant secondly appears new interactions, new
equilibriums and disequilibriums.
Considering the evolution of soil humidity, the observations made monthly (by taking soil samples and laboratory determinations) for
the three cultures showed that in the no-till system, there are more uniform values in the soil profile, and in the variants where the deep work
of soil was made it could be observed a low increase of the water volume in the soil. -
The stinging nettle as an alternative food crop
68-70Views:92Vegetables play an important role in human health and have an important effect on the human diet. It is equally serious to improve the volume, the diversity and the year round equability of vegetable consumption. The stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.) is an alternative vegetable crop and available from the beginning of Spring to the end of Autumn; therefore, it can improve both the diversity and the equability of vegetable consumption. The stinging nettle has a superb nutritive value, it is a prospinach and it can be cooked in many ways.
-
A simplified growing model for mixed black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) and poplar (Populus spp.) plantations in the Danube-Tisza Interfluve
97-100Views:151This study presents a static model of mixed black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) plantation stand structures for inventory stand structures between 10 and 40 years of age. Due to its local character, the model can be advantageous in planning tending operations, making structural factor predictions for the standing stock (main stand) after tending cuts, and preparing local wood production and silvicultural models. The model data presented in this paper show that poplars account for 55–62 % of the volume per hectare due to their faster growth rate in mixed black locust and poplar plantations. Maintaining the black locust part of the stand necessitates harvesting the poplars by the age of 10 at the latest.
-
Examining reaction of sunflower genotypes on planting time on chernozem soil
93-99Views:122We studied the effect of planting time on plant pathological factors, leaf area index and yield production by applying various fungicid treatments on two different sunflower genotypes in 2013.
By delaying planting time, both the extent of Diaporthe, Alternaria and Phoma infections decreased. The differences between the volume of infections were significant in the case of the early and late sowing time results. The application of fungicide treatments induced a notable decrease in the extent of infections for all three pathogens examined. The LAI-values varied between 0.3 and 5.6 m2/m2 in 2013 depending on the hybrid, sowing time and treatment. Stocks planted at distinct times reached maximum leaf coverage at different times. The planting time and the fungicide treatment had a significant effect on the formation of the leaf area. In the case of average and late planting times, fungicide treatments elongated the preservation of the green leaf area.
With respect to the yield amount, average planting time (27 April, 2013) turned out to be optimal in 2013 (control – NK Ferti: 4.621 kg ha-1, PR64H42: 4.196 kg ha-1; double-treated: NK Ferti: 5.282 kg ha-1, PR64H42: 5.090 kg ha-1). Fungicide treatments resulted in significant yield growth in all cases during our research.
We applied Person correlation analysis to evaluate the hybrids’ sensibility to infections and our results varied in the case of Diaporthe and Phoma (r=-0.343*, -0.379**). Infections of the three pathogens were significantly reduced by delaying the planting time and applying fungicides. Late sown stocks preserved the green leaf area for a longer period. Besides, the application of the fungicide treatment and the hybrid itself also led to the preservation of the green leaf area. However, pathogens examined notably decreased the leaf area by the end of the growing year. The fungicide treatment had a remarkable effect on yield growth (r=0.603**). Furthermore, the presence of higher LAI-values in the period prior to August also induced higher yields.