Search
Search Results
-
Examination of the impact of ecological and agrotechnical factors in a maize fertilisation experiment
13-17Views:114The year 2013 was rather extreme breeding year because of the uneven distribution of precipitaion and the summer heat. The experiment was set on with eight different genetic characteristics maize hybrids in 2013. In our study were included different kind of breeding season hybrids. We studied the effect of NKP fertilization and row spacing on the yield. The fertilizer doses are based on 25-year long-term experiment. Compared to control, the N40+PK treatment has also achieved a significant yield increase, although some hybrid of increasing fertilizer doses yield response to loss. The majority of hybrids reached higher yields using the 50 cm row spacing. The water release of hybrids was measured between 21th August and 17th September weekly, at the same time points. The rainy September slowed ripening hybrids and water release, so the grain wet content at harvest showed higher values.
-
Correlation between sowing time of maize hybrids, yield and seed moisture content at harvest on chernozem soil
32-41Views:115In this paper, we analysed the results of maize sowing time experiments conducted by the Department of Crop Sciences and Applied Ecology of the University of Debrecen Agricultural Sciences Centre, during the period from 1997-1999. We made the experiments at the experimental garden of DE ATC, on a chernozem soil with lime deposits.
In 1997, we examined five hybrids, in 1998 six hybrids, and in 1999 three hybrids, with three sowing times. Sowing times were early (10. Apr. and 08. Apr.), optimal (25. Apr. and 28. Apr.) and late (15. May and 17. May).
We examined the following standards: yield, seed moisture content at harvest, thousand kernel mass, duration of flowering, emergence time and profitability.
In 1977, the emergence times, in order of sowing, were: 24, 12 and 9 days. Yields of the sowing times were the following, in mean, for the five hybrids: in the early sowing time (10. Apr.) 11,81 t/ha, in the optimal sowing time (25. Apr.) 11,67 t/ha, and in the late sowing time (15. May) 12,9 t/ha. The seed moisture content of the five hybrids at harvest was 8% less in early sowing time, than in the late sowing time. The thousand kernel mass was the biggest in late sowing time, but we could not prove any significant connection attributable to the effect of sowing time. We examined
profitability, too. Of the five hybrids, four attained the greatest profit with the early sowing time in 1997.
In 1998, the emergence times, in the order of sowing, were: 21, 10 and 11 days. Yields of the sowing times were the following, in mean, for the six hybrids: 08. Apr. 10,34 t/ha, 25. Apr. 11,02 t/ha, 15. May 11,52 t/ha. There were no significant differences between yields in 1998. The seed moisture content of the six hybrids at harvest was 7% less for the early sowing time, than for the late sowing time. In 1998, the profits were greatest for the
early and traditional sowing times.
In 1999, the numbers of days from sowing to emergence were 18, 9 and 9 days, in the order of sowing times. Yields of the sowing times were the following, in mean, for the three hybrids: 13,25 t/ha, 12,51 t/ha and 12,34 t/ha, in the order of sowing times. The seed moisture content of maizes at harvest was 6% less with an early sowing time in the mean of all hybrids. In 1999, hybrid maizes gave big profits with early sowing times.
Summing up the results of the three years, we can conclude that we get a significant yield increase and reduced seed moisture content at harvest if we apply the early sowing time, which can considerably increase the efficiency of maize cultivation. -
The effect of NPK fertilization and the plant density on maize yield and bioethanol production
13-18Views:103For industrial (bioethanol) production of maize, a new production technology is needed. I tested and selected hybrids appropriate for this purpose and set up fertilization and plant density experiments. The experiment were set up on chernozem soil in 2008.
In bioethanol production, the selection of a high-yielding hybrid with high starch content, a slight reduction of N, increase of potassium, the application of the highest plant densities of the optimum interval, harvest at full maturity (when starch content is the highest compared to protein content) are of great importance. -
Effect of NPK fertilization on the yield and yield stability of different maize genotypes
101-104Views:138The yielding capacity and quality parameters of 11 maize hybrids were studied in 2011 on calcareous chernozem soil in a 25-year long-term fertilization experiment in the control (without fertilization), in the base treatment of N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 and in five treatments which were the multiplied doses of the base treatment. The N fertilizer was applied in the autumn and in the spring, while P and K fertilizers were applied in the autumn.The sowing time was 17–18 April, the time of harvest was 8 October. The 30-year average of precipitation (April–Sept) was 345.1 mm, the amount of precipitation did not differ greatly from that, however, its distribution was very unfavourable.
It was found that the largest yield increment (as compared to the control) was in the treatment N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 in the long-term experiment. The largest yields were obtained for the hybrids P9494, PR37N01 and PR35F38 (13.64–13.71 t ha-1). Due to the dry period at the end of the summer – beginning of autumn, the grain moisture content at harvest was favourably low, 12–18% depending on the treatment and the growing season.The N fertilization significantly increased the protein content of the kernel, but the starch content of the kernel decreased (significantly in several cases) with increasing fertilizer doses and yields as compared with the control.
The highest protein content was measured in hybrids GK Boglár and Szegedi 386. The oil content was above 4% for GK Boglár, but the two hybrids were not among the best yielding hybrids in spite of their good inner content. The starch content was around 75 % without fertilization, it decreased with fertilization.
For the tested hybrids, the fertilizer dose N 120 kg ha-1, P2O5 75 kg ha-1, K2O 90 kg ha-1 can be recommended with respect to efficacy and environmental considerations. -
Role of Sowing Time in Maize Production (Review)
36-39Views:79Many authors, both in Hungary and abroad, have reported on experiments carried out to determine the role of sowing time in maize, but the results are often contradictory. This is hardly surprising, since the maize plant exhibits enormous genetic variability and the hybrids created through selection and inbreeding may have very specific requirements as to sowing date. The year effect, too, often complicates the efforts of scientists to provide clear guidance to farmers on the optimal sowing date for each hybrid.
-
The effect of water supply and crop year on the yield potential of sweet maize (Zea mays L. convar. saccharata Koern.) hybrids with different genotypes
203-210Views:176The successfulness of crop production is significantly affected by not only the the average yields that provide cost effectiveness, but also the success of striving for yield safety, therefore, varieties and hybrids tolerant to environmental stress factors are worth being included into the sowing structure. Our aim was to further the decision making of producers in prepaering the right sowing structure by the evaluation of sweet maize hybrids’ tolerance to excess rainfall.
We performed our examinations in an extremely wet year (2010) on chernozem soil on three sweet maize hybrids (GSS 8529, GSS 1477, Overland) in 12 replications. Comparing the yields of 2010 with those that can be expected under optimal rainfall conditions, we showed that the examined hybrids react to the amount of rainfall higher than their needs with yield depression. The excess rainfall tolerance of the examined hybrids is different in the case of each hybrid. -
The impact of climatic factors on the relative chlorophyll content and yield of a maize hybrid in a long-term experiment
71-77Views:213The impact of the climatic factors of crop year on the relative chlorophyll content of maize was examined for three years. The examinations were carried out on the Látókép Experiment Site of the University of Debrecen on calcareous chernozem soil in a small-plot, non-irrigated long-term field experiment with strip plot design. In addition to a non-fertilised (control) treatment, nitrogen (N) fertiliser doses were applied as base and top dressing. The 60 and 120 kg N ha-1 base dressing doses were followed by two top dressing doses at the V6 and V12 phenophases.
Averaged over the different fertiliser treatments, SPAD readings increased in all three years as the growing season progressed. The highes SPAD value increase was observed in the average crop year (2017) at the V12 phenophase (11.8), which further increased at the R1 phenophas, by 3,7. No significant Spad value difference was observed between the average (2017) and the dry year (2018) at the V6 growth phase. However, in the wet crop year (2016), the V690 treatment provided the statistically highest relative chlorophyll content (46.8). At the V12 phenophase, the base dressing dose of 120 kg N ha-1+30 kg N ha-1 (V6150) showed to be successful in two years (2016 and 2018), while in 2017, the base dressing dose of A60 was successful. The impact of crop year on relative chlorophyll content can be clearly shown at the R1 growth stage. In all three years, the significantly highest relative chlorophyll content could be achieved at different nutrient levels: A60 in 2016, V6150 in 2017 and V690.
In a wet year (2016), higher yield could be achieved as a result of the 60 kg N ha-1 base dressing and 30 kg N ha-1 at the V6 growth stage (V690) as top dressing in comparison with 2017 and 2018, when higher fertiliser dose (120 kg N ha-1 base dressing and 30 kg N ha-1top dressing at the V6 growth stage) was needed to achieve a significant yield surplus.
Altogether, averaged over the different treatments, the highest yield (12.48 t ha-1) was observed in the wet year, when the relative chlorophyll content was also the highest (50.6).
-
Effect of cultivation factors on the yield and yield security of maize
263-265Views:132Cultivation factors have a significant effect on the yield and yield security of maize. Ensuring a suitable green crop is important. Tricultural crop rotation (pea–wheat–maize) in the average of 25 years provided a 2 t ha-1 higher yield compared to monocultural cultivation. A harmonious NPK nutriment supply determines yield and yield security, which can be especially realized by means of the application of precision cultivation technologies. Under average circumstances N 80 kg ha-1, P2O5 50 kg ha-1, K20 60 kg ha-1 active ingredient is the agro-ecological dosage of artificial fertilizer.
Plant density is a factor that determines yield. Optimal plant density – beside the genetic characteristics of the hybrid – is mostly influenced by the level of water and nutriment supply. -
Comparison of Variability among Irradiated and Control Inbred Maize Lines via Morphological Descriptions and Some Quantitative Features
70-73Views:67Knowledge of genetic diversity in breeding material is fundamental for hybrid selection programs and for germplasm preservation as well. Research has been done with nine irradiated (fast neutron) and four non-treated inbred lines. The aims of this study were (1) to investigate the degree of genetic variability detected with morphological description (based on CPVO TP/2/2) in these materials, (2) to compare the genetic changes among irradiated and non-irradiated maize inbred lines (based on some quantitative features). The irradiation did not change any of the characteristics clearly in positive or negative way, which can be related to the fact that the effect of induced mutation on genetic structure cannot be controlled. From the irradiated lines we have managed to select plants with earlier ripening times and better phenotypes. We could distinguish 3 main groups by the morphological features; these results match our expectations based on pedigree data. Markers distinguishable on the phenotypic level (e.g. antocyanin colouration, length of tassels) were significant in all lines.
-
Comparative analysis of soil analysing datas on different sempling-plots
85-90Views:70Hibrid maize is cultivated on larger plots, therefore the sown areas of hibrid maize are heterogeneous from a pedology aspect. Heterogenity causes problems during tasseling, chemical plant protection and harvest. The heterogenity of sown areas can be compensated by fertilization which is based on soil analysis. We carried out research into change of the soil on four soil types from 1987 to 2005.
There were no significant changes in pH, hydroiodic acidity, CaCO3-content, humus-content on meadow chernozem soil. We detected equalization of salin content in the examined soil layers. There were no significant changes in the measured values on chernozem meadow soil and solonetz meadow soil in 2005. We discoverd equalization of saline content on chernozem meadow soil, but the changes were not as obvious as the changes on meadow chernozem soil. We found salinization in the 30-60 cm soil layer on type meadow soil that may be due to water movement. -
Technological development of sustainable maize production and its effect on yield stability
379-388Views:173In 2015 and 2016, we examined the effect of NPK nutrients, sowing date and plant density on yield on typical meadow soil. The amount of precipitation was 282.0 mm in 2015 (January–September), 706.0 mm in 2016 and the 30-year averageis 445.8 mm.Agrotechnical factors:– Experiment a)5 Dow AgroSciences hybrid with three sowing dates and three plant densities– Experiment b)In 2015 eight, in 2016 ten hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons, with control (without fertilization), N80+PK and N160+PKtreatments, five plant densities (50–90 thousand) with 10 thousand plants difference between the different densities.
In a drought year, we reached the higher yield in the earlier sowing date and with the lower lower plant density of 70 thousand plants ha-1-. The maximum yield, depending on the agrotechnical factors, was 10–12 t ha-1 in 2015, while in 2016 it was 14–16 t ha-1. Yield stability can be increased using hybrid-specific cultivation techniques. -
Performance of agricultural factors on yield of sweet corn (Zea mays L. Saccharata ) - A review
143-156Views:65Sweet corn producers and industries require more reliable cultivars which could be accomplished by hybrid breeding. However, progressive phenological growth may be affected by different factors. In this paper, we analyze the key factors that determine the growth and yield of sweet corn. Environmental factors such as temperature and photoperiod were strong determinants of dates of flowering and harvest which are often crucial to yield in diverse climates and agricultural systems, besides the country's pedological conditions, especially soil fertility, affected phenological development. The effectiveness of fertilization in improving sweet corn growth performance was significantly influenced by the soil characteristics, the water supply, the genotype, and the agrotechnological factors. Therefore, genetic improvement of hybrids should be incorporated into the climate and soil elements to stabilize sweet corn yields in various agroecosystems. Decisions made in the sowing period are very significant, as up to 30% of the obtained yield may depend on making the proper choice. Deviation from the optimum date (either early or late sowing) may decrease yield. When deciding about the sowing date of maize, one needs to consider climate, soil quality, geographical location, temperature, weed infestation, sowing seed quality, and the ripening time of the hybrid to be produced.
-
Effect of Planting Time of Maize on Factors Influencing Yields in 2001-2002
112-116Views:82In this paper we analysed the results of maize planting time experiments by the Department of Crop Sciences and Applied Ecology of the University of Debrecen, Centre of Agricultural Sciences in 2001. We made the experiments at the experimental garden of DE ATC in Hajdúböszörmény.
We examined in 2001, 2002 ten hybrids with three planting times. The results were analysed by analysis of variance with two factors. In 2001 the yields were high, between 7.2-11.6 t/ha. The seed moisture contant of hybrids was 6-8% less after early planting than after late planting. The vegetation period of the hybrids became longer after early planting, which helped the drying-down of the hybrid and determined the seed moisture content at harvest to a great extent.
In 2002 the yields were high, between 4.02-10.47 t/ha. The seed moisture contant of hybrids was 5-14% less after early planting than after late planting.
On the basis of the above, variety specific technologies should be applied where the planting time is adapted to the hybrids. In accordance with the other cultivation factors. -
Evalution of energy for bioethanol production
77-80Views:121The objective of this study was the ethanol which classified as agro fuels. The aim of our research was the calculation of efficiency of bioethanol production, and evaluates the yield of maize hybrids grown for this purpose. We examined the energy demand of corn production per hectare in two vintages of 2009 and 2010. The focus of the experiment was placed in three different doze of fertilizer. Results show that the control corn plot used the least amount of non-renewable energy. Improving starch yield by adding fertilizer required additional nonrenewable energy inputs. So then the invested energy has a great impact on the efficiency.
-
Genetic progress in winter wheat quality and quantity parameters
71-75Views:152Wheat production is significant branch of Hungarian crop production (with about 1 million hectares of sowing area). Weather anomalies resulted by climate change have increased the importance of biological basis in wheat production. Yield quality and quantity parameters of three wheat genotypes sown on chernozem soil type after maize pre-crop were studied in a long-term field experiment. Yield amount of the studied genotypes varied between 2894 and 8074 kg ha-1 in 2017 and between 5795 and 9547 kg ha-1 in 2018 depending on the applied treatments. Based on our results it can be stated that in both studied crop years the highest yield increment was realized by the application of the nutrient supply level of N30+PK. As the result of the application of the optimum mineral fertilizer level – in contrast to the control – resulted in significant yield increment in both crop years. The results of the long-term field experiment prove that water utilization of the studied wheat varieties / hybrids was improved by the application of the optimal nutrient supply. Furthermore, the water utilization of the latest genotypes was more favorable by both the control and the optimum nutrient supply level treatments. Analyzing the quality parameters of winter wheat using the NIR method it has been stated that the quality results of the well-known genotype (GK Öthalom) were better than those of the new genotypes. A negative correlation between winter wheat quality and quantity parameters has also been confirmed. As the result of the mineral fertilizer application protein and gluten content of winter wheat increased to a significant extent.
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:120During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: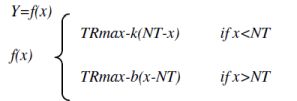
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Grain Moisture of Maize Hybrids in Different Maturity Groups at Various Harvesting Dates
24-25Views:86The experiments were designed to determine the extent to which late harvesting helped to achieve low grain moisture content. The grain moisture contents of 24 hybrids from each of four different maturity groups were recorded during the last decade of September and the first decade of November over a period of three years (1999-2001).
The data indicated that late harvesting led to a substantially smaller difference between the hybrids. While in late September the difference between the grain moisture content of the earliest (FAO 200) and latest (FAO 500) hybrids was 8.9%, this value dropped to 1.5% over the average of three years when measurements were made in early November. With the exception of the earliest group, the grain moisture content in all the maturity groups declined during October. The later the hybrid, the greater the decline.
This change in the grain moisture content during October exhibited a considerable year effect. When the weather in October was warm, with little rain, the decrease was greater, while in cool, wet years the grain moisture content declined to a lesser extent, or in some cases even increased.