Search
Search Results
-
Nutrient and water utilisation analyses of maize on chernozem soil in a long-term field experiment
77-82Views:407We have conducted our research at the Látókép Research Farm of the University of Debrecen RISF Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences during the cropyears of 2007, 2008 and 2009, on chernozem soil. In the case of crop rotation three models were set (mono-,bi- [wheat, maize] and triculture [pea, wheat, maize]). The five nutrient levels applied during the treatments were as follows: control [untreated], N60P45K45, N120P90K90, N180P135K135, N240P180K180. The conclusion of our results was the following: the crop rotation, the nutrient supply and the amount of precipitation all influenced the quantity of maize yield. As an effect of the increasing nutrient doses yield increase was experienced compared with the control treatments. In the average of the years the highest increase in yield excess/1 kg of NPK fertilizer was measured in the case of the monoculture (13 kg ha-1). As a consequence of is soil extorting effect the monoculture responded more intensively to the nutrient supplementation than the biculture or the triculture in the studied cropyears. In addition, we have observed that the three-year average yield amount per 1 mm precipitation was significantly influenced by the nutrient reserve of the soil. In the monoculture during the control treatment this value was 25 kg mm-1, the value measured in the case of the biculture turned out to be more favourable (42 kg mm-1).
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:328During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: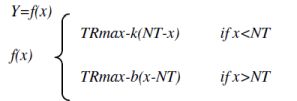
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Comparative analysis of maize hybrides grown for bioethanol production purposes
11-14Views:178The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of crop year on the main components of maize grown for bio-ethanol production yield, starch content and starch yield per hectare of maize hybrids were investigated in a droughty (2007) and in a favourable years with optimal weather conditions (2008, 2009). We measured very low starch yield (1.5 t ha-1) in the year with unfavourable precipitation supply (2007) together with higher starch content (73%). In the case of good precipitation supply we measured a much higher starch yield per hectare (7.7 t ha-1) with lower content (72.4%). In 2009 the starch content (74.5%) exceed the results of the two previous years, but on the other hand the average of starch yield was (4.9 t ha-1) which falls between the other two years values.
-
Influences of water deficiency on the productivity of young plants at different sites
371-378Views:232Water deficiency has become one of the most limiting factors of crop production in Hungary as the tendency in annual amounts of precipitation shows a decreasing tendency; therefore, it has become similar to those of Southern Europe. The most significant decrease in precipitation occurs typically during spring, approximately 20% of the data expressed in the averages of the last century. Studying the relationship between water deficiency as a stress factor and nutrient supply is important in order to improve the production efficiency of crops. Nowadays, this problem receives outstanding attention presented in numerous papers both in Hungary and globally, however, there are several questions yet to be answered. Our pot experiments were carried out under controlled greenhouse conditions in order to establish new data on these relationships. Experimental soils were typical for Western Transdanubia, taken from long-term field experiments representing four different site characteristics of the region. It was concluded from the results that drought periods during the early growth stages (i.e. 4–5 weeks after emergence) of plants may result in significant decreases in both dry matter production, nutrient concentrations, nutrient uptake and shoot:root ratios. Better nutrient supply, especially potassium, plays a significant role in reducing the negative effects of water deficiency.
-
The effect of NPK fertilization and the number of plants on the yield of maize hybrids with different genetic base in half-industrial experiment
103-108Views:375In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize.
The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2, this it was a halfindustrial experiment. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. Yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare at a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants/ha.
In Hajdúszoboszló, in 2015 the amount of rainfall from January to October was 340.3 mm, which was less than the average of 30 years by 105.5 mm. This year was not only draughty but it was also extremely hot, as the average temperature was higher by 1.7 °C than the average of 30 years. In the critical months of the growing season the distribution of precipitation was unfavourable for maize: in June the amount of rainfall was less by 31mm and in July by 42 mm than the average of many years.
Unfavourable effects of the weather of year 2015 were reflected also by our experimental data. The yield of hybrids without fertilization changed between 5.28–7.13 t ha-1 depending on the number of plants.
It can be associated also with the unfavourable crop year that the yield of the six tested hybrids is 6.33 t ha-1 in the average of the stand density of 60, 70 and 80 thousand plants per hectare without fertilization, while it is 7.14 t ha-1 with N80+PK fertilizer treatment. That increase in the yield is only 0.81 t ha-1, but it is significant. Due to the especially draughty weather the yield increasing effect of fertilizers was moderate. In the average of the hybrids and the number of plants, increasing the N80+PK treatment to N160+PK, the yield did not increase but decreased, which is explicable by the water scarcity in the period of flowering, fertilization and grain filling.
The agroecological optimum of fertilization was N 80, P2O5 60 and K2O 70 kg ha-1. Due to the intense water scarcity, increased fertilization caused decrease in the yield. As for the number of plants, 70 000 plants ha-1 proved to be the optimum, and the further increase of the number of plants caused decrease in the yield.
-
Relationship between the change of soil moisture content of different soil layers and maize yield
19-25Views:273The development of chernozem soil water management and its relationship with maize yields was studied in a 30-years long-term field experiment with different crop-rotation systems (mono-, bi- and triculture), in three crop years with different natural precipitation: a drought (2007), a wet (2008) and a dry (2009 one. The relevant soil layer was divided to three sub-layers: (0–60 cm, 61–120 cm, 121–200 cm) in which the development of soil moisture content was investigated during the whole vegetation. From the results it can be stated that change of the water stock of the upper soil layer (0–60 cm) was the most intensive. Both the direct effect of natural precipitation and irrigation could be observed in the most obvious way in it. Yield result of maize and the highest water supply deficit values in the vegetation were compared in our work too. According to the results it was revealed that among the three studied crop rotation systems it was the monoculture, the success of production of which depends the most of water supply. The most favourable crop rotation system was the triculture from both the aspect of the yield of produced crops and the favourable soil properties too.
-
Examination of the population density and sowing date of different maize genotypes in the Hajdúság region
111-115Views:267The experiment was carried out 6 km from Debrecen, next to the main road 47 on a homogeneous field on brown forest soil. Five corn hybrids were tested in the trial (DKC 4795, DKC 4995, KWS Kornelius, NK Cobalt, PR37 N01) at three different sowing times (early – 5th April, average – 21st April, late – 10th May). At each sowing time, three different plant densities were applied (modest – 58 500 plants ha-1, average –70 200 plants ha-1, high – 82 300 plants ha-1). The agrotechnics applied
in the experiment satisfied the requirements of modern corn cultivation.In the study, the best yield result was achieved with the early sowing time out of the three examined sowing times (11 315 kg ha-1), which was significantly different (LSD5%=495 kg) from that of the average sowing time (10 690 kg ha-1), however, there was no statistically justifiable difference between the yield results of the early and the late sowing times. There was a significant difference also between the average and late sowing time. Our results indicate that the different sowing times resulted in a different flowering times. Consequently, the stands of early and late sowing time reached this critical stadium of growth under proper climatic circumstances (precipitation: 39 mm and 136 mm, average temperature at flowering: 18.1 oC and 20.3 oC), while flowering in the case of the average sowing time of 21st April was in the first half of July and the average temperature at flowering was warmer (23.2 oC) with only 10 mm precipitation.
In the experiment, the plant density response was also examined. According to the measured data, four of the five hybrids responded badly to the increasing plant density. We found that the plant density of 58 500 plant ha-1 gave the largest yield results (DKC 4995 11 794 kg ha-1 – NK Cobalt 10 998 kg ha-1, average of five hybrids: 11 430 kg ha-1), while the lowest yields were obtained at the plant density of 82 300 plant ha-1 (KWS Kornelius 11 037 kg ha-1 – NK Cobalt 10 019 kg ha-1, average of five hybrids 10 720 kg ha-1). The difference between the two plant densities was significant (LSD5%=494 kg), however, the 70 200 plant ha-1 plant density did not show any statistical difference from neither the 58 500 ha-1 nor from the 82 300 plant ha-1 stands. When examining the data of the hybrids separately, we found that there was a significant difference between the average yield of the lowest and highest plant densities only in the case of three (DKC 4795, DKC 4995, NK
Cobalt) out of the five hybrids (DKC 4795: 11 757 kg ha-1 – 10 857 ha-1 where LSD5% =816 kg; DKC 4995: 11 794 kg ha-1 – 10 738 kg ha-1 where LSD5%=853kg; NK Cobalt: 10 998 kg ha-1 – 10 019 kg ha-1 where LSD5%=630 kg ha-1), while a significant difference between the second and third plant densities was observed only in one case (DKC 4995: 11 726 kg ha-1 – 10 738 ha-1 where LSD5%=853 kg). In all other cases, there was no statistical difference between the different
plant densities. -
The effect of climatic change on the rheological properties of winter wheat doughs
96-100Views:261In present paper we have examined the effect of climatic change on the extensigraph characteristics of wheat-flours. The baking quality
of winter wheat is largely determined by cultivar, but it can be influenced by weather conditions during growing period. Flours were from 5
cultivars grown at one location in three cropping years. We have found that the extensigraph properties of dough are affected by the weather
conditions, nevertheless, different cultivars distinctly react to the increase of temperature and decrease of precipitation. In generally, the
higher average day temperature and lower precipitation level is favourable to produce winter wheat flour with better quality -
The importance of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and its cultivation in Hungary: A review
71-75Views:99Climate change today is no longer a question for the future. Climate change impacts not only human populations but also plant species, which are increasingly exposed to its negative effects. The increasing number of days of drought, the lack of precipitation and its unfavorable distribution are observed each year, which require adaptation. Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) is a drought-tolerant species characterized by deep root system that enables it to withstand prolonged periods without precipitation. Additionally, it is a thermophilic crop and tolerates moderate increases in average temperature." There is no great tradition of its cultivation and use in Hungary, but it has been cultivated by the Iregszemcse Research Institute since the 1970s. In addition to the positive aspects of its cultivation, it also has good nutritional values, outperforming in some parameters the beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and peas (Pisum sativum L.) what are popular in Hungary. Its high protein and crude fibre content allows it to be used not only for human consumption but also for animal feed. The aim of this review is to describe the importance of chickpea and to identify the advantages and disadvantages of its cultivation.
-
Effect of NPK fertilization on the yield and yield stability of different maize genotypes
101-104Views:317The yielding capacity and quality parameters of 11 maize hybrids were studied in 2011 on calcareous chernozem soil in a 25-year long-term fertilization experiment in the control (without fertilization), in the base treatment of N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 and in five treatments which were the multiplied doses of the base treatment. The N fertilizer was applied in the autumn and in the spring, while P and K fertilizers were applied in the autumn.The sowing time was 17–18 April, the time of harvest was 8 October. The 30-year average of precipitation (April–Sept) was 345.1 mm, the amount of precipitation did not differ greatly from that, however, its distribution was very unfavourable.
It was found that the largest yield increment (as compared to the control) was in the treatment N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 in the long-term experiment. The largest yields were obtained for the hybrids P9494, PR37N01 and PR35F38 (13.64–13.71 t ha-1). Due to the dry period at the end of the summer – beginning of autumn, the grain moisture content at harvest was favourably low, 12–18% depending on the treatment and the growing season.The N fertilization significantly increased the protein content of the kernel, but the starch content of the kernel decreased (significantly in several cases) with increasing fertilizer doses and yields as compared with the control.
The highest protein content was measured in hybrids GK Boglár and Szegedi 386. The oil content was above 4% for GK Boglár, but the two hybrids were not among the best yielding hybrids in spite of their good inner content. The starch content was around 75 % without fertilization, it decreased with fertilization.
For the tested hybrids, the fertilizer dose N 120 kg ha-1, P2O5 75 kg ha-1, K2O 90 kg ha-1 can be recommended with respect to efficacy and environmental considerations. -
Correlation between the weather in 2017 and the productivity of maize
89-93Views:354In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In Hajdúszoboszló in 2017, up to October, 445.8 mm of rain fell, which is in line with the average values of 30 years, and is only 45.7 mm less than those. In 2017, the effect of increasing the plant number was slighter. Averaged over the observed fertilizer treatments and hybrids, the yield was 9.10 t ha-1 with 60 thousand plants ha-1, 9.11 t ha-1 with 70 thousand plants ha-1 and 9.12 t ha-1 with 80 thousand plants ha-1. Without fertilization, in most cases, increasing the plant number from 60 thousand plants ha-1 to 70-80 thousand plants ha-1 does not increased the yield but decreased it. With N80+PK treatment the yield changed between 8.90 and 11.27 t ha-1. The effect of increasing the plant number was just slightly observable and did not show a clear tendency. The effect of changing the plant number, even with the highest dosage of fertilizers, could not be detected adequately. In contrast with the plant number, the effect of the different fertilizer treatments was expressly traceable. Compared to the control treatment (treatment without fertilization), with N80+PK fertilizer dosage with 60 thousand plants ha-1 the yield increased by 3.36–4.99 t ha-1. The smallest demonstrable proof, i.e. the LSD5% was 0.22 t ha-1, which means that fertilization, in each case, significantly increased the yield. When analysing the effect of fertilization in the average of the hybrids and the different plant numbers, a yield of 5.61 t ha-1 could be detected, which value was 10.12 t ha-1 with N80+PK treatment and 11.61 t ha-1 with N160+PK treatment. Thus, it can be calculated that compared to the treatment without fertilization, the N80+PK treatment increased the yield by 4.51 t ha-1, while compared to the N80+PK treatment, the N160+PK treatment increased the yield by 1.49 t ha-1. In addition to agrotechnical factors, in maize production, the impact of the crop year is specifically of high importance.The average yield of hybrids (in the average of the different fertilizer treatments) was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 and 9.11 t ha-1 in 2017. When comparing the yield results against the precipitation data, it is clearly visible that the amount of rain fell in the January– October period is directly proportional to the average yield of maize. The effect of the crop year can be defined in a 5.05 t ha-1 difference in the yield. -
The significance of local meteorological stations in research planning
87-91Views:363The goal of research planning is to optimize human and material resources while maximizing efficiency. If there are databases that can be used as a substitute for own data collection, effective research can be facilitated by reallocating resources. In the case of environmental studies, the knowledge of the climatic conditions of the study period is known to be a key factor in research planning process.
In the present study, the data of our meteorological station in our research area (known as “Szamárháti Tanya”, Kesznyéten, Hungary) was compared with the measurements of meteorological stations operated by the competent water authority. Stations were taken into the study within a 10 and 20 km radius over a period of 21 months, to determine which provided more relevant data from the area.
During the evaluation of results, the relationship between the local and regional weather stations were determined, and deductions were made from the obtained results to support the decision which of the targeted investigations could be of greater benefit.
-
Economic questions of precision maize production on chernozem soil
293-296Views:228It is one of the main topical objective to establish the conditions of sustainable farming. The sustainable development in crop production also calls for the harmony of satisfying human needs and providing the protection of environmental and natural resources; therefore, the maximum consideratio of production site endowments, the common implementation of production needs and environmental protection aims, the minimum load on the environment and economicalness. Precision farmin encompasses the farming method which is adjusted to the given production site, the changing technology in a given plot, the integrated crop protection, cutting edge technologies, remote sensing, GIS, geostatistics, the change
of the mechanisation of crop production, and the application of information technology novelties in crop production. Modern technology increases efficiency and reduces costs. The efficiency of crop production increases by reducing losses and the farmer has access to a better decision support information technology system. In addition, we consider it necessary to examine the two currently most important economic issues: “is it worth it?” and “how much does it cost?”. During the analysis of agricultural technologies, we used the precision crop production experiment database of KITE Zrt. and the Institute for Land Utilisation, Regional Development and Technology of the Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences of the University of Debrecen.
During our analytical work, we examined three technological alternatives on two soil types (chernozem and meadow). The first technology is the currently used autumn ploughing cultivation. We extended our analyses to the economic evaluation of satellite navigationassisted ploughing and strip till systems which prefer moisture saving. On chernozem soil, of the satellite-based technological alternatives, the autumn ploughing cultivation provided higher income than strip till. In years with average precipitation supply, we recommend the precision autumn ploughing technological alternative on chernozem soils in the future. On meadow soil, the strip till cultivation technology has more favourable economical results than the autumn ploughing. On soils with high plasticity – considering the high time and energy demand of cultivation and the short amoung of time available for cultivation – we recommend to use strip till technologies. -
Test of the Plant Density Reaction of Genotype Sunflower Hybrids
113-119Views:446In order to produce sunflower in Hungary today it is important to develop hybrid-specific cropping technologies. The ever widening number of hybrids makes the constant examination of genotypes necessary from the viewpoint of genotype-environment interactions and critical elements. Plant density as a complex factor puts strain on the pathological features, yield and quality of sunflower. The experiment’s main objective is to find the optimal plant density for both the genotype and external factors.
As a result it can be stated that the optimal crop density is between 45,000-75,000 plant/ha. In 2001 the optimal density was 55,000 plant/ha. The Aréna PR and the Alexandra PR hybrids produced the greatest yields (3511 kgha-1; 3338 kgha-1). In the growing season of 2002, the yields were higher than in the previous year and the optimal crop density was 45,000-65,000 plant/ha. The best yields were produced by the Aréna PR and Alexandra PR hybrids in this year again (4102 kgha-1; 4267 kgha-1) and in 2003, 45,000-65,000 plant/ha proved to be the best crop density. The highest yield was produced by the Alexandra PR.
Analyzing the growing seasons of 2001, 2002 and 2003 it can be declared that as a result of dry climate of the three years yields were higher. It can be stated that the yield is decreased by higher than average of precipitation in the growing season. -
The role and impact of N-Lock (N-stabilizer) to the utilization of N in the main arable crops
51-55Views:327The nitrogen stabilizer called N-Lock can be used primarily with solid and liquid urea, UAN and other liquid nitrogen, slurry and manure. In corn it can be applied incorporated before sowing or with row-cultivator or applied with postemergent timing in tank-mix. In postemergent timing need precipitation for long effect. In oil seed rape and autumn cereals the N-Lock should be applied with liquid nitrogen in tank mix late winter or early spring (February-March). The dose rate is 2.5 l/ha. N-Lock increases the yield of maize, winter oil seed rape, winter wheat and winter barley 5-20 %. The yield increasing can be given the thousand grain weight. In case of high doses of nitrogen it can be observed higher yield. The quality parameter also improved, especially the oil content of winter oil seed rape and protein and gluten contents of winter wheat. The use of N-Lock increases the nitrogen retention of soil and reduces nitrate leaching towards the groundwater and the greenhouse effect gas emissions into the atmosphere. The degradation of the applied nitrogen is slowing down and the plant can uptake more nitrogen in long period. The effect of N-Lock the nitrogen is located in the upper soil layer of 0-30 cm and increasing the ammonium nitrogen form. The product can be mixed with herbicide products in main arable crops.
-
Impact of tillage systems on maize emergence
129-136Views:338In Europe, there has been a significant change in the way tillage is approached in recent years. This change is due to a growing awareness among farmers, politicians and society as a whole that soil is not a renewable resource in itself. From an agricultural point of view, the greatest impact on soil condition can be achieved through the use of the applied tillage systems. My research takes this approach as a basis when examining the different tillage systems and their impact on the environment. In this context, conventional and a variety of no-tillage systems are examined in this paper. As a next step, it is examined how the environmental conditions created by the different tillage systems influence the emergence of maize hybrids. The analyses are carried out in a multi-factorial, long-term tillage field experiment. The same batch of the same hybrid seed was sown in several crop years, and the effects of environmental conditions on the emergence process were examined. Environmental effects and emergence-related uptake were measured in the examined plots. Measurements of environmental effects included air temperature, precipitation, soil temperature measured at seeding depth, as well as % cover of stem residue on the surface in the treated plots. The first emergence time measurements of the sown crop in the plots of each treatment were compared and relationships between these factors were investigated.
-
The effect of hybrid, nutrient-supply and irrigation on the grain moisture content at harvest and the starch-content of maize (Zea mays L.)
89-95Views:198Maize is a worldwide dominant plant. According to nowadays plant production principles it is important to investigate and optimize the site-specific nutrient-supply and other production factors, such as hybrid and irrigation, in the case of this plant as well.
At the Research Institute of the University of Debrecen, Center of Agricultural Sciences and Engineering, at Látókép the effect of nutrient-supply and irrigation on the quantity and quality parameters of different hybrids were investigated in a small plot long-term field experiment. In this paper we introduce the results regarding the corn moisture-content and the starch content of the yield.
We have chosen three maize hybrids – that have been bread in Martonvásár – for our investigations. The effect of macronutrients is investigated in this experiment on five levels. The half of the experimental area can be irrigated during the vegetation period – whenever it is needed – by linear irrigation equipment, but on the other half only the water amount originating from the precipitation can be used by plants.
In the year 2008 the hybrid affected the grain moisture content at P=0.1% level, while nutrient-supply had an effect at P=10% significance level. We haven’t revealed either any effect of irrigation or of interrelationship between production factors. It can be stated that there are differences between the hybrids on each nutrient-supply and on both irrigation levels. The grain moisture content increased parallel to the longer vegetation
periods.
The starch content of maize is mostly affected by the hybrid,
so on P=0.1% significance level. Regarding our results, it can be
stated, that the starch content shows a decreasing tendency
parallel to the longer vegetation periods. -
Effect of genotypes and cropyear on thedifferent cultivation parameters of asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.)
31-34Views:275The experiments were performed in the Research Institute of Nyíregyháza Research Institutes and Study Farm, Centre for Agricultural Sciences University of Debrecen of 1500 m2 asparagus plantation. The asparagus was planted in 2011. We were determine the number of shoots, plant height and fold thicknes of asparagus hybrid. We can continuously monitored the growing parameters of asparagus. The harvest of asparagus was started in 2013, so we were able to measure to quantity. The weather was characterized by warm and matched precipitation in the growing season (April–July) in 2011 and 2012. Contrarily, the weather was very hot and dry after the late frost in 2013. The Vitalim produced the largest quantity, then the Cumulus and the end of Grolim hybrid. Number of shoot and plant height sequence is identical to the previous one. The Grolim asparagus hibrid has the largest basal diameter.
-
Drought-induced Losses in Fruit Orchards
37-40Views:176Scientists investigating the causes of the extremities of climate that have become quite frequent in the Carpathian Basin over the past few years are quite often in doubts as to whether increased atmospheric warming and the shortage of rainfall are to be seen as recurrent natural phenomena under our climate, or the first signs of global warming. Climate anomalies have, to a certain extent, always been common in the Carpathian Basin. However, statistical data of the past few decades indicate that the rise in temperature and the fall in precipitation have, by now, become a tendency, which requires further in-depth scientific research.
The series of articles to be published in continuation of this paper endeavors to synthesize the research results and many years of experiences, in order to give an analysis of
I. The economic effects and the symptoms of drought in tree cultures
II. The possibilities of reducing the adverse affects of drought -
The effect of and interaction between the biological bases and the agrotechnical factors on maize yield
83-87Views:252The effect of and interaction between the biological bases and the agrotechnical factors on maize yield In our research, we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons.We analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with a control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In 2015, the highest yield was produced by hybrid P9241 with N80+PK and 70 thousand plants per hectare. With the N160+PK fertilizer dosage, the same hybrid responded the best, followed by hybrids P9486 and DKC4717. Using the same fertilizer treatment, the 80 thousand plants per hectare population density resulted in decrease in the yield with most of the examined hybrids. In 2016, with the increase in the number of plants per hectare, even with non-fertilised treatment (control treatment), the yield could be increased in the case of each hybrid.Averaged over the different hybrids and fertilizer treatments, applying 80 thousand plants ha-1 instead of 60 thousand resulted in 1.0 ha-1 yield increase. In 2017, the number of plants had a slighter effect. With N160+PK treatment, in most cases no significant difference can be observed. The value of LSD5%: plant number: 0.20 t ha-1, hybrid: 0.28 t ha-1, interaction: 0.48 t ha-1. With N160+PK treatment, the hybrids produced yields between 10.07 and 12.45 t ha-1. When examining the three years in the average of the number of plants, with treatment without fertilisation, the average yield of hybrids reached 7.53 t ha-1. With N80+PK treatment, this value was 9.71 t ha-1 and with doubling the fertilizer dosage, this value increased to 10.42 t ha-1. No economic profit was gained as a result of applying double dosage of fertilizer; therefore, the N80+PK dosage can be considered ideal. -
Causes of floods and flood protection in Subcarpathia
72-75Views:169Subcarpathia is one of the richest regions in surface waters in the Ukraine. Due to its geographical, relief and climatic conditions, it belongs to the active precipitation zone, where great floods frequently occur. As a result of many years of observation, it can be concluded that the interactions of many natural factors can lead to various floods in the catchment area of the river Tisza. These are mostly hydro-meteorological factors, which can lead to great floods with the characteristics of the formed flow. Human activity also significantly influences the occurance of floods: clearing, which can accelerate the process of the runoff, ploughing in the catchment area, which can lead to erosion and the utilisation of areas endangered by floods for various economic sectors.
A series of questions arose in recent years regarding the formation of floods: what could be the causes of floods and what actions need to be made to prevent them. The evaluation of floods made us conclude that passive protection by using dams does not always ensure protection against floods as these were constructed in different times for different water levels. Many factors can affect the whole process which cannot be foreseen, therefore the development of new solutions and new technologies is necessary in flood protection. -
Agronomical and economic evaluation of various cultivation systems on meadow soil
103-106Views:186The requirements and objectives of cultivation are in constant change. There are different cultivation aims if the objective is soil protection, the prevention of its moisture content or on areas with different precipitation supply or production site endowments. Based on the experimental database of the Institute for Land Utilisation, Regional Development and Technology of the University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences and the KITE Plc., the various cultivation systems in Hajdú-Bihar country were examined with maize as indicator plant. The sample area can be found in the outskirts of Biharnagybajom on meadow soil. On the examined plot, spring strip basic cultivation, loosening and autumn ploughing were applied on 15-15-15 ha, respectively. At the time of taking undisturbed soil samples, soil conductivity measurements were also performed with a Penetronik penetrometer. Undisturbed soil samples were taken from each treatment before sowing (on 5th April 2012). The yield obtained in the strip cultivation treatment increased that of the ploughing and the loosening technology. The economic indexes are the most favourable in the strip cultivation.
-
Economic questions of maize production on different soil types
289-292Views:232The requirements and objective of cultivation are in constant change. For example, different cultivation systems are developed for the purpose of soil protection, the preservation of its moisture content and on soils with various precipitation supply or production site conditions. Traditionally, one of the most important cultivation aims is crop needs. Further cost saving in fertilisation and crop protection can only be achieved by reducing the quality and quantity of production or it cannot be achieved at all. Furthermore, the costs can be significantly reduced by means of the rationalisation of cultivation. Energy and working time demand can also be notably reduced if ploughing is left out from the conventional tillage method. The key requirement of economicalness is to perform the cultivation at the optimal date, moisture level and the lowest possible cost.
Within production costs, the cost of cultivation is between 3–17%, while they are between 8–36% within machinery costs. It is the vital condition the usability of each technological method to progressively reduce costs. Our evaluation work was carried out with the consideration of the yield data obtained from cooperating farms and the experiment database of the Institute for Land Utilisation, Regional Development and Technology of the Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences of the University of Debrecen. Three technological methods (ploughing, heavy cultivator and loosening tillage) were used on several soil types which differ from in terms of cultivability (chernozem, sandy and sandy clay soils) from the economic/economical aspect. We examined the sectoral cost/income relation of maize production as an indicator plant. The maize price during the analytical period was 45 thousand HUF per t. On chernozem soils, the production of maize can be carried out on high income level, while maize production on sandy soils has a huge risk factor. The role of cultivation is the highest on high plasicity soils, since they have a huge energy
demand and the there is a short amount of time available for each procedure in most cases. -
Effect of sowing technology on the yield and harvest grain moisture content of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids with different genotypes
17-22Views:242From the aspect of the efficiency of maize production harvest grain moisture content shall be considered beside the amount of harvested grain yield. Hybrids with different genotypes and vegetation period length lose their moisture content different that is affected by row spacing and plant density – among agrotechnical production factors – depending on the given crop year. In the present research work three crop years with different weather conditions were studied (2013, 2014, and 2015). The small-plot field experiment was set up at the Látókép Field Research Centre of the University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural Sciences with four replications on a chernozem soil type. The effect of three factors was analysed in the experiment on yield amount and its moisture content. Factors were row spacing (45 and 76 cm), plant density (50, 70 and 90 thousand plants ha-1), while hybrids were of very early (Sarolta: FAO 290), early (DKC 4014: FAO 320, P 9175: FAO 330, P 9494: FAO 390) and medium (SY Afinity: FAO 470) ripening.
In the crop year of 2013 the highest yield was produced – regarding the average of the hybrids – by the application of a row spacing of 45 cm (4.5%, 673 kg ha-1), however there was no significant difference between the yield of the populations of different row spacings. Significant difference (14.9%, 1751 kg ha-1; 6.3%, 583 kg ha-1) could be found in case of yield between different row spacing applications in 2014 and 2015. The effect of insufficiently distributed low amount of precipitation and lasting heat days in 2015 could be revealed in yield amounts and harvest grain yield moisture content results that were lower than in the previous years. In 2015 grain yield moisture content varied between 10.3 and 13.9% in case of a row spacing of 45 cm, while by 76 cm between 11.0 and 13.9%.
-
Production technology development of millet at different ecological conditions
63-67Views:358The millet is a very special plant with good adaptation that gives the possibility for the late sowing and secondary production. However the effects of late sowing modifies the efficiency of the agrotechnological elements. The exainations – focused on this aspect – was conducted in the DU RINY and DU RIK in small plots in four replications in 2014. Among the examined factors (sowing time, nutrient supply, growing area) sowing time had the largest effect. The effectiveness of the agrotechnological elements decreases under unfavourable circumstances caused by the late sowing.
The agrotechnical elements modifies the yields in the examined genotype. Sowing time had the biggest effect on the yields of millet. The genotype „Maxi” had the highest yield in the different treatment variations.
The yield differences were significant between the sowing time and plant density variations, but the nutrient supply had not significant effect (the rate of precipitation was unfavourable in 2014 season).