Search
Search Results
-
Examination of drought stress of two genotype maize hybrids with different fertilization
53-57Views:244In the growing season of 2019, we analysed stress resulting from climatic factors on maize hybrids of different genotypes, with the aim of gaining a better understanding of the physiological responses of each hybrid, which might support the elaboration of a cost-effective irrigation plan.
Our experiments were carried out at the Látókép Experimental Station of the University of Debrecen on calcareous chernozem soil in a small-plot long-term field trial with strip plot design. In the scope of the experiment, N-fertilizer doses were applied as basic fertilizer and top-dressing in addition to the non-fertilized (control) treatment. The 60 and 120 kg N/ha doses applied as basic fertilizers in the spring were followed by top-dressing in the V6 phenophase with a +30 kg N/ha dose. Measurements were carried out with the involvement of the Renfor early (FAO 320) and Fornad (FAO 420) late maturity hybrids-
The stomata of the plants became more and more closed with the progression of the phenological phases; their stomatal conductance decreased. However, the hybrids responded differently to environmental stress. In the case of the Renfor hybrid, the highest conductance (669 mmol/m2-s) was recorded in the V12 phenophase with the 150 kg N/ha treatment. The stomata were more open due to the high turgor pressure, allowing plants to evaporate properly. The plant was in its worst physiological condition on 2nd July, at the time of the appearance of the last leaf in the case of the 120 kg N dose (224 mmol/m2-s). The value measured in the V12 phenophase has already shown that the stomata were closing due to the self-regulating system of the plant. It would have been necessary to dispense irrigation water following the measurement. This confirms the finding that water stress can be prevented by measuring stomatal conductance.
In the case of the Fornad hybrid, stomatal conductance was the highest on 12th June (630 mmol/m2-s) in the 90 kg N/ha treatment and it was the lowest (183 mmol/m2-s) in VT (emergence of the last leaf) phenophase in the 60 kg N/ha treatment. In this case, the appropriate time for applying irrigation water would have been early July, when the conditions for the plants were still adequate. Subsequently, the stomata began to close due to a reduction of the water resources available to them.
There was a significant correlation between soil moisture and stomatal conductance, as well as between temperature and stomatal conductance.
-
Using research findings in precision maize production
227-231Views:461The effect of crop production factors on maize yield are examined on chernozem soil in a more than 30 year old long-term experiment on the Látókép Experiment Site of the Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences of the University of Debrecen. The aim of research is to evaluate the effect of fertilisation, cultivation, plant number, genorype and irrigation. The analysis of the data in the database of the examined period makes it possible to evaluate the effect of maize yield, as well as that of the crop production factors and the crop year, while the correlations and interactions between these factors were also examined. During the examination of the cultivation treatments, it was concluded that the highest yield was obtained as a result of autumn ploughing, but its effect largely differs in the irrigated and the nonirrigated treatments. Based on our examinations, strip cultivation should be applied periodically (e.g. strip – strip – ploughing – loosening) in areas with favourable soil conditions free from compacted layers.
In years with smaller, average precipitation supply or when the precipitation was higher than average, higher plant numbers were more favourable. Under drier conditions, but especially in several consecutively dry years, a lower plant number can be recommended which is not higher than 60 thousand per hectare. In the case of favourable water supply, 70-80 thousand plants per hectare can be used. The yield increasing effect of fertilisation was significant in the case of both non-irrigated and irrigated conditions, but it was much more moderate in the non-irrigated treatment. The extent of weed coverage was significantly affected by the previous crop. In the case of a favourable previous crop (wheat), the weed coverage was significantly lower than after an unfavourable previous crop (maize). In the case of the same previous crop (maize), the extent of weed coverage was mostly determined by the crop year and the extent of precipitation supply. Irrigation is not enough in itself, because if it was not accompanied by intensive nutrient management, yields started to decline.
The results of researhc, development and innovation contributed to the technological method which makes it possible to apply locally adjusted sowing seed, fertiliser and pesticide in a differentiated way, as well as to change the method of operations within the given plot. -
The effect of zinc fertilization on the yield and element content of ryegrass
27-31Views:201The effect of Zn fertilization on the yield and Zn, N, P, K, Mg and Mn content of ryegrass was studied in a greenhouse experiment for 8 chernozem soils with three replicates under uniform NPK supply and irrigation. The applied Zn rates were 0, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg Zn. Due to Zn doses the yield incrased significantly. Zn fertilization increased the plant Zn content and decreased the plant P and Mn content significantly. For N, K and Mg there was no significant effect.
-
The impact of production methods and row orientation on carrot quality in the case of various cultivars
65-69Views:246Carrot is a wellknown and favoured, really important vegetable. Carrot’s cultivation is important, although its growing field has been reduced in last few years. The suitable cultivar and landstructure are essential to produce good quality carrot. The ridge cultivation is widely spread on plasted soils. At this type of cultivation relationship between line orientations and carrot quality is less studied. That is the reason we tried to examine in our experiment the relationship between ridge highness and line orientation (N-S and E-W) and carrot’s morphological features at different genotipes. The experimental was settled in the Experimental Garden of the University of Debrecen on limy chernozem soil by plain, raised bed and ridge cultivation in 2013. In the experiment we examined four longgrowing cultivars (Danvers 126, Fertődi vörös, Rekord, Chantenay). The sowing was at 24th April. The harvest was at 15th October, 2013. In the multi factorial (type of cultivation, line orientation, cultivar) experimental we explained the effect of treatments on carrot root shoulder diameter and root weight.
In our experiment we stated that line orientation had no significant effect on shoulder diameter at different cultivations. The only exception is Fertődi vörös which has reached the biggest shoulder diameter (5 cm <) at N-S direction on raised bed. By examining the carrot rootweight we stated that they were higher in raised bed and ridge cultivation than in plain cultivation with the exception of one cultivar (Chantenay). This carrot had found ideal environment for growing between each cultivation conditions. That is why we can state that if you grow carrot on plasted soil and there is no possibility to make a ridge, use short, tapered and rounded ending root type for successful growing.
-
The effect of sowing date and plant density in three maize hybrids germination and growth dynamics
105-110Views:859The maize research was set up on chernozem soil at Látókép research area of the Centre for Agricultural Sciences University of Debrecen. We examined the following hybrids SY ARIOSO (FAO 300), P9486 (FAO360), DKC 4943 (FAO 410). The experience was set u pin three different plant density. These were 60, 76 and 90 thousand plant ha-1. The experience was set up in three different sawing date, early, average and late. The germination and growing dynamic measurements was measured in three hybrid, three sawing date, three plant density in four replication. well observed at the first sawing date (April 5) the soil was too cold therefore the germination was begins very slowly to be slowly increased. The second sowing time was the average (April 21) there the germination launch as soon as possible more rapid growth in the amount of heat. We experienced the most intense germination was in the case of the emergence late sowing date (May 5). Looking at the growth dynamics for the first two sawing date was side by side and almost equal to the maximum value. This is explained by the adaptive capacity of the maize to compensate for the sawing difference. For the third time, despite the delayed sawing the maize began to grow more dynamically than in previous sawing times due to the results of the initial good conditions it growth faster than halted in the second half of the season because of the high temperatures and lack of precipitation.
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:328During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: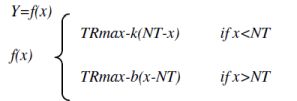
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Site and hybrid-specific agrotechnical models in sweet corn production
105-108Views:177The effect of three agrotechnical factors (sowing time, fertilization, plant density) and two genotypes on the crop yield of sweet corn was examined on chernozem soil in the Hajdúság region in two different crop years. Compared to the 30-year average, the climate was dry and warm in 2009 and humid in 2010. The experiments were conducted at the Látókép Research Site of the University of Debrecen. In the experiments we applied two sowing times (end of April, end of May), six fertilization levels (control, N30+PK, N60+PK, N90+PK, N120+PK, N150+PK) and two crop density levels (45 thousand ha-1, 65 thousand ha-1). The hybrids we used were Jumbo and Enterprise. As regards the requirements of sweet corn production, the crop year of 2009 was dry and warm. The effect of moisture deficiency was more adverse on the crop yields with the second sowing time. On the contrary, the other examined year (2010) was significantly humid; the precipitation was 184 mm above the 30-year average and the temperature was average.
In the dry and hot crop year, the best yields were obtained with the hybrid Jumbo (25677 kg-1) at 65 thousand ha-1 plant density level on the average of the fertilization levels. The crop yields of Enterprise were also the highest at high plant density level (24444 kg ha-1). With the second sowing time the highest yields were obtained at the higher plant density level (65 thousand ha-1) with both hybrids (Jumbo 18978 kg ha-1, Enterprise 18991 kg ha-1), which confirmed the good adaptation capability of these hybrids at high plant density level. In humid crop year with early sowing time the highest yielding hybrid was Enterprise (at 45 thousand ha-1 crop density level 20757 kg-1), at the same time, Jumbo was best yielding at the higher plant density level (18781 kg-1). With the second sowing time the highest crop yield was obtained with Enterprise again (20628 kg ha-1 at 65 thousand ha-1 plant density level). With this sowing time the average yields of Jumbo, was 18914 kg ha-1 respectively. We found that dry crop year and early sowing time provided the best conditions for sweet corn production; the highest yields were obtained under these circumstances, which might be the results of the outstanding water management of chernozem soils. -
Technological development of sustainable maize production
83-88Views:250In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize.
The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly eight ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2, this it was a half-industrial experiment. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. Yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare at a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants per ha.
In Hajdúszoboszló, in 2016 the amount of rainfall from January to October was 605 mm, which was more than the average of 30 years by 160 mm. The yield of hybrids without fertilization changed between 9.63–11.6 t ha-1 depending on the number of plants.
The six tested hybrids is 10.65 t ha-1 in the average of the stand density of 60, 70 and 80 thousand plants per hectare without fertilization, while it is 12.24 t ha-1 with N80+PK fertilizer treatment. That increase in the yield is 1.6 t ha-1, it is significant.
Da Sonka hybrid is sensitive to weather, it is able to produce 6 t ha-1 additional yield in case of favourable condition. However, it has a low stress tolerance. The most stable yields were observed at Kamaria and Pioneer hybrids. The effect of vintage is also an important factor on the yield. In average, the yield of maize was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, which was a drought year and 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 that was a favourable year. -
The effect of crop year and agrotechnical factors on the yield of various maturity groups of Limagrain maize hybirds
19-23Views:236The Limagrain maize hybrids in different maturity groups were examined at the Látókép Experimental Station of the Centre of Agricultural Sciences and Engineering, University of Debrecen on a calcareous chernozem soil with loam texture, between 2001 and 2007 in a multifactorial long-term field trial. Doses of fertilizers: 1 N:0.75 P2O5:0.88 K2O fixed proportion of NPK doses. The basic dose of nitrogen is 30 kg ha-1. The application of fertilization was 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 times more than the basic dose, beside of untreated control. The long-term field trial is performed in none irrigated and in irrigated version.
The goal of the study was to analyze the effect of precipitation (environment factor) in one hand, and to evaluate the effect of fertilization and irrigation (agrotechnical factors) on the yield of maize hybrids in different maturity groups in the other hand. At the same time I studied the effect of interaction of different factors on the yield of maize.Analysis the yield of Limagrain hybrids revealed: the years considerably affected the level of the yield. In dry years the yield was 1.351 t ha-1 less, than in rainy years. As the effect of fertilization the yield increased, the statistically proved biggest increment was at level of 90 kg N ha-1. Evaluating the maturity groups, FAO 300 hybrids reached higher level of yield.
In non irrigated conditions in the average of the seven years 60 kg N ha-1 was sufficient to reach the maximum yield. The efficiency of fertilization on yield in irrigated version increased, 120 kg N ha-1 assured the reliable level of yield.
Without irrigation in comparison to the results of FAO 200 group, with the growth of FAO numbers the yield is increasing in all cases. The most significant increase was at FAO 300 (3.562 t ha-1). With irrigation the greatest difference in yield was in FAO 400 (+2.720 t ha-1) compared to FAO 200. -
Baking quality of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the long-term experiments on chernozem soil
152-156Views:249Agriculture has traditionally an important role in Hungarian economy and rural development. About 75 % of Hungary’s total territory
is under agricultural land use. Because of ecological conditions and production traditions cereals (wheat, maize etc) have the greatest
importance in Hungarian crop production. In the 1980’s the country-average yields of wheat were about 5,0-5,5 t ha-1 („industrial-like”
crop production-model). In the 1990’s the yields of wheat dropped to 4,0 t ha-1 because of low input-using and wide application of the issues
of environmental protection and sustainability. Winter wheat production for quality has a decisive role in certain regions of Hungary
(eastern and middle-parts).
The quality of wheat is complex and different. Three major growing factor groups determine the quality of winter wheat: genotype,
agroecological conditions and agrotechnical factors. In wheat production for quality the selection of the variety is the most important
element. Our long-term experiments proved that the quality traits of a variety means the highest (maximum) limit of quality which could not
be exceeded in fact. During the vegetation period of wheat the different ecological and agrotechnical factors could help or on the contrary
could demage the quality parameters of wheat.
The agrotechnical factors determining the baking quality of wheat can be divided into two groups: the first group means the factors with
direct effects on quality (fertilization, irrigation, harvest); the second group contains the elements with indirect effects on quality (crop
rotation, tillage, planting, crop protection).
Appropriate fertilization could help to manifest the maximum of quality parameters of a wheat genotype and could reduce the qualityfluctuation
in unfavourable ecological and agrotechnical conditions. -
Effect of season and sowing time on the moisture loss dynamics and yield of maize
255-265Views:381The effect of sowing date on maize development and yield was studied in field experiments. The experiment was set up at the experimental garden of the University of Debrecen Centre of Agricultural Sciences Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Plant Sciences in 2005 and 2006 on calcareous chernozem soil. Six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and vegetation period were tested (Sze 269, DK 440, PR37D25, NK Cisko, Mv Maraton, PR34B97) at three different sowing dates.
2005 was a very wet year. The amount of precipitation in the vegetation period was about 150 mm higher than the average of 30 years. No significant differences were observed in temperature. However, the number of sunny hours was much lower during the summer than as usual. This had an influence on yields.
In 2006, there was no risk of inland water in spite of the large amount of precipitation at the beginning of the year. The amount of water available for plants was satisfactory during the season due to the favorable amount of precipitation. Therefore, plants suffered less from the heat in July. However, hail on 22 July caused significant damage. The number of sunny hours in the summer was high enough. The warm, dry autumn helped the water release of plants.
In 2005, the results of the third sowing date could not be evaluated due to the large number of missing plants. The yield of hybrids ranged between 12-14 t/ha for the first sowing date. For the second sowing date, yields ranged between wider boundaries. The hybrid PR37D25 has a very high yield in the case of the second sowing date, and its seed moisture content was favorably low. The yield of hybrid PR34B97 was the lowest at the later sowing date, the prime reason of this was damage caused by Diabrotica virgifera. The seed moisture content at harvest varied between 16-24% for the first sowing date. In the case of the second sowing date, higher values were measured. Hybrids Sze 269 and NK Cisko had favorable water release characteristics. The maximum value of leaf area index was the best in the case of the first sowing date (5-5.5 m2/m2).
In 2006, yields for the first sowing date ranged between 8-10 t/ha. At the second sowing date, more favorable results were obtained. The reason for this is probably that hail caused a higher damage in hybrids with the early sowing date. Plant stock with later sowing date could recover more successfully. Hybrid PR37D25 had very high yields for the second and third sowing dates. The high-yielding hybrid PR34B97 also had high yield, but this was accompanied by higher seed moisture content. Due to the warm, sunny autumn weather, the hybrids had good water-release dynamics and were harvested with a lower seed moisture content than in the previous year. For the first sowing date, the seed moisture content was around 13-14% except for hybrid PR34B97. For the second and third sowing dates, higher values were observed. Leaf area index was significantly reduced in August for all three hybrids due to the hail in July. For the first two sowing dates, the leaves of hybrid Sze 269 were the first to dry similarly to the previous year.
Year had a strong effect on the results in both years. -
Changes in the herbicide tolerance of maize genotypes in wet and dry years
124-127Views:204The tolerance of 15 inbred maize lines grown on chernozem soil with forest residues in Martonvásár was tested against herbicides applied post-emergence in two dry, warm years (2003 and 2011) and in two cool, wet years (2004 and 2010). The herbicides mesotrione + terbutylazine, nicosulfuron and dicamba were applied to maize inbred lines in the 7–8-leaf stage at the maximum dose authorised for practical use and at double this rate. The plants were scored for the intensity of visible phytotoxic symptoms 14 days after treatment.
The level of phytotoxicity observed in dry, warm years was 5.14%, averaged over the lines, herbicides and rates. The intensity of visible symptoms was almost 2.5 times as great in cool, wet years (12.76 %).
Averaged over the four years, the lines and the rates, the least damage was caused by dicamba (5.77 %), followed by mesotrione + terbutylazine (7.23 %). The most severe symptoms were induced by nicosulfuron (16.17 %). This could be attributed to the fact that some of the inbred lines were extremely sensitive to herbicides, especially those of the sulfonylurea type.
A difference of more than 1.5 times was observed between the two doses, but the correlation between the concentration and the severity of the visual symptoms was not strictly linear. Compared to the normal dose (100 %) the double rate resulted in a 162.5% increase in symptom severity. In most cases plants treated with the normal dose were symptom-free or only exhibited a low level of phytotoxicity. -
Study of some physiologic properties of different genotype sweet corn hybrids
105-110Views:198The effect of nutrient-supply (control, N120+PK) and two different genotypes on the physiologic properties of sweet corn has been investigated in the crop-year of 2011 on chernozem soil in the Hajdúság region. The experiments were carried out at the Experimental Station of the University of Debrecen in Debrecen-Látókép. The experiment was sewn in two different sowing times: the 21st April can be considered as an early, while the 19th May as a late sowing time. The two involved hybrids were Jumbo and Enterprise. The applied plant density was 65 000 plants per hectare.
Our aim with this experiment was to study the plant production, just as the main affecting factors of its development and dynamics, like nutrient-supply and genotypes. We aimed to study and analyse the relationships between these factors and plant production. In this study following parameters were measured and calculated: photosynthetic activity, chlorophyll-content (SPAD-value), leaf area index (LAI) and leaf area duration (LAD). Regarding the analysis of photosynthetic activity values no obvious relationship between the measured values and the applied hybrids, just as nutrient-supply has been revealed.
Analysing the SPAD-values it can be stated that the chlorophyll-content of the measured leaves showed an increasing tendency due to the nutrient-supply. The highest values have been measured in the intensive cob development phase of the early sowing time plots.
Regarding the LAI-values we have found significant differences between the fertilizer treatments in both sowing time treatments. In case of the leaf area duration values – that is derived from the LAI values – nutrient-supply has positively affected the duration of the assimilation area. -
Effect of Irrigation on the Yield and Quantity of Potato Varieties
53-61Views:255In Hungary, the growing area of potato area dropped dramatically in the last few decades. Additionally not only are we lagging behind Western European countries as regards yields, but the competitiveness of production is further decreased by the great alternation in yields from year to year, unpredictable market conditions, poor consumption habits and, often the lack of quality products.
The experiment was carried out at the experimental site of the University of Debrecen, Farm and Regional Research Institute, at Látókép. In our experiment, we examined the yield and some quality parameters of 9 medium-early varieties in large parcels. Of the examined varieties, 3 are of Dutch, and 6 are of Hungarian breeding.
The experiment was set up in 2003 and 2004, in two years of significantly different precipitation, on 50 m2 parcels on calcareous chernozem soil after winter wheat as a forecrop in both years. The 9 varieties were examined in 4 repetitions in randomized blocks, from which two repetitions were irrigated, and two were non-irrigated.
We examined the yields of the varieties, the distribution of tubers according to size and their percentages, and the changes in specific parameters of quality and inner content due to irrigation. We studied the dry matter content, the starch content, the underwater mass, the amount of reducing sugars, and the colour index of frying of the tubers.
In Summary, it can be stated that among the agrotechniques, year effect, variety and irrigation factors have considerable impact on potato yield quality and quantity. However the effect of irrigation depends on the crop year. In a draughty year, like in 2003, irrigation could increase the yield by 10%, while in a more favourable wet year, the improving effect of irrigation was low. -
Effect of the crop-year on plant protection feature of sunflower
71-75Views:255Our study focused on plant density reactions of sunflower hybrids on chernozem soil in years with different levels of available water (2011 and 2012). We studied factors (i.e.infections, yield) that are most affected by the amount of precipitation.
However the amount of precipitation varied in 2011 (average amount of precipitation) and 2012 (drought), Sclerotinia and Diaporthe infections were significant in both years. Diaporthe was stronger in 2011 while in 2012 Sclerotinia infections were greater than average. Higher plant density provided for a favorable microclimate for pathogens meaning that increased stock density enabled enhanced infections. Maximum levels of infections in both the cases of Diaporthe and Sclerotinia were measured at a plant density level of 65 000 plants ha-1.
2012 yields (control: between 2 289 and 3 261 kg ha-1, two-time treated: between 2 699 and 3 659 kg ha-1) were significantly lower compared to the results of 2011 (control: between 2 825 and 3 672 kg ha-1, two-time treated: between 3 059 and 4 059 kg ha-1). Fungicide treatments led to an increased yield in both years: 9.5% in 2011 and a notable, 15.1% growth in 2012. We applied regression analysis to calculate optimum plant density for the examined years and treatments. Based on the calculations we found that in the cases of both treatments optimum plant density was 53 000 plants ha-1, while in 2012 the optimum was higher due to lower level of infections: 56 000 plants ha-1 in the control stock and 64 000 plants ha-1 in the stock treated twice.
-
Role of some agrotechnical elements in the precision crop technology of cereals
241-244Views:271The crop models and precision technology have an important role in the development of winter wheat and maize agrotechnics, which crops have determinative role in Hungarian crop production. The effects of agrotechnical elements (crop rotation, fertilization, irrigation, crop protection, plant density) were studied in our longterm experiments on chernozem soil. Our scientific results proved that the high yields, and good yield stability were obtained in the input-intensive crop models. Maize had lower ecological adaptive capacity than winter wheat. The optimatization of agrotechnical elements reduces the harmful climatic effects so we can increase the yield and yield stability of cereals agro-ecosystems. The yields of wheat varied between 2 and 7 t ha-1 in extensive and 8 and 10 t ha-1 in intensive crop models and the yields of maize ranged between 2 and 11 t ha-1 and 10 and 15 t ha-1, respectively.
-
The impact of climatic factors on the relative chlorophyll content and yield of a maize hybrid in a long-term experiment
71-77Views:345The impact of the climatic factors of crop year on the relative chlorophyll content of maize was examined for three years. The examinations were carried out on the Látókép Experiment Site of the University of Debrecen on calcareous chernozem soil in a small-plot, non-irrigated long-term field experiment with strip plot design. In addition to a non-fertilised (control) treatment, nitrogen (N) fertiliser doses were applied as base and top dressing. The 60 and 120 kg N ha-1 base dressing doses were followed by two top dressing doses at the V6 and V12 phenophases.
Averaged over the different fertiliser treatments, SPAD readings increased in all three years as the growing season progressed. The highes SPAD value increase was observed in the average crop year (2017) at the V12 phenophase (11.8), which further increased at the R1 phenophas, by 3,7. No significant Spad value difference was observed between the average (2017) and the dry year (2018) at the V6 growth phase. However, in the wet crop year (2016), the V690 treatment provided the statistically highest relative chlorophyll content (46.8). At the V12 phenophase, the base dressing dose of 120 kg N ha-1+30 kg N ha-1 (V6150) showed to be successful in two years (2016 and 2018), while in 2017, the base dressing dose of A60 was successful. The impact of crop year on relative chlorophyll content can be clearly shown at the R1 growth stage. In all three years, the significantly highest relative chlorophyll content could be achieved at different nutrient levels: A60 in 2016, V6150 in 2017 and V690.
In a wet year (2016), higher yield could be achieved as a result of the 60 kg N ha-1 base dressing and 30 kg N ha-1 at the V6 growth stage (V690) as top dressing in comparison with 2017 and 2018, when higher fertiliser dose (120 kg N ha-1 base dressing and 30 kg N ha-1top dressing at the V6 growth stage) was needed to achieve a significant yield surplus.
Altogether, averaged over the different treatments, the highest yield (12.48 t ha-1) was observed in the wet year, when the relative chlorophyll content was also the highest (50.6).
-
The effect of agrotechnological factors and the cropping season on sweetcorn (Zea Mays L. convar. saccharata Koern.) production in a humid year
146-151Views:171We have examined the effect of three agrotechnological factors (sowing time, fertilization, crop density) and four genotypes on the yield
of sweetcorn on chernozem soil in the Hajdúság region in 2009. The experiment was set up at the Látókép Research Site of the University of
Debrecen. We have included two sowing times (27 April, 26 May), six nutrition levels (control, N30+PK, N60+PK, N90+PK, N120+PK,
N150+PK) and four genotypes (Jumbo, Enterprise, Prelude, Box-R) at two crop density levels (45 thousand ha-1).
In the humid cropyear of 2010 the amount of precipitation exceeded the 30-year average by 184 mm in the cropping season; the average
temperature exceeded the same by 0.8 C on the average of the examined months. The circumstances were most favourable for sweetcorn
production with the first sowing time, thus, this was when the yield of all hybrids was the highest.
With early sowing time, the highest yield (23437 kg ha-1 yield) was obtained with Enterprise at 45 thousand ha-1 crop density level at
N150 + PK nutrition level. The highest yield of the other three hybrids was 22253 kg ha-1 (Jumbo) 22286 kg ha-1 (Box-R) and 1873 kg ha-1
(Prelude). With the second sowing time, the highest yield was obtained with Enterprise again (22237 kg ha-1) at 65 thousand ha-1 crop
density level. With this sowing time the yield of Jumbo, Box-R and Prelude was 20888 kg ha-1, 17796 kg ha-1 and 17401 kg ha-1, respectively.
We found that the highest yield was obtained at the highest nutrition levels (N120 + PK, N150 +PK) with the first sowing time, while the same
was obtained at lower nutrition levels (N90 + PK, N120 + PK) with the second sowing time. -
Effect of NPK fertilization on the yield and yield stability of different maize genotypes
101-104Views:317The yielding capacity and quality parameters of 11 maize hybrids were studied in 2011 on calcareous chernozem soil in a 25-year long-term fertilization experiment in the control (without fertilization), in the base treatment of N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 and in five treatments which were the multiplied doses of the base treatment. The N fertilizer was applied in the autumn and in the spring, while P and K fertilizers were applied in the autumn.The sowing time was 17–18 April, the time of harvest was 8 October. The 30-year average of precipitation (April–Sept) was 345.1 mm, the amount of precipitation did not differ greatly from that, however, its distribution was very unfavourable.
It was found that the largest yield increment (as compared to the control) was in the treatment N 40 kg ha-1, P2O5 25 kg ha-1, K2O 30 kg ha-1 in the long-term experiment. The largest yields were obtained for the hybrids P9494, PR37N01 and PR35F38 (13.64–13.71 t ha-1). Due to the dry period at the end of the summer – beginning of autumn, the grain moisture content at harvest was favourably low, 12–18% depending on the treatment and the growing season.The N fertilization significantly increased the protein content of the kernel, but the starch content of the kernel decreased (significantly in several cases) with increasing fertilizer doses and yields as compared with the control.
The highest protein content was measured in hybrids GK Boglár and Szegedi 386. The oil content was above 4% for GK Boglár, but the two hybrids were not among the best yielding hybrids in spite of their good inner content. The starch content was around 75 % without fertilization, it decreased with fertilization.
For the tested hybrids, the fertilizer dose N 120 kg ha-1, P2O5 75 kg ha-1, K2O 90 kg ha-1 can be recommended with respect to efficacy and environmental considerations. -
The Effect of Year and Irrigation on the Yield Quantity and Quality of the Potato
12-16Views:286In Hungary, the growing area of potato area reduced dramatically in the last few decades, additionally we are lagging behind the Western European countries as regards yields and the competitiveness of production is further decreased by the great alternation in yields from year to year, the unpredictable market conditions, bad consumption habits and many times unfortunately the lack of quality products.
The ecological and climatic conditions of Hungary are not everywhere suitable for potato, in the area of Debrecen the amount of rainfall was lower, and the monthly average temperature was higher than the requirement of potato in its growing season in 2002 and 2003.
The experiment was carried out at the experimental site of the University of Debrecen, Farm and Regional Research Institute, at Látókép. In our experiment we examined the yield and some quality parameters of 8 and 9 medium-early varieties in large parcels in 2002 and 2003 respectively. Out of the examined varieties 3 are of Dutch, and 6 are of Hungarian breeding.
The experiment was set up on 49.5 m2 parcels on calcareous chernozem soil after winter wheat as a forecrop in both years. The 9 varieties were examined in 4 repetitions in randomized blocks, out of which two repetitions were irrigated, and two were non-irrigated.
We examined the yields of the varieties, the distribution of tubers according to size and their percentages, and the changes in specific parameters of quality and inner content due to irrigation. We studied the dry matter content, the starch content, the under-water mass, the amount of reducing sugars, the colour index of frying and the element contents of tubers.
Summing up, it can be stated that among the agrotechnical year effect, variety and irrigation factors have considerable impact on potato yield quality and quantity. On the basis of our results, it can be stated that in potato production variety should be chosen in accordance with the aim of production and technology should be adapted to that specific variety. -
The significance of biological bases in maize production
61-65Views:258The comparative trial has been set up in the Demonstration Garden of the Institute of Crop Sciences of the University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Studies, Faculty of Agricultural and Food Sciences and Environmental Management in 2012, with 24 hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing periods. The soil of the trial is lime-coated chernozem, with a humus layer of 50–70 cm.
The weather of the trial year was quite droughty; the monthly average temperature was 3–4 oC higher than the average of 30 years. High temperature, together with lack of precipitation occurred during the most sensitive phenophases of maize (flowering; fecundation, grain saturation).
The following characteristics have been observed: starting vigour, date of male and female flowering, plant and cob height, dry-down dynamics during maturation and the change of yield composing elements has also been quantified. The yield was recalculated to 14% moisture content grain yield after harvesting.
The beginning of the growing period was advantageous, therefore the analysed hybrids could grow a high (above 300 cm) and strong stem. The yield of the hybrids changed between 10.33 and 11.87 t ha-1, but as a result of the unfavourable climatic extremes, their genetic yield potential prevailed only at a rate of 30–40%. However, moisture content by the time of harvesting was good despite its early date (12th September); it remained under below 14% in most cases. Dry-down was measured on a weekly basis between 14th August and 5th September.
The analysis of the qualitative parameters of the maize hybrids (protein %, oil % and starch %) resulted in significant differences. The most significant difference has been observed in the case of protein content (LSD5%=2.01). Oil content was the most advantageous in the case of hybrids belonging to the mid-late growing group (FAO 400). The X9N655 and 36V74 hybrids had the highest oil content (around 4%), while hybrids P9915 and 37F73 had significantly lower oil content. Starch content was above 70% in the case of every hybrid.
Hybrid selection is highly important in terms of yield and yield security of maize, as well as the application of modern biological fundamentals and hybrid specific technology for the improvement of the level of cultivation technology.
-
Evaluate the nutritional reaction at winter wheat after different forecrops
77-80Views:212Our field researches took place on the Látókép test farm of Agricultural Science Centre of University of Debrecen, Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences, in long-term experiment, on calcareous chernozem soil, in growing season of 2014/2015. In our experiment we examined the fertilizer reaction and the yield of different winter wheat genotypes (GK Öthalom, GK Csillag, Mv Csárdás, Mv Toldi) with grain maize and sweetcorn forecrops. According to our results, the sweetcorn forecrop strongly affected the yield. In the average of the fertilizer treatments and the varieties, after sweetcorn forecrop 6.9 t ha-1, after grain maize forecrop 5.4 t ha-1 average yield was gained. According to our data, the fertilizer reactions of the varieties were significantly different.
-
Examining reaction of sunflower genotypes on planting time on chernozem soil
93-99Views:204We studied the effect of planting time on plant pathological factors, leaf area index and yield production by applying various fungicid treatments on two different sunflower genotypes in 2013.
By delaying planting time, both the extent of Diaporthe, Alternaria and Phoma infections decreased. The differences between the volume of infections were significant in the case of the early and late sowing time results. The application of fungicide treatments induced a notable decrease in the extent of infections for all three pathogens examined. The LAI-values varied between 0.3 and 5.6 m2/m2 in 2013 depending on the hybrid, sowing time and treatment. Stocks planted at distinct times reached maximum leaf coverage at different times. The planting time and the fungicide treatment had a significant effect on the formation of the leaf area. In the case of average and late planting times, fungicide treatments elongated the preservation of the green leaf area.
With respect to the yield amount, average planting time (27 April, 2013) turned out to be optimal in 2013 (control – NK Ferti: 4.621 kg ha-1, PR64H42: 4.196 kg ha-1; double-treated: NK Ferti: 5.282 kg ha-1, PR64H42: 5.090 kg ha-1). Fungicide treatments resulted in significant yield growth in all cases during our research.
We applied Person correlation analysis to evaluate the hybrids’ sensibility to infections and our results varied in the case of Diaporthe and Phoma (r=-0.343*, -0.379**). Infections of the three pathogens were significantly reduced by delaying the planting time and applying fungicides. Late sown stocks preserved the green leaf area for a longer period. Besides, the application of the fungicide treatment and the hybrid itself also led to the preservation of the green leaf area. However, pathogens examined notably decreased the leaf area by the end of the growing year. The fungicide treatment had a remarkable effect on yield growth (r=0.603**). Furthermore, the presence of higher LAI-values in the period prior to August also induced higher yields.
-
Effects of the cropyear and the agronomical factors on agronomical elements of different sweet corn (Zea Mays L. convar. saccharata Koern.) genotypes in long-term experiment
105-110Views:215In the crop season of 2010 (rainy year), we studied the effect of three agrotechnical factors (sowing time, fertilization, plant density) and four different genotypes on the agronomical characteristics of sweet corn on chernozem soil in the Hajdúság. The experiments were carried out at the Látókép Experimental Farm of the University of Debrecen. In the experiment, two sowing dates (27 April, 26 May), six fertilization levels (control, N30+PK, N60+PK, N90+PK, N120+PK, N150+PK) and four genotypes (Jumbo, Enterprise, Prelude, Box-R) were used at two plant densities (45 thousand plants ha-1, 65 thousand plants ha-1). The amount of precipitation in the season of 2010 was 184 mm higher, while the average temperature was 0.8 oC higher in the studied months than the average of 30 years. Weather was more favourable for sweet maize at the first sowing date, if we consider the yields, however, if we evaluate the agronomical data and yield elements (number of cobs, cob length and diameter, the number of kernel rows, the number of kernels per row) it can be stated that the size of the fertile cobs was greater at the second sowing date due to the lower number of cobs. The largest number of fertile cobs was harvested in the case of the hybrid Enterprise (72367.9 ha-1) in the higher plant density treatment (65 thousand ha-1) at the fertilization level of N120+PK when the first sowing date was applied. The largest cobs were harvested from the hybrid Box-R (cob weight with husks: 516.7 g, number of kernels in one row: 45.7) at the lower plant density (45 thousand plants ha-1) in the second sowing date treatment. Cob diameter and the number of kernel rows were the highest for the hybrid Prelude.
-
Correlation between the weather in 2017 and the productivity of maize
89-93Views:354In our research we examined the effect of the hybrid, the nutrient supply, the number of plants and the abiotic factors (temperature, amount of precipitation) on the yield, crop quality and yield stability of maize. We devoted special attention to the natural nutrient utilization ability and fertilizer reaction of maize. The experiment took place in Hajdúszoboszló on chernozem soil, on a nearly 8 ha field. The size of one plot was 206 m2; therefore, this experiment was half-industrial. We tested six hybrids with different genetic characteristics and growing seasons. I analysed the correlation between the nutrient supply and the yield of maize hybrids with control treatment (treatment without fertilization) and with N 80, P2O5 60, K2O 70 kg ha-1 and N 160, P2O5 120, K2O 140 kg ha-1 fertilizer treatments. The yield increasing effect of the fertilizer also depended on the number of plants per hectare to a great extent. The number of plants of the six tested hybrids was 60, 70, and 80 thousand plants ha-1.In Hajdúszoboszló in 2017, up to October, 445.8 mm of rain fell, which is in line with the average values of 30 years, and is only 45.7 mm less than those. In 2017, the effect of increasing the plant number was slighter. Averaged over the observed fertilizer treatments and hybrids, the yield was 9.10 t ha-1 with 60 thousand plants ha-1, 9.11 t ha-1 with 70 thousand plants ha-1 and 9.12 t ha-1 with 80 thousand plants ha-1. Without fertilization, in most cases, increasing the plant number from 60 thousand plants ha-1 to 70-80 thousand plants ha-1 does not increased the yield but decreased it. With N80+PK treatment the yield changed between 8.90 and 11.27 t ha-1. The effect of increasing the plant number was just slightly observable and did not show a clear tendency. The effect of changing the plant number, even with the highest dosage of fertilizers, could not be detected adequately. In contrast with the plant number, the effect of the different fertilizer treatments was expressly traceable. Compared to the control treatment (treatment without fertilization), with N80+PK fertilizer dosage with 60 thousand plants ha-1 the yield increased by 3.36–4.99 t ha-1. The smallest demonstrable proof, i.e. the LSD5% was 0.22 t ha-1, which means that fertilization, in each case, significantly increased the yield. When analysing the effect of fertilization in the average of the hybrids and the different plant numbers, a yield of 5.61 t ha-1 could be detected, which value was 10.12 t ha-1 with N80+PK treatment and 11.61 t ha-1 with N160+PK treatment. Thus, it can be calculated that compared to the treatment without fertilization, the N80+PK treatment increased the yield by 4.51 t ha-1, while compared to the N80+PK treatment, the N160+PK treatment increased the yield by 1.49 t ha-1. In addition to agrotechnical factors, in maize production, the impact of the crop year is specifically of high importance.The average yield of hybrids (in the average of the different fertilizer treatments) was 6.81 t ha-1 in 2015, 11.86 t ha-1 in 2016 and 9.11 t ha-1 in 2017. When comparing the yield results against the precipitation data, it is clearly visible that the amount of rain fell in the January– October period is directly proportional to the average yield of maize. The effect of the crop year can be defined in a 5.05 t ha-1 difference in the yield.