Search
Search Results
-
The scientific background of competitive maize production
33-46Views:274The effect and interaction of crop production factors on maize yield has been examined for nearly 40 years at the Látókép Experiment Site of the University of Debrecen in a long-term field experiment that is unique and acknowledged in Europe. The research aim is to evaluate the effect of fertilisation, tillage, genotype, sowing, plant density, crop protection and irrigation. The analysis of the database of the examined period makes it possible to evaluate maize yield, as well as the effect of crop production factors and crop year, as well as the interaction between these factors.
Based on the different tillage methods, it can be concluded that autumn ploughing provides the highest yield, but its effect significantly differed in irrigated and non-irrigated treatments. The periodical application of strip tillage is justified in areas with favourable soil conditions and free from compated layers (e.g. strip – strip – ploughing – loosening). Under conditions prone to drought, but especially in several consecutive years, a plant density of 70–80 thousand crops per hectare should be used in the case of favourable precipitation supply, but 60 thousand crops per hectare should not be exceeded in dry crop years. The yield increasing effect of fertilisation is significant both under non-irrigated and irrigated conditions, but it is much more moderate in the non-irrigated treatment.
Selecting the optimum sowing date is of key importance from the aspect of maize yield, especially in dry crop years. Irrigation is not enough in itself without intensive nutrient management, since it may lead to yield decrease.
The results of research, development and innovation, which are based on the performed long-term field experiment, contribute to the production technological methods which provide an opportunity to use sowing seeds, fertilisers and pesticides in a regionally tailored and differentiated way, adapted to the specific needs of the given plot, as well as to plan each operation and to implement precision maize production.
-
Economic questions of maize production on different soil types
289-292Views:103The requirements and objective of cultivation are in constant change. For example, different cultivation systems are developed for the purpose of soil protection, the preservation of its moisture content and on soils with various precipitation supply or production site conditions. Traditionally, one of the most important cultivation aims is crop needs. Further cost saving in fertilisation and crop protection can only be achieved by reducing the quality and quantity of production or it cannot be achieved at all. Furthermore, the costs can be significantly reduced by means of the rationalisation of cultivation. Energy and working time demand can also be notably reduced if ploughing is left out from the conventional tillage method. The key requirement of economicalness is to perform the cultivation at the optimal date, moisture level and the lowest possible cost.
Within production costs, the cost of cultivation is between 3–17%, while they are between 8–36% within machinery costs. It is the vital condition the usability of each technological method to progressively reduce costs. Our evaluation work was carried out with the consideration of the yield data obtained from cooperating farms and the experiment database of the Institute for Land Utilisation, Regional Development and Technology of the Centre for Agricultural and Applied Economic Sciences of the University of Debrecen. Three technological methods (ploughing, heavy cultivator and loosening tillage) were used on several soil types which differ from in terms of cultivability (chernozem, sandy and sandy clay soils) from the economic/economical aspect. We examined the sectoral cost/income relation of maize production as an indicator plant. The maize price during the analytical period was 45 thousand HUF per t. On chernozem soils, the production of maize can be carried out on high income level, while maize production on sandy soils has a huge risk factor. The role of cultivation is the highest on high plasicity soils, since they have a huge energy
demand and the there is a short amount of time available for each procedure in most cases. -
The Effect of Tillage Treatments on Soil Temperature at Planting and on Corn (Zea mays L.) Yield
40-44Views:92The effect of soil temperature was evaluated on the yield of the Occitan corn hybrid at a depth of 5 cm. We examined this effect on the time required from planting to emergence for three average durations: five, ten and fifteen days, all calculated from the day of planting. Winter plowing (27 cm), spring plowing (23 cm), disc-till (12 cm) treatments and 120 kg N per hectare fertilizer were applied. As a result of our analysis, we determined the post planting optimum soil temperatures for various time periods. The average soil temperature for a time period of 15 days post planting is the most usable for determining actual yields, followed by ten days, with five days proved to be the least usable (winter plow R2 = 0.86, spring plow R2 = 0.87, disc-till R2 = 0.64).
-
Agricultural relations of the increasing carbon dioxide emissions
197-201Views:184Emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) have deserved more and more attention of humanity since decades, but inspite of theme asures already taken there are no substantial results. CO2 is a very important chemical, one of the greenhouse gases, which on the one hand offsets the cooling of the Earth, but on the other hand the too high CO2 emission leads to the global warming. The emission from the soil contributes substantially to the global cycle. This type of emission is influenced by the soil moisture, temperature, the soil quality and the cultivation. Through our measurements we have studied the relationships between the type of cultivation and the emissions of carbon dioxide.
-
The possibilities and limitations of organic fruit production
41-45Views:68In this review, direct and indirect technological elements of organic production are discussed. Today, there is a growing interest in production prepared without chemicals. We discuss the following issues: site selection, soil, rootstock and cultivar requirements, plant material, planting distances, crown formation, phytotechical operation, irrigation, soil tillage, soil covering and muchning, nutrition supply. Separate section deals with methods of plant protection.
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:112During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: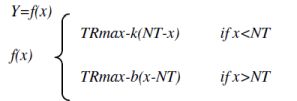
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Complex evaluation of agrotechnical factors in rape seed
59-63Views:95A polifactorial field trial with rape was carried out in the crop-years of 2007/2008 and 2008/2009 at the Látókép Research Centre of University of Debrecen, 15 km away from Debrecen. The soil type of the research area was a calcaric chernozem, with a levelled and homogeneous surface. Our investigations on the dynamics of lodging proved that rape can easily be lodged under unfavourable weather conditions, which results in a significant crop failure: In crop-year 2009 yields were 1.0-1.5 t ha-1 higher than in 2008, when the weather conditions were more unfavourable. In both crop-years the influence of sowing time on the crop yield of rape was examined in three soil cultivation systems, with ploughing, loosening or disking. Different sowing time influenced the yield of rape in both crop-years significantly. In the crop-year of 2007/2008 – due to mild winter – we got the highest yield in the first sowing time (at the end of August) with loosening (3930 kg ha-1) and disking (3727 kg ha-1), while in case of ploughing we experienced the highest yield (3770 kg ha-1) in the second sowing time. There were no significant differences between the first and second sowing time (the end of August and the beginning of September), and in the third sowing time (end of September) also a moderate crop failure (-6.7%) cold be obtained, due to the favourable weather in winter and the water supply of the crop-year 2007/2008. In 2008/2009 all the three cultivation systems showed the best yield-results in the second sowing time (ploughing: 4886 kg ha-1, loosening: 5186 kg ha-1, disking: 5090 kg ha-1), and the first sowing time hardly differed from this (-4.1%), while the late September sowing time resulted in a significant crop failure of -11.1%.
-
Weed control with herbicide incorporation in sunflower
73-76Views:151During the last decade certificate registration of 13 active ingedients were removed by European Union from sunflower herbicide market, including the basis for the incorporating technology, the trifluralin active ingredient as well. Its relative, the benfluralin active ingredient, which include the Balan 600 WDG herbicide product in sunflower, will be sold again from 2015 spring in Hungarian pesticide market. It has a broad-spectrum and lond residue besides it has very high level selectivity on sunflower. It has very good effect against annual monocotweeds such as common barnyadgrass, foxtail species, large crabgrass and wild proso millet, dicotyledonous weeds such as common lambsquarters,and redroot pigweed. It has significant side-effect against common ragweed, black nightshade, wild buckweed and prostrate knotweed. The long effect residue provide the weed-free til harvest. Benfluralin is totally selective on sunflower, as no colouring, any deformation or growth inhibition was not observed during the entire growing season. It should be sprayed 3-4 days before sowing within 1 hour and to be incorporated into the soil in 4-6 cm depth with tillage equipment. It can be used in tank mix with fluorochloridon in incorporated technology against annual dicotyledonous weeds. After the Balan incorporation can be used postemergence timing imazamox and tribenuron-metil active substances against hard kill and deeply germinating weeds. The products can not be used in tank mix with bacterial products.
-
Baking quality of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the long-term experiments on chernozem soil
152-156Views:69Agriculture has traditionally an important role in Hungarian economy and rural development. About 75 % of Hungary’s total territory
is under agricultural land use. Because of ecological conditions and production traditions cereals (wheat, maize etc) have the greatest
importance in Hungarian crop production. In the 1980’s the country-average yields of wheat were about 5,0-5,5 t ha-1 („industrial-like”
crop production-model). In the 1990’s the yields of wheat dropped to 4,0 t ha-1 because of low input-using and wide application of the issues
of environmental protection and sustainability. Winter wheat production for quality has a decisive role in certain regions of Hungary
(eastern and middle-parts).
The quality of wheat is complex and different. Three major growing factor groups determine the quality of winter wheat: genotype,
agroecological conditions and agrotechnical factors. In wheat production for quality the selection of the variety is the most important
element. Our long-term experiments proved that the quality traits of a variety means the highest (maximum) limit of quality which could not
be exceeded in fact. During the vegetation period of wheat the different ecological and agrotechnical factors could help or on the contrary
could demage the quality parameters of wheat.
The agrotechnical factors determining the baking quality of wheat can be divided into two groups: the first group means the factors with
direct effects on quality (fertilization, irrigation, harvest); the second group contains the elements with indirect effects on quality (crop
rotation, tillage, planting, crop protection).
Appropriate fertilization could help to manifest the maximum of quality parameters of a wheat genotype and could reduce the qualityfluctuation
in unfavourable ecological and agrotechnical conditions.