Search
Search Results
-
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:366During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: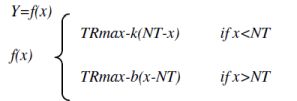
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
An Applicable Method for Elaborating Agricultural Logistics Trends
66-69Views:206Hungarian scientific practice focuses mainly on statistical methods to elaborate sector-specific trends. This paper aims to offer another alternative. The author’s view is that in rapidly and significantly changing markets, data extrapolation is not necessarily the ideal way to forecast certain trends of the sector. Agricultural Supply Chains have been restructured lately. There are remarkable developments in fields such as: warehousing systems, telematic systems, transportation. This is one of the reasons several drivers may alter the trends determined previously by statistical professionals. AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process) synthesizes expert opinions concerning the future, so it is a decision-supporting method and therefore more flexible to the changes of the sector. The author introduces the application of the AHP for Agricultural Logistics Trends.
-
Activity of some enzymes, participating in nitrogen compounds transformation in chernozem, polluted by fluorine compounds
99-104Views:211Contamination of chernozem by fluorine compounds variously affects those enzymes (urease, asparaginase, glutaminase, arginase, amidase), which takes part in the metabolism of nitrogen-bearing organic compounds. In broken soils the inhibited desaminisations is stronger, than enzymatic hydrolysis of asparagine and arginine. The features of seasonal dynamics of change activity of urease and correlation dependence of its activity from some physical and chemical soils properties are described. These tendencies well comport with the results of model experiments. At minimum HF influence there is inhibition of processes of monohydrocarboxylic acids desaminisation, hydrolytic breaking up of arginine and glutamine. By a side with this there is activating of urea and asparagine breaking up processes on the initial stages of toxicant influence. The study of kinetics of process of urea enzymatic hydrolysis in chernozem at the different level of HF influence showed changes of initial and maximal velocity of enzymatic reaction, and also Michaelis-Menten constant.
-
The Development of a Plot Fertilizer and Distributor, Analyses of How it Works
35-38Views:182stribution of the different types of fertilizers is essential. In my study, I recommend a solution for the mechanization of fertilizer distribution on probe parcels. I have designed and constructed a new plot fertilizer distributor. This machine of moderate price can be controlled easily; it provides accurate distribution and versatility. In my paper I give an outline of its basic principles of operation.
The spreading pattern of the complete plot fertilizer distributor was investigated on the top of a test-desk. I constructed a test-desk, which has 16 collecting trays in transversal direction and 1o collecting trays in longitudinal direction. I developed a new method for data interpretation. A map of distribution was designed to process the data of the measured 16o trays. In the distributor, a map precisely traced the pattern of granule distribution and the amount of fertilizer as well. After this, I defined the transversal and longitudinal coefficient of variations for spreading. On the basis of my investigations I can conclude that the plot fertilizer distributor has excellent, even spreading (longitudinal and transversal) patterns. -
The fishfauna of the Crişul Repede river and its threatening major factors
13-18Views:201The Crişul Repede River is belonging at Cris (Körös) Rivers system which is a tributary on the left shore of Tisa River. In the last decades the fishfaunaofthenaturalwatershasundergoingadeclineinthespeciesnumber.Theothersuccessiveprocessisthefishspeciesreplacement due by the immigration of some exotically fishesandtheretirementofsomeofthenativespecies.
The Crişul Repede fishfaunahasregisteredadeclinecausedmainlybytheriverdamming,waterpollutionandeutrophisation.Ondespite of that negative factors the fishesfromtheupperriverwasmaintainlessaffectedunliketotheotherrivers.Thereaftertheeconomical transition and the industries reorganization process were redounded to diminishing the impact of these harmful factors. The former studies about the Cris fishfaunacitedanumberof48nativespeciesand12exoticones.Duringtheresearchtripscarriedoutsince10yearsago (beginning in 1995) was identifiedanumberof40fishspeciesandthepresenceoftheother8 speciesarestilluncertain.Thesturgeonspecies Acipenser ruthenus and the migratory fishAnguillaanguillahaveascarcepresenceandtheycannotbefoundinthelastdecade.A number of 5 exotically fishesarebehavedasremarkableintrudersinnaturalwaters:Pseudorasboraparva,Carassiusauratusgibelio,Ictalurus nebulosus, Ictalurus melas, and Lepomis gibbosus. Some of the exotically fishesalreadyrecordedintheHungarianstretchesofthe Crisuri (Körös) was not recorded in the Romanian section of the river (Mylopharyngodon piceus, Ictiobus bubalus, Ictalurus punctatus, Clarias gariepinus, Micropterus salmoides, Oreochromis niloticus, Perccottus glenii). The pervading of these species is expecting also in the Romanian section of the rivers.
The present major threatening factors concerning the fishfaunaarerepresentedbythehabitatchanges.Theriverdammingandtheriverside levees have a negative influenceonthefishfauna.Theformerphenomenonofwaterpollutionitseemsthatisreplacedbythehabitat changes. The dam lakes caused unregulated fluctuationsonthewaterlevelandtemperaturedownstreamofit.Theembankmentforpreventing the floodingwasperformedthroughshorteningtherivermeander.Thelostmeandersoftheriversarerepresentinganoptimalhabitat for fishspawning. -
External (border) peripheries in Hungary
105-108Views:206This study examines the development of external (cross-border) peripheries, as well as the opportunities of catching up in view of the European integration, most specifically the unfolding of the Schengen processes. A conclusion is drawn that the paradigm shift that is to be expected in cross-border relations and the modern, mainly local, small region-based and inter-settlement forms of interregional cooperations could contribute to diminishing the highly unfavourable circumstances from the aspect of rural development and the fostering of the socio-economic cohesion of the Carpathian basin. The new institutionalised legal frameworks of cross-border relations, the EGTCs can successfully promote in the future the acquisition and more efficient use of different development resources, parallel to this the socio-economic catching up of adjacent peripheries, lagging regions on the two sides of the same borders. Above all, they can be important for the utilisation of the direct relations and local resources
in the Hungarian–Slovak, Hungarian–Ukrainian and Hungarian– Romanian borders along the northeast part of Hungary and for the
Hungarian–Croatian and Hungarian–Slovene border areas along South Transdanubia. -
Harvesting system established for the utilisation of Miscanthus sinensis ‘tatai’ “energy cane” in biomass power plants
143-150Views:249The increasing demand for energy worldwide and the resulting environmental impacts of fossil fuels forced many countries to turn to renewable energy resources as a clean and sustainable alternative. More than a third of Europe’s binding renewable energy source target of 20% by 2020 will come from solid biomass for electricity and heating according to the National Renewable Energy Action Plans submitted by member states of the European Union (EU) to the European Commission. To achieve this goal long-term yield studies in renewable energy plants are important to determine mean annual biomass and energy yield, and CO2 emission. Field experiments worldwide and also in Europe have demonstrated that Miscanthus, a fast-growing C4 rhizomatous grass can produce some of the highest biomass and energy yield per hectare of all potential energy plants. Miscanthus is a plant that originates from the southern slopes of the Himalayas. It was bred for the Hungarian climatic conditions in 2006 under the name of Miscanthus sinensis ‘Tatai’ (MsT). The species has high frost and drought tolerance and high energy value. This is why there is growing demand for the biomass (lignocellulose) produced by growing this plant. The biomass, produced from the high yield energy reed, can be transported to power plants in large quantities, in forms of bales. Its household consumption is not yet significant. This study presents the external features, characteristics, propagation and plantation process of MsT energy reed. The study also demonstrates the harvest technology of the species worked out between 2009–2012 in Tata, Hungary and the options of supplying to biomass
power stations.
-
Status and Prospects of Integrated Pest Management in Apple Production in Hungary
307-316Views:197Farming methods supporting the ecological function of agriculture will play an even more dominant role in the near future than they do now, as much in Hungary as in the rest of the EU.
Several farming techniques supporting sustainable development have already evolved, and in this essay, I deal with integrated production i.e. integrated fruit production in Hungary and its perspectives. I analyze both European and Hungarian regulations on integrated production and their development.
It is obvious that in the orchards of Europe, integrated production is gaining ground. We can expect the increased spread of this western trend to Hungary, too, because one of the conditions for remaining on the market will be a product from integrated production. However, we cannot expect any rapid increase in the future. In my opinion, there are three ways to propagate integrated production:
− changes in the approach of farmers;
− vocational training of farmers because of the greater „knowledge-demand”; improving the consultant network;
− strict monitoring of the production process. -
Significance of risk assessment metric in audit of financial statements and reports
215-225Views:201Management and decision-support of today’s businesses require design and application of management reports based and high-end controlling systems. One of the main source of information for controlling systems is financial accounting that should be designed to support planning, controlling and monitoring systems. Financial and accounting information is essential for decision making support of organizations. Therefore
eligible assurance is needed that these information are true and fair. Internal and external financial audits as assurance qualifiers are linking to the controlling systems through assurance. Weaknesses of and threats to controlling systems shall be recovered and communicated to the management during qualifying process. Recovering of threats should be based on risk analysis, assessment. In this study I would like to present some methods and tools of risk assessment of financial reports, statements and a way on they can be further developed. -
The results of the investigation of the β-casein gene polymorphism in sheep breed – Review
75-80Views:561β-casein is the most abundant protein fraction in sheep milk, and has at least six different alleles (A, B, C, G, X, Y). The alleles of the β-casein gene may influence on the quality and quantity of milk. Knowing the gene polymorphism has an important role in the process of milk production. The properties of milk could be positively influenced by themolecular genetic methods.
-
Cross-Sectional Examination of Agricultural Firms in Relation to the Leaders’ Attitude
261-269Views:82As a PhD student at the Management Department of Debrecen University my project was to find examine circumstances of agricultural business entities in connection with structural, social and economic changes. This topic is integral part of the research program „Functional Study of Business-Management”, specified the topic „Structural Management Researches”.
My setting of objectives were to find any connection between changes and attitude of leaders. I tried to explore the direction, tightness and tendencies of these relations, to choose some special management-method, which ones are much more succesfull than the other ones during the change-managing process. The base of my experiences are the results of special questionnaires, which were sent to several member of different type of enterprises relating to agricultural activity. -
Food Safety in EU Higher Education
188-197Views:166Under the aegis of the Lisbon Strategy, special attention is paid to education and areas left untouched by the European integration process. Human capital and research inputs were identified as major driving forces for long-term development. The European Union is keen on meeting its target of boosting research spending to 3% of GDP by 2010. In order to contribute towards his goal, the European Commission has set aside an amount
which is double the budget of the 7th Framework Programme. Accordingly, preferences were given to research and development projects encouraging competitiveness in the food industry and other initiatives, such as the European Technology Platforms. Major obstacles to innovation in Hungary are: lack of funds, weakness of research network, poor structural relations. Better utilization of our comparative advantages should be targeted in order to have the Hungarian food industry become a driving force sector. This is to be promoted by the newly transformed food
engineer training (as a result of the Bologna Declaration) which can adapt better to the changing requirements of the labour market. Food science and related research could become determining factors for the food economy by setting up accredited training systems and enhancing food safety education and training in Hungary. -
Comparative Study on Different Water Bodies and their Sediments
17-21Views:205Hungary is rich in natural water resources, therefore investigation of these biotopes is an important task. The Szarvas- Kákafok deadarm is the largest horse-shoe lake of the Tiszántúl, its lenght is 28 km. It has an important role in recreation and agricultural utilization. The quality of the deadarm is influenced by the river Körös, but also by communal and agricultural pollution. Our goals were to estimate the intensity of the
sedimentation processes, and the water- and the sediment quality as well. Also, we examined an artificial wetland system, constructed by the Fish Culture and Irrigation Research Institute, Szarvas.
The calculated sedimentation was 0.4-0.5 cm year-1, which indicated an intensive eutrophication process. The constructed wetland system was able to decrease the organic load of the intensive fish culture company. On the basis of our TOC measurements, the organic matter content of the effluent water remained whitin the water quality limits.
The changes of the material cycling could be more intense in the water body, then in the sediment. The oxido-reduction potential of the sediment could indicate the ecological state of the shallow lakes, therefore it could be an easily measurable indicator in the water classification. -
Seed biology and possibility of improvement of seed germination capacity on Virginia mallow (Sida hermaphrodita L. Rusby)
71-76Views:249Sida hermephrodita or Virginia mallow is a perspective perennial herb in the Malvaceae family able to yield a biomass crop through the last two decades. Additionally, the plants have a lot of uses and benefits for instance it can use as a fodder crop, honey crop, ornamental plant in public gardens. It has favourable features like fast growing and resistance against the disease and climatic fluctuations, etc. Sida is in the beginning phase of domestication therefore it has a serious disadvantage: the low and slow germination as a big part of wild plants. Due to the expressly low germination percent the need of seed showing of driller is should tenfold, 200 thousand seeds/acre instead of 10–20 thousand what is not available and expensive Therefore practical purposes of our research of seed physiology was to increase the seed germination percent in a available, basically wild Sida population. In the first stage of our experiments we examined two factors relating to seed germination percent and seed germination power during our research: the influence of hot water treatment and the effect of exogenous or endogenous infection of seed. However, in our germination tests, utilizing scarified seeds with hot water (65 oC, 80 oC, 90 oC), from 29,3% to 46% germinated from those samples which were collected from the population of Sida hermaphrodita in Debrecen. The average germination for all season was 5–10% without treatment and rinsed using hot water up to almost 50%. When physically scarified used, the oldest seeds showed the best germination (46%) after the hot water operation in spite of the previous studies. We discovered that apparently there are close relationship between the seed fresh weight or water uptake capability and the percentage of infection. Following these recognition we modified our technique,in such a way that we fractionated the seeds based on their fresh weight/or relative density before we carried out the treatment. When we filtered the floating seeds on the surface of water, the hot water treatment was performed considerably better on the sunk seeds after separation. Therefore, by this special priming process we were able to reach 80% germination capacity of Virgina mallow seeds under laboratory conditions (26 oC without illumination).
-
Effect of noninvasive castration method on weight gain, behavior and meat quality of ram lambs
21-29Views:364In the course of producing heavyweight lambs (above 35 kg), males need to be separated from females at the end of the fattening period. If not, the rams must be castrated because they reach sexual maturity, and their activity bothers the ewes or unwanted pregnancy may occur. The present study surveys if the Hungarian sheep keepers know or use the non-surgical elastrator method for castration and assess the effect of castration (surgical and non-surgical) on daily weight gain, behavior, moving activity, and meat quality of rams, respectively. We found many advantages regarding the use of the elastrator method. Based on the survey results, 100% of farmers who used elastrator had a positive experience and favorable opinion about this method. There is no need to separate the rams, which allows for less area requirement and more economical technological conditions. The traditional castration (with a knife) process is longer (4–6 minutes), and caused longer-lasting stress while the elastrator application is bloodless, took only 20–30 seconds, and were stress-free. The number of steps of ring-gelded individuals was much lower than that of the non-castrated rams. The difference in steps number could also be seen in ewes separated into different ram groups. The weight gains of individuals castrated by the ring were better than the surgically castrated ones and also individuals with testicles. The palatability of the meat from the non-castrated group was less favorable, and the chewiness of the ringed group was the best. Finally, our results highlighted the benefits of the noninvasive elastrator method in animal welfare aspects.
-
Practical experiences in Moodle LMS
129-133Views:150We use Moodle at the University of Debrecen, Business- and Agricultural Department since January 2007. Moodle is an open source Learning Management System.
Learning Management System (or LMS) is a software package that enables the management and delivery of learning content and resources to students. Most LMS systems are web-based to facilitate "anytime, anywhere" access to learning content and administration. LMS tracks student progress in a course and indicates completions. At the least, learning management systems track individual student progress, record scores of quizzes and tests within an online learning program, and track course completions.
Moodle has more and more function at our Department in education. At present, we work to introduce Moodle in our Faculty. Therefore, we took lessons for the tutors about the usage of the Moodle. Our aim to develop such a learning system, which is an integral part of educational process. -
Changes in toxic elements content of soil after sewage sludge treatment in energy willow plantation
7-10Views:260The primary purpose of our experiment was the solution of municipal excess sludge treatment by a renewable energy resource used willow (Salix viminalis L.) plantation. Tests were carried out to state whether the applied sewage sludge has caused any accumulation of the toxic elements in the studied soil layers, and - based on the results –to see whether the plantation is suitable for the treatment of municipal sewage sludge.
The excess sludge (sludge before dewatering) is beneficial for the willow, because it contains a 3–5% dry matter and therefore, a lot of water, too. This high water content ensures the high water amount needed for the intensive growth of the willow. On the other hand, the wastewater treatment plant can save the dewatering cost which corresponds to about 30% of the water treatment process costs. The amounts of the sprinkled sewage sludge were calculated on the basis of its total nitrogen content. Treatments were the followings: control, 170 N kg ha-1 year-1 and 250 N kg ha-1 year-1. The mean values of the toxic element concentrations in the sewage sludge did not cross the permitted limits of the land accommodating.The measured toxic element values of the soil were compared to the limits of the 50/2001. (IV.3.) Government Regulation.The sprinkled sewage sludge on the bases of the total N content did not cause accumulation of heavy metals in the soil and the treated plants were also healthy without any signs of toxicity.
-
Study on Human Resource Management in Agriculture
171-181Views:182The human factor has been reassessed with regard to strategic initiatives towards obtaining and preserving competitive advantage. Knowledge, experience and special skills are a specific form of capital, forming part of the organisations’ assets and serving as an organisational strategic resource. Their development and use require major investments, both on the part of the individual and the organisation. In a Europe undergoing integration, the quality of human resources enjoy priority among our really important values and specific features. The opportunities of the near future can be utilised, and agricultural economic organizations can survive and increase their organizational effectiveness, if they possess a basis of human capital which is able to make a shift in perspective and behaviour which is of primary importance from the point of view of incorporating market mechanisms and implementing them in practice. My investigations were focused on the current position of human resource management in a comprehensive manner; further, on the approach of top managers regarding the future. Analysing the business and other indicators of the companies studied, I have set the objective to describe the differences and special features of the human resource management practice of companies, which are different in size, operational form, and from the perspective of success or failure.
Human resource management is directed to attracting, retaining, motivating and utilising labour. A given work process can be successful or unsuccessful – given the same conditions – depending on who performs it. Therefore, human resource management related tasks require special attention when enterprises are planned, established and operated. On analysing the responsibilities of human resource management, I have found that the functions and responsibilities of human resource have low or medium importance in the operation of economic organisations today. Regarding the future, top managers have expressed higher expectations of human resource management responsibilities in all areas and they consider individual functions to be more important. The establishment and operation of a human resource information system has been presented as the most important need for change. Correlation analyses have proved that the higher the sales revenues of a company, the higher the development of human resources is regarded by its manager, and the same holds for training, career support and a proper establishment and continuous evaluation of job profiles. -
Violation prooxidative-antioxidant stability at maize shoots at different level of accumulation of cadmium and nickel
89-94Views:155Joint influence of cadmium and nickel was investigated on the feature of their accumulation by the vegetative organs of 10-days' old maize shoots. It was established that most intensively noted metals are taken in by the roots of shoots in the first 7 hours stressing influencing, while in leaves they appear only after a 7-hour long exposition. It was stated that the absorption process of the noted metals by a root system is carried by two-phase character. The indexes of inner-tissue contamination are calculated. Activating by the cadmium and nickel ions of lipid peroxidation as marker of the stressing influencing, and also was shown the proper increase of intensity of functioning of ascorbate peroxidase as the antioxidant enzyme protection of cell.