Search
Search Results
-
Evaluation of harvesting technology of vineyard pruning based on a Mátra wine region case study
91-100Views:222Wineyard pruning utilization for energy purpose is not only a theoretical possibility, the machine background has also been developed. Economic- and environmental experimentations has made by specialists and they seek to developed the best practice in logistics suitable for local conditions and they propagate the results for the potential users. Nevertheless, the utilization does not seem to be typical in Hungary and some other wine-grower countries. For example, in Hungary the additional energy from vineyard pruning eventuates – tillage, nutrient supply; – phy+tosanitary, environmental pollution; – energy management and economic questions.
In Hungary the most important problem is practice of the vineyard pruning utilization were mentioned by the users is the establishment of collection system and the high logistic costs as Marczinkó (2007) experiences confirm this. As I experienced in practice, the winegrowers are uninterested in utilization. Most of them burn it at the end of the vineyard in many cases without considering of the relevant statutory prohibition.
As my own several years expriment shows at Mátra wine region it is not the technical background which causes the failure. We can use effectively balers or chippers for collection. The cost of chipping is 14 535–27 000 Ft per hectars with the introduced technologies on Mátra wine region. The cost of 1 GJ of heat production is 606–1125 Ft. We can substitute the fuel with vineyard pruning and it means approximately 115 000 Ft saving for a family household per year.
-
The online marketing possibilities and judgment of the domestic food-sector
77-84Views:344The theme of my PhD research is the online marketing possibilities and judgment of the domestic food-sector. This article is based on the important bibliography of my research theme. I show the new categorization of the tools of marketing communication. I examine the recent years’ changes of the social approach and the interactivity. Based on the meeting of the Internet I separate our ages’ generations. Furthermore I examine the transformation of consumers into users in the digital environment. I prove the changes of the Internet’s penetration and the presence of enterprises in the Internet with statistic data. I touch the tendency of information searching in online environment. I present new methods to measure the online marketing activities’ return.
Finally, I define my objectives of research based on my own experience and bibliography overview over and above I draw up my concrete future’s research which I separate seconder and primer section.
-
Mapping agricultural performance and environmental parameters aimed at generic regional studies
29-34Views:491In this paper we present the interim results and the methodology applied to create web GIS ready cartographic representations of agricultural performance related information and environmental parameters. The main aim of the research is to eventually create a web GIS based decision support system that can enable decsision makers and general users to create useful and representative map layouts of certain environment and agriculture related phenomena that can be easily analyzed and interpreted to make strategic decisions on environmental issues. In this aim the initial steps are to evaluate the available data for cartographic representation, analyze the possibilities of visualization, create a GIS ready data structure and implement the database and revise additional possibilities to incorporate further environment related datasets of auxiliary sources. The main results of the study are a comprehensive set of visual layouts that could serve as guideline for mapping statistical information of agriculture and some steps towards the incorporation of environmental parameters to the system.
-
Discussion of an Electronic Examination System in Agricultural HigherEducation
160-163Views:212The development of an internet based electronic examination system at the University of Debrecen Centre of Agricultural Sciences, Department of Land Cultivation and Regional Development was enforced by the dynamic increase in the recent years in the number of students participating in classes taught by the department staff. This paper covers the system’s historical background, the usability factors we were focused on during its development, and the experiences of the testing phase.
The findings of a questionnaire carried out among our students aimed to clarify the acceptance, expectations and fears of future users. -
Evaluation of reduced tillage technologies in corn production based on soil and crop analyses
47-54Views:554Despite new cultivation methods, the proportion of conventionally cultivated land is still very high in Hungary.
Although these technologies demand more time, labour and fuel, they are still attractive to users because they require less professional skill and simple machinery. In Hungary, conventional tillage methods usually lead to soil deterioration, soil compaction and a decrease in organic content. These side effects have caused gradually strengthening economic and environmental problems.
The technologies for those plants which are dominant on Hungarian arable lands use (winter wheat, maize, sunflower and barley) need to be improved both in the interest of environmental protection and the reduction of cultivation costs.
The Department of Land Use at Debrecen University is cooperating with KITE Sc. to carry out soil tillage experiments at two pilot locations to prove tillage technologies already used in the USA.
The aim of our examination is to adapt new technological developments and machinery, and to improve them on Hungarian soil for local environmental conditions. With these improved machines, the field growing of plants could be executed by less manipulation and better suited to economic and environmental needs. The most significant task is to investigate and improve the conventional cultivation replacing, new soil-protecting tillage technologies, and to apply no-till and mulch tillage systems.
On the basis of the experiments’ survey data, we established that the looseness and moisture content of the soil using reduced tillage is more favourable than after using conventional technologies. The results of no-till and shallow spring tillage are behind those of winter plough or disk ripper cultivation in corn yield and production elements.
To preserve moisture content in the soil, the ground clearing and sowing while simultaneously performing no-till method presents the most favourable results. The surplus moisture gained using no-till technology is equal to 40 mm precipitation.
Regarding the yield of winter wheat we established that the tillage methods do not affect plant yield. Both disk ripper and conventional disc cultivation showed nearly the same harvest results (5.55 or 5.5 t/ha), where the difference is statistically hardly verifiable from the no-till method. From the individual production of corn and the number of plants planted in unit area, calculated results prove that no significant difference can be detected between the production of winter plough and disk ripper technology. Although the yield achieved with the no-till method is less than with the previously mentioned technologies, the difference is only 9-10%. We received the lowest production at shallow spring tillage.
Evaluations have shown a 1.1 t/ha (13%) difference in the yield of maize, between winter tillage and the disk ripper method, in this case the traditional method resulted in higher yield. In winter tillage, the yield of maize was 1.9-2.1 t/ha (23-25%) higher than in the case of direct sowing and cultivator treatments. No significant difference could be noted between the yields of direct sowing and cultivator treatments.
Our research so far has proved the industrial application of reduced tillage methods in crop cultivation technologies. -
When and what quantity shall we buy? Optimal cereal – acquisition strategies
175-181Views:184For farm products, it is typical that goods appear in a certain period of time in gross; therefore, from the viewpoint of forestallers/users, it is an important question how much and when to buy and for growers how much and when to sell. Among the costs that have affects on income, we have to emphasize stockkeeping costs (i.e. cost of tied-up capital, ordering costs) and acquisition costs. The last one is very important, because we can
notice great divergences in prices for cereals associated with the significant seasonal factors for a given year, so acquisition prices affect substantially the evolution of our costs.
We can establish the strategies in two steps: setting up 2 models and interconnecting them. One means the strategies that differ from each other in ordering quantities and these comparative analyses. This model contains the analyses of seasonal effects and also the results that we apply in the model. The other one is a dynamical mathematical programming model which – by considering alternative investments – helps us to choose from the strategies in the previously mentioned model that one, which assures us maximum income. -
Assessment of Environmental Susceptibility/Vulnerability of Soils
62-74Views:229Soils represent a considerable part of the natural resources of Hungary. Consequently, rational land use and proper soil management – to guarantee normal soil functions – are important elements of sustainable (agricultural) development, having special importance both in the national economy and in environment protection.
The main soil functions in the biosphere are as follows: conditionally renewable natural resource; reactor, transformer and integrator of the combined influences of other natural resources (solar radiation, atmosphere, surface and subsurface waters, biological resources), place of „sphere-interactions”; medium for biomass production, primary food-source of the biosphere; storage of heat, water and plant nutrients; natural filter and detoxication system, which may prevent the deeper geological formations and the subsurface waters from various pollutants; high capacity buffer medium, which may prevent or moderate the unfavourable consequences of various environmental stresses; significant gene-reservoir, an important element of biodiversity.
Society utilizes these functions in different ways (rate, method, efficiency) throughout history, depending on the given natural conditions and socio-economic circumstances. In many cases the character of the particular functions was not properly taken into consideration during the utilization of soil resources, and the misguided management resulted in their over-exploitation, decreasing efficiency of one or more soil functions, and – over a certain limit – serious environmental deterioration.
Soil resources are threatened by the following environmental stresses:
– soil degradation processes;
– extreme moisture regime;
– nutrient stresses (deficiency or toxicity);
– environmental pollution.
Environmental stresses caused by natural factors or human activities represent an increasing ecological threat to the biosphere, as well as a socio-economic risk for sustainable development, including rational land use and soil management.
The stresses are caused by the integrated impacts of various soil properties, which are the results of soil processes (mass and energy regimes, abiotic and biotic transport and transformation and their interactions) under the combined influences of soil forming factors. Consequently, the control of soil processes is a great challenge and the main task of soil science and soil management in sustainable development.
The efficient control of these processes necessitates the following consecutive steps:
• registration of facts and consequences (information on land and soil characteristics, land use, cropping pattern, applied agrotechnics, yields, with their spatial and temporal variability);
• evaluation of potential reasons (definition and quantification of soil processes, analysis of influencing factors and their mechanisms);
• assessment of the theoretical, real, rational and economic possibilities for the control of soil processes (including their risk-assessment and impact analysis);
• elaboration of efficient technologies for the „best” control alternatives (best management practice).
Scientifically based planning and implementation of sustainable land use and rational soil management to ensure desirable soil functions, without any undesirable environmental side-effects, require adequate soil information. In the last years such data were organized into a computer-based GIS soil database in Hungary, giving opportunities for the quantification, analysis, modelling and forecasting of the studied environmental stresses and for the efficient and scientifically based prevention, elimination or reduction of environmental stresses and their unfavourable ecological and economical consequences.
Special attention was paid to the assessment of various soil degradation processes, as: (1) soil erosion by water or wind; (2) soil acidification; (3) salinization and/or alkalization; (4) physical degradation (structure destruction, compaction); (5) extreme moisture regime: drought sensitivity and waterlogging hazard; (6) biological degradation; (7) unfavourable changes in the plant nutrient regime; (8) decrease of natural buffering capacity, (9) soil (and water) pollution.
The actions against undesirable environmental stresses and their unfavourable consequences are important elements of sustainable, efficient, economically viable, socially acceptable and environmentally sound crop production and agricultural development. These are joint tasks of the state, decision makers on various levels, the land owners, the land users and – to a certain extent – of each member of the society. -
Development and Economic Benefits of Open Source Software
161-168Views:169This paper discusses open source software which became one of the most important trends in the software industry recently. The most often asked questions in this area are those related to intellectual property rights. The author used a more general approach and tried to give a survey of the advantages and disadvantages that the market players (developers, government and last but not least users) have to face.
After sketching the history of open source software and discussing some of the prevailing definitions, we turn out attention to the starting point: what motivates the developers? Then we give a general overview of the advantages and disadvantages of open source software. In the next part, the author analyses the software policies of the EU partially based on the abovementioned advantages and disadvantages. Finally the paper concludes with the discussion of user benefits and costs. -
Dimensionality Expressed by Caseendings and Spatial Prepositions
7-15Views:199The purpose of this essay is to investigate some of the uses of English prepositions and Hungarian case endings employed to express spatial relations. The observation of invariant mistakes Hungarian native speakers learning English make initiated the investigation. The questions raised are: (a) where do the two systems match and where do mismatches lie, (b) how do language users perceive the world, and (c) do speakers observe spatial relations as two-dimensional or three-dimensional cognitive models? Do different languages see the same thing as either three-dimensional, or two-dimensional?
Abondolo (1988) gives an adequate morphological analysis of ten Hungarian case-endings (inessive, illative, elative, superessive, delative, sublative adessive, ablative, allative and terminative) used in spatial reference, which give a closed set in references made to factors, such as (1) location which can be broken down as interior vs. exterior location with the latter being further analysable as superficial and proximal, and (2) orientation which can be analysed as zero orientation (position), source and goal. In addition to those in this list, two other case endings (genetive/dative and locative) are also used for expressing spatial relations but the last is only a variant of the inessive and superessive case-endings and is only used with place-names. The set is closed in the sense that the same item is meant to refer to the same sort of spatial relation in every case. Language textbooks, c.f. Benkő (1972) seem to suggest a neat match between the above Hungarian case endings and their English prepositional counterparts, e.g. London-ban (inessive) = in London.
The picture, however, is far from being so clear-cut. The data, which were taken from various dictionaries and textbooks, show that the choices of both the prepositions and the case endings listed above depend on how the speaker considers factors (1) and (2) and that proximity is very important. Instead of a one-to-one match between the prepositions and the case endings, we rather find that the above case endings will match a dual, and in some cases a tripartite system of prepositions with the correspondences found in the two languages, which yield the following chart: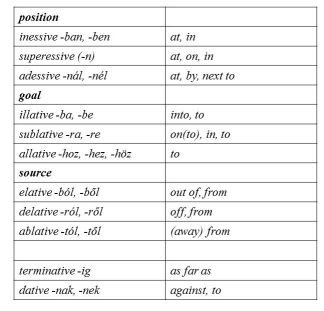
We suggest that languages may view or map the same physical entities in different ways, for example along surface vs. volume or goal vs. passage, etc.
Furthermore, we also find it possible that it is the language specific, inherent coding of the nominal phrase that decides – in many cases – upon the choice of prepositions and case endings. -
Visualization techniques in agriculture
95-98Views:342This paper describes a dynamic map representation method which provides a flexible, spectacular and cost-effective opportunity for the illustration and description of spatial data due to its parametrability, web-based publication and the free sowftare it uses in multi-user circumstances.
The tasks of the database serves and the processing were performed by an ASUS WL-500 G Premium v2 router and a 80 GB hard disk. The database contains the measured data of the nitrogen fertilisation experiment established on the Látókép Experiment Site of the Centre for Agricultural Sciences of the University of Debrecen. The tests showed that the generation time of the processor which was run through the router did not significantly increase. Therefore, the configuration developed by us is suitable for users who do not wish to invest into a large and expensive server, but they still want to view their data quickly and easily, as well as to reach them from anywhere.
The available data were not sorted into a database which was performed with Quantum GIS in a way to have an optimum database structure which is adjusted to the expected areas of use and the expected running speeds were also taken into consideration. The processor which processes the database items was written in PHP language. The main role of the processor is that it produces a KML file real time which is suitable for viewing with a given map viewer client (e.g. Google Earth). This application makes it possible to view information related to geographical objects, values stored in the database or those calculated by the processor on a map in 2D or 3D in a versatile way.
-
Customer Relationship Systems and Business Models
99-106Views:229The object of this study is a comprehensive review of customer relationship management (CRM) systems applied increasingly in several fields of economy. The CRM is not merely a subsequent software technology and application in the field of Business Intelligence, but rather a novel, comprehensive customer-centric approach to an organization’s philosophy in dealing with its customer for the sake of realization of short- and long-range business target contrary to the traditionally widespread productcentric approach. The object of the study, following a short
synopsis of the theoretical and practical aspects of the CRM systems, is to analyse the range of the actual and potential users and to survey the CRM market. It will be analysed the scope of CRM supported business activities and processes, the terms and possible methods of launching and will be outlined a feasible model, too. The aim of conspectus of different CRM strategies (layers) is to reveal the urging need of turning approach in the field of management. -
A földhasználat alakulása az ezredfordulón - egy felmérés eredményei
58-66Views:212There were no significant changes in land ownership and use in 2000, compared to the period following the compensation process. Land is mainly owned by people who do not want to use their property, so they generally turn to renting it out to others. Although farming on rented land is performed under various conditions, farms try to rent the lands of better quality. In general, examined farms would like to increase their size by tenancy or land purchase. Buying land is a good investment, considering the price increase in the future, but because of the lack of capital, tenancy remains the main form of territory increase.
Farms which rent land are in connection with a lot of owners, the land within their use is frittered away, it is in a lot of parts. Most rental contracts are written, but the ratio of oral contracts is still quite high. To reduce this ratio is one future aim. One more characteristic of the rental contracts is the dominance of a medium length period – which is acceptable for both the owner and user, but the ratio of short time contracts is still high. Land rent, on average for the examined farms, is quite balanced, it is on the level of about 16.000 HUF/hectare.
The land users mainly pay the same land rent to the owners, but in some cases, there are exceptions. Generally, land rent is a fix cost, but sometimes this cost depends on the level of the yield or the change of product price. Land rent, on average, is 16% within the production costs on the examined farms, which try to choose better and larger lands for rent. Sometimes, farmers can pay higher land rent for the unit of better land, but this is not a general tendency. It is mainly true that they pay the same land rent for the unit, regardless of land quality. Land owners can not interfere in the use of their land within the rental period, and also is a main characteristic of contracts that important particulars are not spelled out sufficiently by the partners. It follows that their content has to be improved in the future. -
Examination the users’s opinion of the electronic submission programme
47-51Views:174In Hungary the Agricultural and Rural Development Agency (ARDA) started to introduce electronic filling and submission of application forms for the two-hundred-thousand farmers in 2008. For submission it is recommended to be registered using by client gate. The producers' benefits have more results from electronic filling. Filling in and submitting the applications electronically ensure data will be correct and the application technically flawless and this can be the basis on the payment of former financial support and avoidance of sanctions or subtractions due to technical faults. The farmers may ensure the money more quickly. Based on survey is analysed the users of system conceive of the electronic submission programme.
-
Internet Browsing Habits and Domain Choice Preferences of Economic Agricultural Engineers
134-137Views:152The findings below are based on a questionnaire survey carried out in order to establish an internet-based service at the Center of Agricultural Sciences of Debrecen University:
• The typical target group of the service in the short run with a weekly average of 5.9 hours on the web is more active than that for average Hungarian, adult Internet users.
• A professional webportal with a searchable database, primarily incorporating an archive of organized agricultural news, articles, publications, fits well into the internet habits of the target group, which mainly consists of keyword-based information searces and browsing of the latest news.
• The group prefers a short, easily recognizable domain name that refers to agriculture. Accents and foreign sounding words are not taken into account during selection.
• As result of the choice from 43 eligible domains, the order would be the following: agrarunio, agroland, farmvilag, infoagro, farmland.
• The names of magyargazda.hu, agrotrend.hu, agromester.hu, agronomus.hu are acceptable from the individual ideas. -
Some basic problems concerning world animal production at the beginning of the XXI century
77-80Views:217The author summarizes the main new challenges facing animal agriculture: growing GDP in many countries increasing animal protein demand, bioenergy industry as a new player using potential food or feedstuffs, increasing demand, Growing water and land scarcity, weaking the position of plant agriculture, feed production. Forecasts are summarized regarding the magnitude of meat consumption increases, and the possible plant biomass quantities required additionally in the next 20 years to cover the needs of food, feed and biofuel on a global scale.
Efficiencies of various animal production sectors, poultry, pork, beef, mutton meat, milk and eggs and their environmental footprints are compared, summarizing the most important research results concerning UK, USA, OECD evaluations. Intensive systems using highly productive plant and animal population will play an even more important role in the future especially in poultry, pig, milk and aquaculture production system being efficient users of resources (feed, water, land) and the environmental foot print is smaller per unit product. -
Viability and Economies of Scale in EU Farms
332-338Views:129With this study, the author intends to draw up the main characteristics of the institutional background of the Farm Accountancy Data Network, operated by the European Union. Among the factors that contribute to the formation of the institutional background of the FADN database, special emphasis is laid on the Commission and member state level legal framework, in order to provide potential Hungarian users of the database with authentic and substantial information. Also, much attention is paid to definitional misunderstandings which cause, or might cause the farm business management type utilization of the database to be imperfect. As for this goal, some of the elements of the FADN information structure are investigated in a conventional Hungarian cost structure. In order to facilitate an easier understanding of the database, the different relations of economic size classes are also reviewed in this study. The author of this study is – in the first place – trying to analyze the meaning of Standard Gross Margin, the index used in the FADN structure to categorize farms, by localizing the position of the different cost constituents of SGM in a conventional Hungarian cost matrix. Last, but not least, the author is trying to draw all researcher’s attention on the possibilities, hidden in the FADN database by introducing some analyses from his own field of interest based on FADN information.