Search
Search Results
-
A global bibliographic review of soil variability trends on arable land: An impetus to sustainable land management
27-39Views:187Crop production is significantly affected by soil properties under the influence of climate, management practices, and geographical location. Soil variability affects the development, quality, biochemical reactions, and heterogeneity of soil. The most recent research has focused on soil variability monitoring, highlighting the importance of soil testing. This review aimed at identifying global research trends and assessing soil testing in monitoring variability on arable land, based on the bibliographic method. Literature search in Scopus Database (2020-2023) yielded 8,898 documents, refined to 815 articles. VOSviewer 1.6.20 Software was used for analysing exported data. The results revealed a growing emphasis on monitoring soil variability, with key countries including India, United States of America (USA), China, Australia, Canada, United Kingdom, and Brazil. Funding mainly came from Asia, North America, and Europe. Common monitoring approaches included soil tests and remote sensing, focusing on organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, microorganisms, and soil moisture. However, digital illiteracy and high costs were major hindrances to using remote sensing and modern soil testing tools. The study suggests that whereas soil variability monitoring is essential for sustainable land management, development of affordable soil testing equipment and improved digital education are needed for its enhanced adoption.
-
Nitrogen Content of Hungarian Soils and Nitrogen Fertilization
51-61Views:229For crop production and agricultural production, the most important natural resource is the soil that can optionally renew. Paralelly with this, soil plays a major role in the geological and biological cycle of elements. As a result of the big (geological) and small (biological) element cycles, the elements and combines neccessary for organisms can accumulate in the soil creating suitable living conditions for plants and other organisms. Soil is a heterogenous system both horizontally and vertically, and soil constituents show great variety in all the three dimensions, in addition, most of the parameters can also change between two examination dates. When talking about the factors influencing plant production, one should take into account this variation and heterogenity in time and space. When making fertilization recommendations, these factors should all be considered. In any consultation system, most of the mistakes and errors made are due to the unsatisfying soil testing and the negligence of soil heterogenity. In the practice of fertilization the biggest mistake is the improper soil sampling, then comes the methodical mistake of soil testing, which is followed by the inaccuracy of instrumental analysis and the subjectivity of result evaluation, but the latter two are negligible compared to the others. Under normal, i.e. production conditions, the quantity and distribution of nutrients in the soil are greatly dependent upon the applied technology, the amount and form of the applied natural and artificial fertilizers and the quality of fertilization.
Fertilization recommendations are needed because in the layer which is accessible for plant roots only a part of the nutrient content is available for plants in a specific production cycle. An illustration of this is that though the upper 1 m layer of an average chernozem soil contains more than 5000 kg N, 12000 kg K2O and 1500 kg P2O5 (form of expression mostly used in Hungary), the application of fertilizer doses which are just fractions of these quantities is essential. This is due to the fact that the available amount of the total nutrient content depends from the quality of soil, the environmental factors (the physical and chemical qualities of the soil) and the specific nutrient’s qualities (solubility, adsorption). Knowledge of these processes and the examination of the factors influencing the actual nutrient content are vital for working out a fertilization practice, which does not put more strain on the environment than neccessary.All of the above mentioned should be considered when applying inputs in the fields. In a well-functioning practice that considers the economic and environmental conditions (unfortunately the present production and economic conditions do not enable an appropriate level and degree), three nutrients are supplemented generally (and were supplemented in the last decades): nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium.
Studying the nutrient balance of the Hungarian field production’s last hundred years, we can draw some interesting conclusions.
The nutrient balance became positive for nitrogen and potassium in the second half of the 1960’s, while for phosphorus it was positive from the first half of the 1960’s and this period lasted until the end of the 1980’s.
Neither before the 1960’s, nor since the 1990’s has the amount of nutrients supplemented in a specific year reached the amount of the nutrient uptake of the same year. -
Review of research on salt-affected soils in the Debrecen agricultural high educational institutions, with special focus on the mapping of Hortobágy
471-484Views:183The history of the research of Debrecen scholars on salt-affected soils of Hortobágy and the region is very rich and diverse.
Focusing on mapping, the following stages can be distinguished, indicating the completeness of the maps and the purpose of the performed work
− First, quantitative maps (Arany, 1926) for the utilization of the lands at 1:75,000 (Figure 1).
− Second, quantitative map (Kreybig, 1943) for the utilization of the lands at 1:25,000.
− Third, category map (Kreybig et al., 1935) testing the suitability of the classification system at :75,000.
− Fourth, partial category map (Szabolcs, 1954), showing the reasons of unsuccessful management at 1:10,000.
− Fifth, partial quantitative map (Csillag et al., 1996), showing the utility of digital sampling at 1:25,000.
− Sixth, partial quantitative map (Tamás and Lénárt, 2006), showing the capacity of multispectral remote imagery at 1:100.
− Seventh, partial quantitative map (Douaik et al., 2006), showing the usefulness of geostatistical mapping at 1:10,000.
− Eight, national quantitative maps (Pásztor et al., 2016), showing the applicability of geostatistics for administrative purposes at 1:10,000.
− Ninth, partial quantitative/category map (authors, 2019), finding the optimal methods at 1:10,000. -
Evaluation of long term experiments from a new aspect
55-60Views:381During our work, we developed a new, simple method to show the effects of fertilization on yield, which can both be applied over the long term as well as in series of independent experiments.
During the testing of this method, at the experimental farm of the Debrecen University Center for Agricultural Sciences at Látókép on a chernozem soil with lime deposits, we examined the fertilizer reaction of maize hybrids between 1989 and 1994. The treatments were: winter tillage, plant density of 70-80 thousand, unfertilized, N 120, N 240 kg/ha fertilized treatments, long term experiments using Dekalb 524 and Volga SC hybrids in long term experiments.
Four parameters are shown in the model. In the examined period TRmax represents the greatest yield in the fertilized treatments, NT the yield in unfertilized treatment, k the „efficiency of fertilizer” to NT and b the depression-coefficient, where the expected value is zero. The expected grain yield of the fertilized treatments (Y), in the function of the unfertilized grain yield (x) is the following: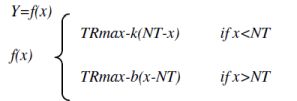
The parameters were determined using the Monte Carlo method, in the optimizing process the sum of deviation square was minimized. The correct conformation of the functions was determined by the greatness of the R-value and the standard error. We found that during six years of testing, the tendency of fertilization efficiency was similar in the case of both hybrids. There was an unfavorable weather interval and, in these years, the yields were low, fertilization did not have an effect and moreover, in extremely bad conditions resulted in an obvious yield decrease. With the improvement of conditions, which in the case of our country means an increase in precipitation, the efficiency of fertilization increases and reaches its peak at 13-14 t/ha. At this point, the yield increasing effect of fertilization is 4-4,5 t/ha. If the yield of the unfertilized treatments increases from 8-9 t/ha, then the efficiency of the applied fertilizer decreases.
Most likely, the k and b parameters depend on the soil of the experimental location (nutrient and water management) and on the amount of pplied fertilizer and the characteristics of the hybrid. With the increase of fertilizer dosage the k-parameter also increases. The greater value though does not obviously mean a more favorable situation. It is true that in medium and good years this means great fertilizer efficiency, but in low or extreme precipitation conditions it also means greater risk. With the increase of the k-parameter, the yield deviation also increases which, from a cultivation point of view, is quite unfavorable. If the value of the b-parameter is other than, zero then the effect is clearly unfavorable, because with the increase of this value, the yield decrease is also greater. The fertilizer reaction of the two examined hybrids can be well characterized by these two hybrids.
Examining the six years, our created model estimated the effect of fertilization on the yield accurately and with a high degree of safety. Both in highly unfavorable and extremely good years, it gave an exact estimate. In our opinion, it can be used well to evaluate the effects of fertilization on yield in the future. -
Untersuchungen mit 15N-Tracern in agrikulturchemischen Systemen
23-28Views:158Agricultural chemical states and processes are arranged in open and closed systems. Investigations of state are static systems independent of time, testing of process is dynamic systems dependent on time.
In order to follow up special facts and occurrences the stable isotope 15N is suited. It is demarcated of native nitrogen of existing systems.
In the report as well as results of experiments with 15N tracers in systems soil, fertilizer, plant and animal and too the path as brigde between soil and fertilizer, fertilizer and plant and soil and plant are represented. -
Effects of Site on Winter Wheat Quality 2002/2003
100-107Views:410The demand of modern societies for high food quality is evident. Thus, it is important for agriculture to produce row materials that are valuable for nutrition and have favourable characteristics for food processing. For this we need a knowledge about the factors which determine the quality of products. One of the main features of plant production is the “immobility”. This way the characteristics of the field influence the quality of the product, like example winter wheat, which is the main cereal in Hungary and Europe.
The Concordia Co. has charged the Central Laboratory of Debrecen University, Agricultural Centre with laboratory testing of the 2002/2003 winter wheat crop. The samples consist of thirteen winter wheat varieties from six different sites under the same cultivating conditions. Therefore, the important wheat quality factors were analysed solely against site conditions with the use of Győri’s “Z” index, which contains these parameters.
Soils were tested first. In this experiment excepting the negligible differences between the sites, there were no linear relations found between quality factors, productivity and soil features. The case is the same with the relation between precipitation, temperature and quality parameters. However, it must be noted that additional soil analyses are required to interpret the extreme results obtained from Karcag.
The calculated Győri’s Z-index shows relative stability concerning certain varieties, although considerable deviation can be found in varieties related to the sites. According to these results, it can bestated that winter wheat quality was not linearly influenced by soil and weather in the 2002/2003 vegetation period. As the same cultivation technology was used in the experiment, the index was determined by genetic features. It must be noted that these findings are relevant only to this experiment. -
Effects of paraffine oil on leaf and berry mycobiota on two grape varieties
61-66Views:482Application of fungicides have advantages and also some direct or indirect disadvantages, such as imbalance and/or fungicide resistance in microbe population. To avoid these problems the development of alternative, eco-friendly methods like mostly spraying with oils are in the focus nowadays. The investigations of the effects of fungicides on microbiota in some cultivations can give a more complex view to this topic and developmental possibilities. In the present study, our aim was testing of the effects of paraffine oil (as alternative fungicide) on microbial properties (CFU and rate of filamentous fungi and yeasts) of Chardonnay and Kékfrankos leaves and berries.
Our results from 2014 showed that the application of paraffine oil as sole spray agent can decrease the presence of saprophytic filamentous fungi on the berries of Chardonnay (susceptible for fungal infections). In the case of Kékfrankos berries opposite properties were observed, which may be the result of the absorption of oil by the thick wax layer of this variety. The oil treatment did not affect the yeast population of Chardonnay and Kékfrankos berries contrary to negative effect of the regular pesticide treatment. The selective fungicide effect of paraffine oil against filamentous fungal population caused the accumulation of yeast cells in the mycobiota of grape berries. The careful use of this yeasts in spontaneous fermentation can improve the aroma profile of wines. The year of 2015 did no prefer the growth of fungi, therefore no interesting properties were detected in the mycobiota of grape varieties. The occurence of the harmful saprophytic filamentous fungi predicted to be increased in mild climate agricultures as the result of the climate change.
In summary, the paraffine oils are seem to be promising tools for the eco-friendly control of harmful fungi of grapes.
-
Testing a biological active plant extract’s antifungal effect against soil fungi
247-252Views:226In Hungary today is about 5 million hectares of agricultural land contaminated with ragweed. The ragweed problem a year is about 60 billion HUF to be paid, of which 30 billion are used to reduce the agricultural damage. Experiments with ragweed pollen has mainly been carried out in connection with terms of allergy. The other biochemical experiments and studies with this plant, have so far been the scientific horizons of public life, boosted the edge. We wanted to demonstrate that the ragweed, which is a weed, containsbiological active (for example: antifungal) compounds. For our experiments in the previous cycle of flowering, plants were collected manually, with its roots and with each plant part. The extraction of the substance from dry plant – meal was carried out using appropriate solvents. The biological activity of ragweed-extracts were tested against fungi isolated from soils and meadow with different mode of cultivation. Our results suggest that ragweed contains biologically active substances, which inhibit the growth of fungi, depending on the concentration of active ingredients of the plant.
-
Accuracy of Location Identification by GPS and Possibilities for its Application in Agriculture
157-160Views:267A description of the design and operating principle of the GPS system and the explanation of key terms of telemetric and chronometric measurements is followed by several examples characteristic of the results of factors which may influence accuracy of the identification of geographic location by satellites. In addition, results of accuracy testing of absolute GPS measurements and improvements of accuracy experienced and attributable to the alteration of the periods used for establishing average values are highlighted. Furthermore, we examined certain practical possibilities for the use of GPS systems in agriculture, emphasizing the advantages hidden in the use of GIS-GPS integration, crop mapping, soil maps and gross produce maps, in the application of the VRT (Variable Rate Technology) and in combinations of the same.
-
Correlation between cultivation methods and quality in some vegetable species
313-317Views:286Quality parameters of 5 table root varieties were tested on 3 sowing dates with different cultivation methods: open field on 15 April and 9 July 2010 and under plastic tents on 19 August. The highest red pigment content (betanin) was measured in the varieties Akela and Mona Lisa (~ 80 mg 100 g-1) of the second (July) crop. This crop is in general use in Hungary. In comparison, in the late sown varieties (August, under plastics) a further pigment increase (10–20 mg 100 g-1) was observed in the same varieties as related to the earlier sowing dates. Yellow pigments (vulgaxanthins) showed similar trends. Roots of the late sowing date (with harvest in December) contained the highest vulgaxanthin values (103.3–124.18 mg kg-1).
Varieties reacted differently to temperature changes during the production period and thus to sugar accumulation. In the second crop (July) higher water soluble solids content was measured on the average of varieties (10.12%) in comparison to the April sowing (7.76%). Beetroots of the spring sowing are recommended for fresh market while the second (July) crop with autumn harvest can satisfy industry requirements. Late sowing under unheated plastic tents supply us with fresh beetroot in late autumn and early winter and prolong the usability of plastic tents.
Six lettuce species/subspecies were tested in the open field and under plastic tents in 3 repetitions for nitrate nitrogen, vitamin-C, polyphenol (gallus acid equivalent – mg GAE 100 g-1) and mineral element (Ca, K, Mg, Na) contents. Our measurements showed lower nitrate nitrogen values under plastic than in the open field (89.10± 8.13 and 127.06±14.29 mg kg-1) on the average of genotypes. Lettuce grown in the field had higher vitamin-C content (1.4 mg%) which is nearly 50% more than in plants under plastic. The highest polyphenol content was found in samples from the field with a conspicuous value of 804.17±56.47 mg GAE 100 g-1 in Piros cikória. Samples grown under plastic were richer in mineral elements (Ca, K, Mg, Na) which can be explained by the higher nutrient content of the soil. In this environment superior Mg content was observed in Edivia (4616.33±
311.21 mg kg-1).Besides the well- known headed lettuce, Piros cikória (Red chicory),the red leaved Lollo Rossa and Tölgylevel (Oak leaf lettuce) should be
mentioned which well deserve further testing in order to supply us with nourishing, healthy food.